LamPORE SARS-CoV-2 with flow cell recalibration (LMPR_9105_v1_rev3_13Oct2025)
GridION: Protocol
LamPORE SARS-CoV-2 with flow cell recalibration V LMPR_9105_v1_rev3_13Oct2025
This is a Legacy product
This product has been discontinued. If customers require further support for any ongoing critical experiments using a Legacy product, please contact Customer Support via email: support@nanoporetech.com.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
- 1. Overview of the protocol
- 2. Equipment and consumables
- 3. Computer requirements and software
- 4. Check your flow cell
LAMP and library preparation
- 5. Reverse Transcription Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP)
- 6. Library preparation
- 7. Priming and loading the flow cell
Sequencing and data analysis
- 8. Data acquisition and basecalling
- 9. Downstream analysis
- 10. Prepare the system for a subsequent run
Recalibrating a flow cell
Overview
This is a Legacy product
This product has been discontinued. If customers require further support for any ongoing critical experiments using a Legacy product, please contact Customer Support via email: support@nanoporetech.com.
1. Overview of the protocol
This is a Legacy product
This product has been discontinued. If customers require further support for any ongoing critical experiments using a Legacy product, please contact Customer Support via email: support@nanoporetech.com.
LamPORE with flow cell recalibration
This protocol, similar to the LamPORE SARS-CoV-2 protocol, is used to test patient samples for the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. However, this protocol is targeted at users who are working in lower-throughput facilities and do not have enough samples to fill up a 96-well plate at a time. Here, users are instructed to test 20 samples and 4 controls (two wells of Positive Control and two wells of No Template Control), each with an individual combination of barcodes, at a time. After the test is complete, the first library is flushed from the flow cell using the Flow Cell Recalibration Kit, and a second library with different barcode combinations can be loaded and tested.
The Flow Cell Recalibration Kit allows sequential runs of multiple LamPORE tests on the same flow cell. This procedure provides the opportunity to use the same flow cell several times, reducing the cost per test. Following the recalibration step, Storage Buffer can be introduced into the flow cell, allowing storage of the flow cell before subsequent library additions. Alternatively, the flow cell can be re-used immediately.
Introduction to LamPORE
LamPORE has been developed by Oxford Nanopore Technologies to enable the simple and rapid detection of target regions of single or multiple genomes in a highly multiplexed manner.
In this kit, LamPORE is designed to detect the presence or absence of the SARS-CoV-2 virual RNA responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic in respiratory specimens (such as oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal swabs) and saliva.
LamPORE combines barcoded multi-target isothermal amplification, 15-minute barcoded library preparation and real-time nanopore sequencing. By placing unique molecular barcodes in the Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) reaction and coupling these with Oxford Nanopore's rapid barcoding adapters, a dual indexing approach is achieved, enabling a large number of barcode combinations to be generated and analysed.
The test deploys a simple workflow:
Amplification
Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) is a single-tube technique of targeted amplification which can generate micrograms of product from tens of copies of the target region. Reverse Transcription LAMP (RT-LAMP) combines LAMP with a reverse transcription step to allow the amplification and subsequent detection of RNA targets.
LamPORE deploys an RT-LAMP specific to three regions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome:
- N Gene
- E gene
- ORF1a gene
Additionally, a set of primers to amplify the human β-actin mRNA are included. The primers target either side of a splice junction and do not amplify from genomic DNA. As long as the sample has been collected and prepared correctly, β-actin RNA should be present in all the swab and saliva samples, regardless of their SARS-CoV-2 status, and so this provides a way to differentiate between true negatives and invalid samples.
To perform amplification, a strand-displacing polymerase is added to an RNA sample, primers and the reaction is incubated at 65°C for 35 minutes. In the initial stages of the reaction, the enzyme produces a series of dumbbell-shaped cDNA molecules and these are then exponentially amplified. Amplification of the dumbbell-shaped molecules results in long DNA strands consisting of concatenated copies of the original target regions.
To enable pooling of multiple samples into a single analysis run, the LamPORE SARS-CoV-2 primers include a 10-nucleotide molecular barcode on the Forward Inner Primer (FIP). Following amplification, several copies of this barcode are incorporated into each DNA concatemer.
At the end of the reaction, the enzymes are inactivated by incubation at 80°C for 5 minutes. LAMP produces a variety of products including multimeric DNA with inverted repeats. These complex amplification products are converted into nanopore sequencing libraries using the rapid barcoding chemistry.
Rapid barcoding
Successful LAMP reactions are often inferred from a proxy measurement, such as increased turbidity or a colour change. However, although the LAMP reaction itself is very robust, these proxy measurements are less robust and can be affected by substances present in biological samples. It is also not uncommon to see a colour change or increase in turbidity in no-template controls, arising from amplification of primer artefacts, which would lead to a false positive call. Instead of relying on proxy measurements, sequencing can be used as a readout. On-target amplification events contain sequences that are not present in the primers and can be identified without ambiguity by alignment. In addition, sequencing provides an opportunity to amplify and detect multiple targets in a single tube.
To enable sequencing as a readout, a sequencing library must first be prepared. LamPORE uses the rapid barcoding library preparation method for three reasons: the first reason is speed and simplicity. Secondly, being transposase-based, the preparation method cuts the loop products generated during LAMP, turning them into linear molecules ready for sequencing. Finally, rapid barcoding chemistry incorporates a barcode in the sequencing adapter enabling a combinatorial barcode approach which delivers a far higher capacity for multiplexing samples into an analysis run.
To prepare a rapid barcoded library, you will need to:
- Tagment your DNA using the rapid barcodes; this cuts the DNA and simultaneously attaches a pair of barcodes to the fragments
- Pool the barcoded samples
- Purify the sample using SPRI beads
- Attach sequencing adapters to the DNA ends
- Prime the flow cell, and load your DNA library into the flow cell
Data analysis
Per-sample results of the assay are returned as positive, negative, inconclusive, or invalid.
