Rapid sequencing amplicons - 16S barcoding (SQK-16S024) (16S_9086_v1_revZ_14Aug2019)
MinION: Protocol
V 16S_9086_v1_revZ_14Aug2019
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
Library preparation
Sequencing and data analysis
Troubleshooting
1. Overview of the protocol
This is a Legacy product
This kit is soon to be discontinued and we recommend all customers to upgrade to the latest chemistry for their relevant kit which is available on the Store. If customers require further support for any ongoing critical experiments using a Legacy product, please contact Customer Support via email: support@nanoporetech.com. For further information on please see the product update page.
16S Barcoding Kit 1-24 features
This kit is recommended for users who:
- wish to multiplex samples to reduce price per sample
- want to do 16S sequencing
- are interested in genus level bacterial identification
Introduction to the 16S Barcoding Kit 1-24
This protocol describes how to carry out rapid barcoding of 16S amplicons using the 16S Barcoding Kit 1-24 (SQK-16S024). Due to the presence of both highly conserved (adequate for universal primers and phylogenetic signal) and highly variant regions (different across species), the 16S rRNA gene is often used for sequence-based bacterial identification.
The 16S Barcoding Kit 1-24 enables access to rapid 16S sequencing for organism identification. By narrowing down to a specific region of interest, a user can see all the organisms in the sample without sequencing unneccesary regions of the genome, making the test quicker and more economical. There are 24 unique barcodes, allowing the user to pool up to 24 different samples in one sequencing experiment.
Steps in the sequencing workflow:
Prepare for your experiment
You will need to:
- Extract your DNA, and check its length, quantity and purity. The quality checks performed during the protocol are essential in ensuring experimental success.
- Ensure you have your sequencing kit, the correct equipment and third-party reagents
- Download the software for acquiring and analysing your data
- Check your flow cell to ensure it has enough pores for a good sequencing run
Library preparation
You will need to:
- Amplify the 16S gene using barcodes supplied in the kit
- Clean up the library on beads
- Attach rapid sequencing adapters supplied in the kit to the DNA ends
- Prime the flow cell, and load your DNA library into the flow cell

Sequencing and analysis
You will need to:
- Start a sequencing run using the MinKNOW software, which will collect raw data from the device and convert it into basecalled reads
- Start the EPI2ME software and select the FASTQ 16S workflow
Compatibility of this protocol
This protocol should only be used in combination with:
- 16S Barcoding Kit 1-24 (SQK-16S024)
- R9.4.1 (FLO-MIN106) flow cells
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
- Auxiliary Sequencing Vials (EXP-AUX001)
- RAP Top-Up Kit (EXP-RAP001)
2. Equipment and consumables
材料
- 10 ng high molecular weight genomic DNA
- 16S Barcoding Kit 1-24 (SQK-16S024)
- Flow Cell Priming Kit (EXP-FLP002)
消耗品
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- 0.2 ml 薄壁のPCRチューブ
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. ThermoFisher, AM9937)
- LongAmp Hot Start Taq 2X Master Mix (NEB, M0533)
- Freshly prepared 70% ethanol in nuclease-free water
- 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0 with 50 mM NaCl
装置
- 小型遠心機
- タイマー
- サーマルサイクラー
- P1000 ピペット及びチップ
- P200 ピペットとチップ
- P100 ピペットとチップ
- P20 ピペットとチップ
- P10 ピペットとチップ
- P2 ピペットとチップ
- Multichannel pipette and tips
オプション装置
- Agilent Bioanalyzer (or equivalent)
- Qubit蛍光光度計(またはQCチェックのための同等品)
- Eppendorf 5424 centrifuge (or equivalent)
For this protocol, you will need 10 ng high molecular weight genomic DNA per barcode.
For optimal output, we currently do not recommend using fewer than 4 barcodes. If you wish to multiplex less than 4 samples, please ensure you split your sample(s) across multiple barcodes so at least 4 barcodes are run (e.g. for 2 samples, use 16S Barcode Primers 01-02 for sample A, and 16S Barcode Primers 03-04 for sample B). Please note that the required sample input for each barcode is 10 ng gDNA.
Input DNA
How to QC your input DNA
It is important that the input DNA meets the quantity and quality requirements. Using too little or too much DNA, or DNA of poor quality (e.g. highly fragmented or containing RNA or chemical contaminants) can affect your library preparation.
For instructions on how to perform quality control of your DNA sample, please read the Input DNA/RNA QC protocol.
Chemical contaminants
Depending on how the DNA is extracted from the raw sample, certain chemical contaminants may remain in the purified DNA, which can affect library preparation efficiency and sequencing quality. Read more about contaminants on the Contaminants page of the Community.
16S Barcoding Kit contents
| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | No. of vials | Fill volume per vial (μl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S Barcode Primers 01-24 | 1-24 | - | 2 plates, 3 strips per plate | 15 μl per well |
| Rapid Adapter | RAP | Green | 1 | 10 |
| Sequencing Buffer | SQB | Red | 1 | 300 |
| Loading Beads | LB | Pink | 1 | 360 |
Please note that the Sequencing Tether (SQT) tube will NOT be used in this protocol.
Flow Cell Priming Kit contents (EXP-FLP002)

| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | No. of vials | Fill volume per vial (μl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flush Buffer | FB | Blue | 6 | 1,170 |
| Flush Tether | FLT | Purple | 1 | 200 |
The RAP Top-Up Kit (EXP-RAP001) is available to provide enough reagents for another six reactions depending on how the barcodes are used.
This kit contains reagents to