During nanopore sequencing, an electrical current is measured as strands pass through each pore on the flow cell. Conversion of this current into basecalls can start while a strand is translocating.
LamPORE reads
A LamPORE reaction creates an end product with multiple copies of the barcoded target region and a sequencing barcode at the start of each read.
Basecalling
Raw signal data processing basecalling algorithms are contained in the MinKNOW software.
The data at this point is deposited in files according to the barcode on the rapid sequencing chemistry with all files containing rapid barcode 1 in folder 1 and all files containing barcode 2 in folder 2 etc.
At the end of the experiment, when all reads have been basecalled and placed in appropriate folders, MinKNOW initiates the downstream analysis pipeline.
Analysis pipeline
The LamPORE analysis pipeline:
- Demultiplexes the reads by the FIP barcodes
- Aligns the reads against the SARS-CoV-2 genomic targets and human β-actin
- Generates a TSV file describing the number of reads for each barcode which align to the targets.
A PDF report is also generated, containing classification results for every barcoded sample.
Analysis pipeline in detail
The first step of the enalysis pipeline is to classify reads containing the LAMP barcodes. After this step is performed, the classified reads move onto an alignment step.
The LamPORE primers are designed such that they leave a gap where genuine SARS-CoV-2 sequence is replicated by the LAMP reaction in the case of a positive sample.
All reads are aligned against the SARS-CoV-2 genome and only reads with sequence information in that region are called positive.
Distinguishing between valid reads and primer artefacts by alignment works by: a) valid reads consist of repeats that align across the majority of the target region, whereas b) primer artefacts align as short segments interspersed with gaps.
By pairing LAMP with nanopore sequencing, it is easy for a genuine positive to be differentiated from amplification artefacts. This enables the assay to be highly specific as reads containing the necessary sequence serve as an unambiguous identification for the presence of the target.
The determination of the sample result applies the following rules:
- Positive: SARS-CoV-2 detected (≥50 SARS-CoV-2 reads)
- Inconclusive: The test should be repeated (20 ≤ SARS-CoV-2 reads ≤ 49)
- Negative: SARS-CoV-2 not detected (<20 SARS-CoV-2 reads)
- Invalid: insufficient number (<50) of classified reads from both SARS-CoV-2 and β-actin to make a call; the test should be repeated
It is important to note that this read-out is to be used by a healthcare professional in combination with patient symptoms and healthcare history to inform the next course of treatment.
2. Equipment and consumables
Materials
- RNA samples
- LamPORE COVID-19 Test Kit 96-plex S (OND-SQK-LP0096S)
- SARS-CoV-2 Control kit S (OND-EXP-SCT001)
- Flow Cell Recalibration Kit (OND-EXP-FRK001)
Consumables
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- 0.2 ml 96-well PCR plate
- 96-well plate lids or seals
- 0.2 ml thin-walled PCR tubes
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Freshly prepared 80% ethanol in nuclease-free water
- Nuclease-free pipette filter tips
Equipment
- PCR hood or bubble
- Thermal cycler or heat block with 96 wells
- Magnetic separation rack
- Microfuge
- Centrifuge capable of taking 96-well plates
- Timer
- Ice bucket with ice
- P1000 pipette
- P200 pipette
- P100 pipette
- P20 pipette
- P10 pipette
- P2 pipette
- Multichannel pipettes suitable for dispensing 0.5–10 μl, 2–20 μl and 20–200 μl, and tips
LamPORE COVID-19 Test Kit 96 Plex S contents (OND-SQK-LP0096S)
| Kit component | Description | Number of tubes/wells |
|---|---|---|
| LAMP Master Mix (LMM) | Reagents and enzymes needed for the LAMP reaction | 1x pre-filled 96-well plate of LMM |
| LAMP Primer Mixes (LPM) | Primers for the LAMP reaction that hybridise to the ORF1a, N2 and E1 genes of the SARS-CoV-2 genome, as well as the B-actin gene as an internal control. LAMP primers contain barcodes 1-8 for multiplexing samples | 1x pre-filled 96-well plate of LPM. LAMP barcoded primers are arranged in rows, i.e. Row A contains primers with barcode 1, Row B contains primers with barcode 2 etc. |
| Rapid Barcodes (RBxx) | Rapid Barcodes 1-12 for multiplexing samples | 1x 96-well plate with Row A of the Rapid Barcodes plate containing barcodes 1-12 in wells A1-A12. |
| SPRI Beads (SPRI) | SPRI beads for purifying the pooled, barcoded library | 1 tube |
| Rapid Adapter (RAP) | Oligonucleotide adapter loaded with a processive enzyme that regulates the DNA passage through the nanopore | 1 tube |
| Sequencing Buffer (SQB) | Fuel and other chemical co-factors for powering DNA translocation through the nanopore | 1 tube |
| Loading Beads (LB) | Polymer beads for improved sequencing yields | 1 tube |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | Buffer for eluting the prepared DNA library from SPRI beads | 1 tube |
| Flush Buffer (FB) | Buffer used to flush the flow cell prior to loading the library | 6 tubes |
| Flush Tether (FLT) | Chemical tether added to Flush Buffer; brings the DNA library to the flow cell membrane and in closer proximity to the nanopores | 1 tube |
SARS-CoV-2 Control kit S contents (OND-EXP-SCT001)
| Kit component | Description | Number of tubes/wells |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Control (CTL) | Positive control containing synthetic SARS-CoV-2 RNA | 6 tubes |
| No Template Control (NTC) | Negative control containing nuclease-free water | 4 tubes |
Flow Cell Recalibration Kit contents (OND-EXP-FRK001)
| Kit component | Description | Number of tubes/wells |
|---|---|---|
| Wash Mix (WMX) | Solution containing DNase I | 1 tube |
| Wash Diluent (DIL) | Buffer to dilute and maximise the activity of DNase I | 2 tubes |
| Storage Buffer (S) | Buffer to allow flow cells to be stored for extended periods of time | 2 tubes |
Kit shelf life and storage
The LamPORE COVID-19 Test Kit 96 Plex S, the SARS-CoV-2 Control kit S and the Flow Cell Recalibration Kit have a shelf life of 3 months when stored at -20°C.
The Positive Control (CTL) tubes should be taken out of the kit and stored at -80°C for up to 3 months.
We do not reccomend repeated freeze-thaw of the Positive Control (CTL) and as such, sufficient aliquots are provided in the kit to minimise this.
3. Computer requirements and software
GridION IT requirements
The GridION device contains all the hardware required to control up to five flow cells and acquire the data. The device is further enhanced with high performance GPU technology for real-time basecalling. Read more in the GridION IT requirements document.
Software for nanopore sequencing
MinKNOW
The MinKNOW software (OND 19.12) controls the nanopore sequencing device, collects sequencing data in real time and processes it into basecalls. MinKNOW can also demultiplex reads by barcode.
Analysis
At the end of the sequencing experiment, when all reads have been basecalled, MinKNOW initiates the downstream analysis pipeline.
4. Check your flow cell
Consumables
- Flow Cell (OND-FLO-M106D)
Equipment
- GridION (OND-GRD003)
In this step, you will use the MinKNOW software to check that the flow cell meets warranty. This has to be done prior to loading your sample onto the flow cell.
Switch on the GridION device. When the login screen appears, enter the password and log in.

Open the GridION lid and insert the flow cell. Press down firmly on the flow cell to ensure correct thermal and electrical contact.

Click the Nanopore wheel icon on the desktop to load the MinKNOW software. You will see the MinKNOW user interface appear.

Check the "Available" box for all flow cells to be checked.

Click "Check flow cells" at the bottom of the screen.
Click "Start test". The flow cell check will take approximately 10 minutes.

The quality of the flow cell will be shown as one of the two outcomes:
A green tick - The flow cell is within warranty and can be used for a LamPORE test.

A yellow exclamation mark - The flow cell is below warranty and should not be used for the LamPORE test. Please contact support@nanoporetech.com to arrange a replacement.

Note: The indicator of quality (exclamation mark or tick) will only remain visible during a MinKNOW session. Once the MinKNOW service has ended, the status of the flow cell will be erased.
Flow cell check complete.
5. Reverse Transcription Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP)
Materials
- RNA samples
- LAMP Primer Mix (LPM) plate
- LAMP Master Mix (LMM) plate
- No Template Control (NTC)
- Positive Control (CTL)
Consumables
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- 96-well plate lids or seals
- 0.2 ml 96-well PCR plate
- 0.2 ml thin-walled PCR tubes
- Nuclease-free pipette filter tips
Equipment
- PCR hood or bubble
- Thermal cycler or heat block with 96 wells
- Vortex mixer with plate adapter
- Centrifuge capable of taking 96-well plates
- Multichannel pipettes suitable for dispensing 2–20 μl and 20–200 μl, and tips
- P20 pipette
- P2 pipette
- Ice bucket with ice
LAMP can produce large numbers of easily-amplifiable molecules after a successful reaction, and therefore the risk of cross-contamination between samples must be mitigated.
- The Amplification (RT-LAMP) must be performed in a PCR hood or bubble in a completely separate area to the library preparation
- Use dedicated pipettes for liquid handling, with filter pipette tips for the RNA processing and LAMP
- Wear a fresh pair of gloves that are immediatley discarded after this step
- After the LAMP reaction is complete, remove the seal from the PCR plate very carefully to avoid splashing/cross-contamination between wells
- Clean down hoods and surfaces with an appropriate cleaning agent (e.g. bleach) before and after the RT-LAMP step and between reagent plates
Barcoding of samples
This method uses a combinatorial barcoding approach. One set of barcodes is contained in the FIP primers used in the LAMP reactions, and an additional set of Rapid Barcodes is also supplied. All samples and controls in a given row of the plate will receive the same FIP barcode, and all samples and controls in a given column of the plate will receive the same Rapid Barcode, as shown in the figure below.
Here, samples in row A of the plate receive FIP barcode 01, samples in row B receive barcode FIP 02 etc. Meanwhile, samples in column 1 receive the Rapid Barcode 01, samples in column 2 receive the Rapid Barcode 02 etc. This way, each sample will receive a unique combination of FIP barcode and Rapid Barcode.
It is necessary to include at least two wells of No Template Control and at least two wells of Positive Control per plate, which leaves a maximum of 92 samples per plate. If you are running fewer than 92 samples at a time, we recommend filling up columns rather than rows with samples. Any unused wells in a column should be filled with LAMP Master Mix/LAMP Primers and 20 μl nuclease-free water and processed in the same way as a sample.
Prepare the RNA samples and reagents as follows:
| Reagent | Thaw | Mix/spin | Store |
|---|---|---|---|
| RNA samples | On ice | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
| LAMP Master Mix (LMM) | At room temperature | Spin down the plate | On ice |
| LAMP Primer Mixes (LPM) | At room temperature | Spin down the plate | On ice |
| Positive Control (CTL) | On ice | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
| No Template Control (NTC) | At room temperature | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
Add 2 ml of nuclease-free water directly to the CTL tube. Mix well by vortexing, and spin down.
Set a multichannel pipette to 5 μl. Mix the contents of column 1 of the LAMP Primer Mix (LPM) plate by pipetting up and down several times. Then transfer 5 μl of LAMP Primer Mix from column 1 of the LPM plate into column 1 of a clean 96-well plate. Repeat the mixing and pipetting steps for additional columns depending on the number of samples being tested: for 24 samples (inclusive of any controls and empty wells), transfer three columns of reagents, for 48 samples transfer six columns of reagents etc., up to 96 samples (all 12 columns). Use new pipette tips for each column.
Mix by pipetting up and down
Transfer LPM to clean plate
Set a multichannel pipette to 25 μl. Mix the contents of column 1 of the LAMP Master Mix (LMM) plate by pipetting up and down several times. Then transfer 25 μl of LAMP Master Mix from column 1 of the LMM plate into column 1 of the 96-well plate. Mix the contents of the wells by pipetting up and down. Repeat the mixing and pipetting steps for all columns with LAMP Primer Mix added, using new tips for each column.
Add 20 μl of RNA sample or NTC to each well. For positive control wells, add 5 μl of CTL to each well, followed by 15 μl nuclease-free water to bring the total volume to 20 μl. Make up any unused wells with 20 μl nuclease-free water. The minimum number of RNA samples to be tested at a time is 20, with two wells of CTL and two wells of NTC.
In the diagram below only four RNA samples are shown, however at least two more columns will also be filled with RNA samples.
Mix the contents of each well by pipetting up and down, taking care not to cross-contaminate different wells.
Seal the plate and spin down.
Incubate the plate in a thermal cycler at 65°C for 35 minutes, then at 80°C for 5 minutes.
If necessary, the protocol can be paused at this point. The samples should be kept at 4°C and can be stored overnight.
6. Library preparation
Materials
- Rapid Barcodes plate
- SPRI beads (SPRI)
- Rapid Adapter (RAP)
- Elution Buffer (EB)
Consumables
- 0.2 ml thin-walled PCR tubes
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Freshly prepared 80% ethanol in nuclease-free water
- Nuclease-free pipette filter tips
Equipment
- Thermal cycler or heat blocks
- Microfuge
- P10 pipette
- Multichannel pipettes suitable for dispensing 0.5–10 μl, 2–20 μl and 20–200 μl, and tips
- Magnetic separation rack
Library preparation should be carried out in a separate area of the laboratory to the RT-LAMP PCR hood/bubble.
Prepare the remaining reagents as follows:
| Reagent | Thaw | Mix/spin | Store |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Barcodes plate (RBxx) | At room temperature | Spin down the plate | On ice |
| SPRI beads (SPRI) | At room temperature | Vortex and spin down | At room temperature |
| Rapid Adapter (RAP) | At room temperature | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | At room temperature | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
Spin down the plate with the LAMP reactions to bring all samples to the bottom of the wells. Remove the seal from the plate carefully, avoiding sample splashing and cross-contamination between wells.
For each column of the plate (e.g. wells A1-H1), pool the reactions by transferring 2 μl of LAMP products from each well into a clean 0.2 ml thin-walled PCR tube. Pipette very carefully to avoid cross-contamination between columns on the plate.
Mix the contents of each tube by pipetting up and down using a multichannel pipette, and spin down.
Add 6.5 μl nuclease-free water to clean 0.2 ml thin-walled PCR tubes, one for each pool of reverse-transcribed and amplified RNA samples. Then add 1 μl of the RNA sample pools to each tube:
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Nuclease-free water | 6.5 μl |
| 1 μl of each pool of RNA samples | 1 μl |
| Total | 7.5 μl |
To each tube, add 2.5 μl of Rapid Barcodes (one for each pool of LAMP products). These are in row A of the Rapid Barcode plate: RB01-12 are in wells A1-A12.
Mix gently by flicking the tubes, and spin down.
Incubate the tubes in a thermal cycler at 30°C for 2 minutes and then at 80°C for 2 minutes. Briefly put the tubes on ice to cool them down, and spin down in a microfuge.
If necessary, the protocol can be paused at this point. The samples should be kept at 4°C and can be stored overnight.
Combine all reactions into a single 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube for a total volume of 120 μl (or less, if fewer than 96 wells were used).
Resuspend the tube of SPRI beads by vortexing.
To the entire pooled barcoded sample from Step 9, add 0.8x volume of resuspended SPRI beads (e.g. add 96 μl SPRI beads to 120 μl sample), and mix by pipetting up and down.
| 3 columns | 6 columns | 9 columns | 12 columns | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pooled sample volume | 30 μl | 60 μl | 90 μl | 120 μl |
| SPRI beads | 24 μl | 48 μl | 72 μl | 96 μl |
Incubate for 5 minutes at room temperature.
Prepare 500 µl of fresh 80% ethanol in nuclease-free water.
Spin down the sample and pellet the beads on a magnet for a minimum of 2 mins, or until the solution becomes clear. Keep the tube on the magnet, and pipette off the supernatant.
Take the tube off the magnet, and wash the beads by resuspending them thoroughly with 200 µl of freshly-prepared 80% ethanol. Return the tube to the magnet and pellet the beads for 2 mins, or until the solution is clear. Remove the ethanol using a pipette and discard.
Repeat the previous step.
Spin down and place the tube back on the magnet. Pipette off any residual ethanol. Allow to dry for 30 seconds, but do not dry the pellet to the point of cracking.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack and resuspend the pellet by pipetting in 15 µl Elution Buffer (EB). Spin down and incubate for 5 minutes at room temperature.
Pellet the beads on a magnet for 2 mins, or until the eluate is clear and colourless.
Remove and retain 11 µl of eluate into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Add 1 µl of RAP to the barcoded DNA.
Mix well by pipetting and spin down in a centrifuge.
Incubate the reaction for 5 minutes at room temperature.
The prepared library is used for loading onto the flow cell. Store the library on ice until ready to load.
7. Priming and loading the flow cell
Materials
- Flush Tether (FLT)
- Flush Buffer (FB)
- Sequencing Buffer (SQB)
- Loading Beads (LB)
Consumables
- Flow Cell (OND-FLO-M106D)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
Equipment
- GridION (OND-GRD003)
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- P10 pipette and tips
Prepare the remaining kit reagents as follows:
| Reagent | Thaw | Mix/spin | Store |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer (SQB) | At room temperature | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
| Loading Beads (LB) | At room temperature | - | On ice |
| Flush Tether (FLT) | At room temperature | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
| Flush Buffer (FB) | At room temperature | Vortex and spin down | On ice |
To prepare the flow cell priming mix, add 30 µl of thawed and mixed Flush Tether (FLT) directly to the tube of thawed and mixed Flush Buffer (FB), and mix by vortexing at room temperature.
Slide the priming port cover of the flow cell clockwise to open the priming port.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back 20-30 µl to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl
- Insert the tip into the priming port
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip
Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the priming port across the sensor array.
Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
Load 800 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the priming port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait for five minutes. During this time, prepare the library for loading by following the steps below.

Thoroughly mix the contents of the Loading Beads (LB) by pipetting.
The Loading Beads (LB) tube contains a suspension of beads. These beads settle very quickly. It is vital that they are mixed immediately before use.
In a new tube, prepare the library for loading as follows:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer (SQB) | 37.5 µl |
| Loading Beads (LB), mixed immediately before use | 25.5 µl |
| DNA library | 12 µl |
| Total | 75 µl |
Note: Load the library onto the flow cell immediately after adding the Sequencing Buffer (SQB) and Loading Beads (LB) because the fuel in the buffer will start to be consumed by the adapter.
Complete the flow cell priming:
- Gently lift the SpotON sample port cover to make the SpotON sample port accessible.
- Load 200 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell priming port (not the SpotON sample port), avoiding the introduction of air bubbles.

Mix the prepared library gently by pipetting up and down just prior to loading.
Add 75 μl of the prepared library to the flow cell via the SpotON sample port in a dropwise fashion. Ensure each drop flows into the port before adding the next.

Gently replace the SpotON sample port cover, making sure the bung enters the SpotON port, close the flow cell priming port and close the GridION lid.
8. Data acquisition and basecalling
Click the Nanopore wheel icon on the desktop to load the MinKNOW software. You will see the MinKNOW user interface appear.

Select the flow cells to be run by checking the "Available" box.

Click the "New Experiment" button at the bottom left of the GUI.
On the New experiment pop-up screen, select the running parameters for your experiment from the individual tabs:
Experiment
The Experiment tab will show the flow cells chosen. An experiment name can then be assigned to all flow cells.
Fill in the Experiment field with the operator name or ID. Fill in the Sample field with a unique name. Experiment name and Sample ID should not contain personally-identifiable information.
The other tabs will not become available until an experiment name has been provided. 
Kit selection
You will be presented with four kit options. Choose OND-SQK-LP0096S. 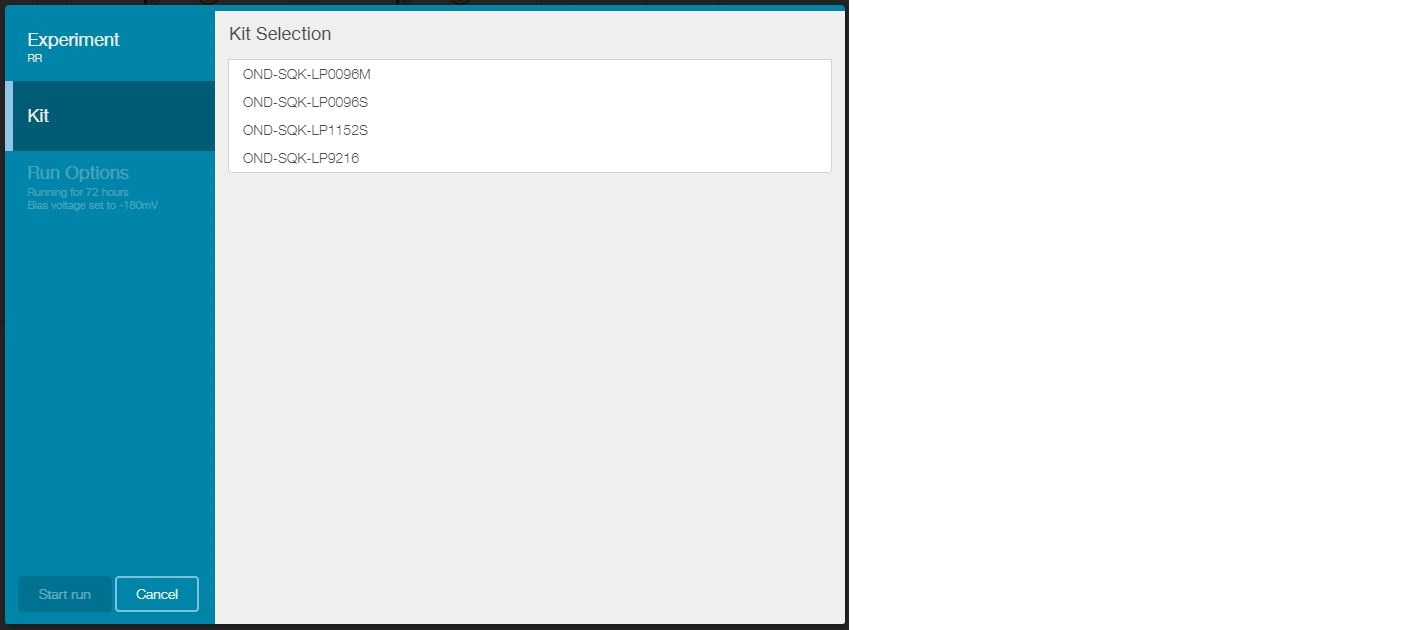
Run Options
Adjust the Run Length based on the number of samples you are sequencing:
| Number of samples | Run length (hours) |
|---|---|
| 24 | 0.5 |
| 48 | 0.5 |
| 72 | 1 |
| 96 | 1 |
Keep the Bias Voltage at its default value.
Click "Start run"
The pop-up box will disappear, and the flow cells will become greyed out.

Allow the script to run to completion.
The Message panel in the GUI will inform you when the experiment is complete.
The data analysis pipeline will start automatically at the end of the sequencing experiment.
Note: clicking the Stop button during the run will cancel the downstream analysis.
9. Downstream analysis
Output of the sequencing and analysis pipeline
The files with test results are placed in the /data folder, with the following structure/file naming convention:
{data}/
{experiment_id}/
{sample_id}/
{date_time}_{device_id}_{flowcell_id}_{protocol_unique_identifier}/
e.g. `/data/lampore_20200617/lampore/20200617_1636_X1_FAO39500_e29f6fcd`
The experiment results can be found in the lamPORE_report PDF and the lamPORE_results TSV file.

Analysis report
The report is a TSV file describing number of reads which align to given targets and have given barcodes, as well as metadata for run tracking. A PDF report is also generated, containing results for every barcoded sample.
The fields in the TSV file are as follows:
| Column | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Barcode | RB and FIP barcode combination |
| target_human_ACTB | Number of reads aligning to the human β-actin target |
| target_nCoV2019_AS1 | Number of reads aligning to the ORF1a target in the SARS-CoV-2 genome |
| target_nCoV2019_E1 | Number of reads aligning to the E1 target in the SARS-CoV-2 genome |
| target_nCoV2019_N2 | Number of reads aligning to the N2 target in the SARS-CoV-2 genome |
| target_unclassified | Number of unclassified reads (reads with barcodes that do not align with the correct specificity) |
| acquisition_run_id | A unique alphanumeric number to identify the run |
| protocol_group_id | Experiment name assigned when setting up the run in MinKNOW |
| sample_id | Name assigned to the flow cell when setting up the run in MinKNOW |
| flow_cell_id | Unique identification code of the flow cell |
| started | Experiment start date and time |
| call | Positive: SARS-CoV-2 detected (≥50 SARS-CoV-2 reads) Inconclusive: The test should be repeated (20 ≤ SARS-CoV-2 reads ≤ 49) Negative: SARS-CoV-2 not detected (<20 SARS-CoV-2 reads) Invalid: insufficient number (<50) of classified reads from both SARS-CoV-2 and β-actin to make a call; the test should be repeated |
An example PDF report from the analysis pipeline and example TSV file are shown below.

Analysis of controls
During the RT-LAMP and library preparation, two controls from the kit are included: CTL (positive control), and NTC (no template control).
When preparing your samples, make a note of the positions of the CTL and NTC wells in each plate. Check the results in the analysis reports (found in the lamPORE_results TSV file and lamPORE_report PDF file) for these positions:
- NTC contains no SARS-CoV-2 RNA, and should give an Invalid result in the call column of the TSV file or PDF report. If it shows a Positive, Negative or Inconclusive result, this means that all tests in this plate are invalid and need to be re-run.
- CTL contains SARS-CoV-2 RNA, and is expected to give a Positive result in the call column of the TSV file or PDF report. If it shows a Negative, Inconclusive or Invalid result, this means that all tests in this plate are invalid and need to be re-run.
10. Prepare the system for a subsequent run
Flow cell removal
At the end of the experiment, remove the flow cells, flush them and place them in their return packaging.
Wipe down the GridION with an IPA wipe taking care to clean up any buffer that may have spilt during handling.
The GridION is now ready for new flow cells.
There is a simple-to-follow process for the return of old used flow cells to Oxford Nanopore for recycling.
Data management
The GridION device is provided with 4 Tb of sotrage, suffiient for several LamPORE runs.
At the start of a new experiment, the onboard software will look to ensure there is sufficient storage for a new experiment, so it is advised to always keep 1 Tb of hard drive availble for new experiments.
With this in mind, at the end of each run, we recommend users to verfy that they have sufficient space left for upcoming runs.
Please see the GridION IT requirements for recommendations on how to move data.
LIMS integration
For users wishing to integrate ther GridION with their LIMS. please contact the Support team to discuss options.
11. Recalibrating a flow cell
Materials
- Flow Cell Recalibration Kit (OND-EXP-FRK001)
Equipment
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- Ice bucket with ice
Preparation to run the recalibration procedure
- The aim is to remove most of the initial library and prepare the flow cell for the loading of a subsequent library
- The Flow Cell Recalibration Kit contains all solutions required for removal of the initial library
- The experiment in MinKNOW should be allowed to end before recalibrating the flow cell
- After the flow cell has been recalibrated, a new library can be loaded or the flow cell can be stored at 4°C
We recommend running a maximum of four libraries on one flow cell, with recalibration steps between library loads.
Place the tube of Wash Mix on ice. Do not vortex the tube.
Thaw one tube of Wash Diluent at room temperature.
Mix the contents of Wash Diluent thoroughly by vortexing, then spin down briefly and place on ice.
In a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, prepare the following mix:
| Component | Volume |
|---|---|
| Wash Mix (WMX) | 20 μl |
| Wash Diluent (DIL) | 380 μl |
Mix well by pipetting, and place on ice. Do not vortex the tube.
Make sure the sequencing experiment in MinKNOW has finished, and leave the flow cell in the device.
Ensure that the flow cell priming port cover and SpotON sample port cover are closed, as indicated in the figure below.
Remove all fluid from the waste channel through waste port 1 using a P1000 pipette.
As both the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed, no fluid should leave the sensor array area.

It is vital that the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed before removing the waste buffer to prevent air from being drawn across the sensor array area, which would lead to a significant loss of sequencing channels.
Slide the flow cell priming port cover clockwise to open.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back a small volume to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the flow cell priming port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer/liquid entering the pipette tip.
- Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the flow cell priming port across the sensor array.
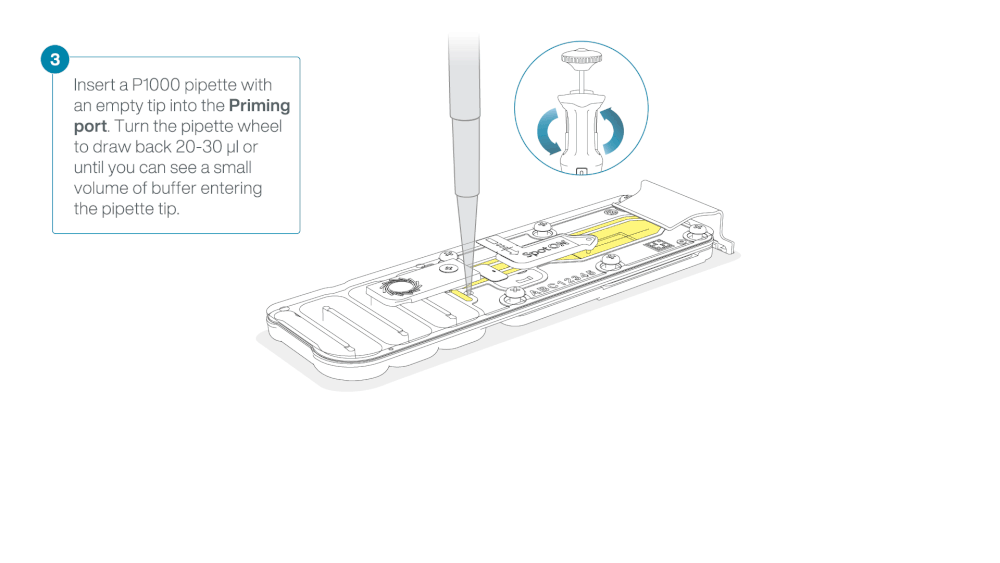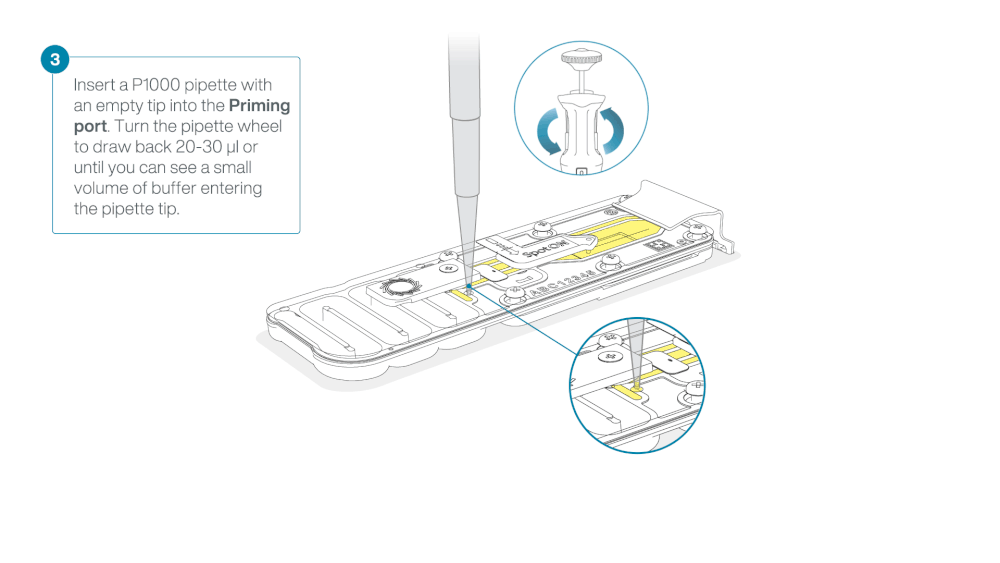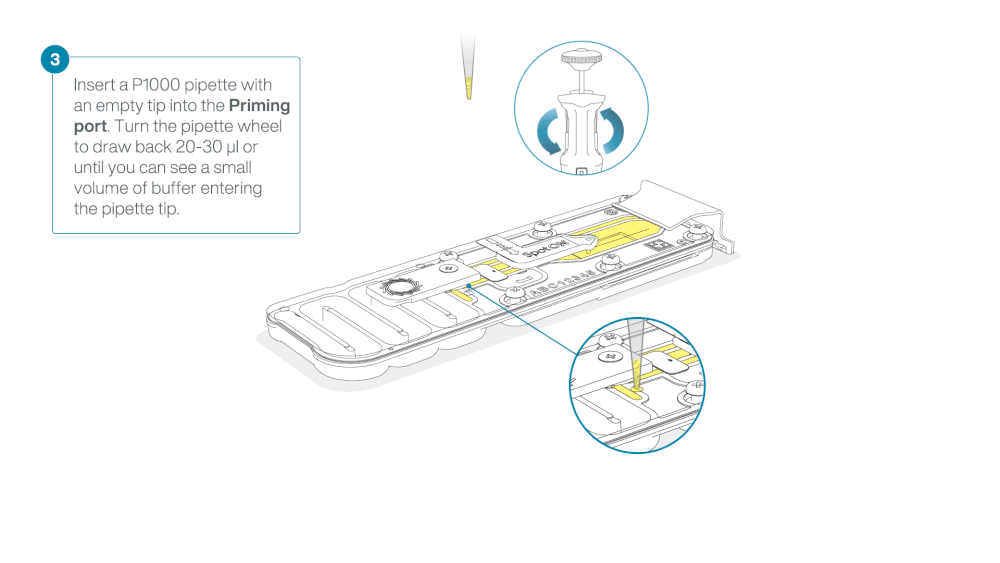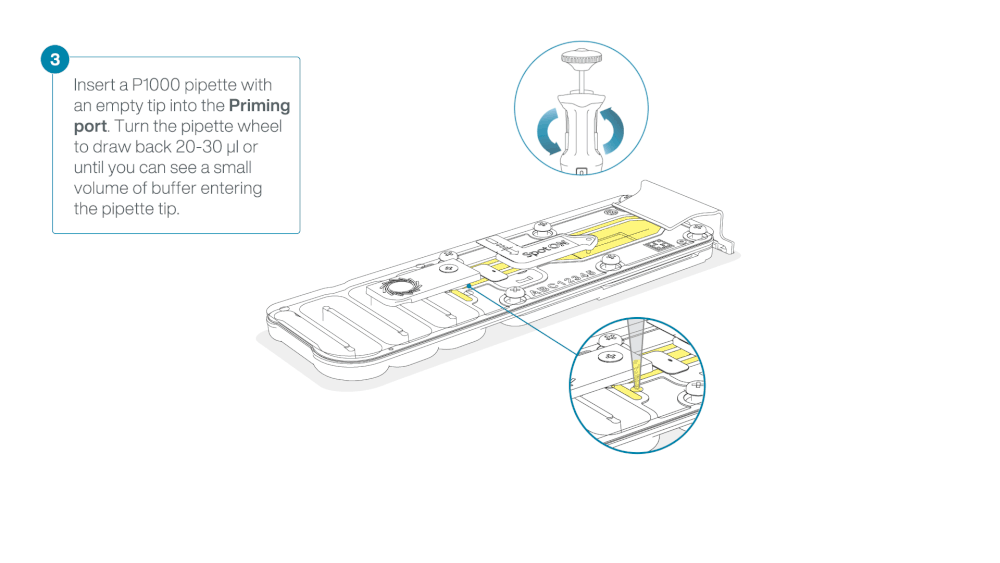
Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
Load 400 µl of the prepared WMX and DIL mix into the flow cell via the priming port, avoiding the introduction of air.
Close the priming port and wait for 30 minutes.
Ensure that the flow cell priming port cover and SpotON sample port cover are closed, as indicated in the figure below.
Remove all fluid from the waste channel through waste port 1 using a P1000 pipette.
As both the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed, no fluid should leave the sensor array area.

It is vital that the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed before removing the waste buffer to prevent air from being drawn across the sensor array area, which would lead to a significant loss of sequencing channels.
Follow one of the two options described in the next steps of the protocol.
- Run a second library on the flow cell straight away
- Store the flow cell for later use
12. To run a second library on the flow cell straight away
Materials
- Flow Cell Recalibration Kit (OND-EXP-FRK001)
- SARS-CoV-2 Control kit S (OND-EXP-SCT001)
Consumables
- Flow Cell (OND-FLO-M106D)
Equipment
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- Ice bucket with ice
- GridION (OND-GRD003)
Prepare a second library using a minimum of 24 samples and a different set of LAMP primers and Rapid Barcodes to the ones used for the first library.
Load the recalibrated flow cell with the second library, following the instructions in the "Priming and loading the flow cell" section of this protocol.
Once the flow cell has been primed and loaded, start a new sequencing experiment in MinKNOW.
Library storage recommendations
We recommend storing libraries in Eppendorf LoBind tubes at 4°C for short term storage or repeated use, for example, re-loading flow cells after recalibrations. For single use and long-term storage of more than 3 months, we recommend storing libraries at -80°C in Eppendorf LoBind tubes.
13. To store the flow cell for later use
Materials
- Flow Cell Recalibration Kit (OND-EXP-FRK001)
Optional equipment
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
Thaw one tube of Storage Buffer (S) at room temperature.
Mix contents thoroughly by pipetting and spin down briefly.
Slide the flow cell priming port cover clockwise to open.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back a small volume to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the flow cell priming port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer/liquid entering the pipette tip.
- Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the flow cell priming port across the sensor array.

Slowly add 500 μl of Storage Buffer (S) through the flow cell priming port.
Close the priming port.
Remove all fluid from the waste channel through waste port 1 using a P1000 pipette.
As both the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed, no fluid should leave the sensor array area.

It is vital that the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed before removing the waste buffer to prevent air from being drawn across the sensor array area, which would lead to a significant loss of sequencing channels.
The flow cell can now be stored at 4-8°C.
When you wish to reuse the flow cell, remove the flow cell from storage, and allow it to warm to room temperature for ~5 minutes.
Library storage recommendations
We recommend storing libraries in Eppendorf LoBind tubes at 4°C for short term storage or repeated use, for example, re-loading flow cells after recalibrations. For single use and long-term storage of more than 3 months, we recommend storing libraries at -80°C in Eppendorf LoBind tubes.







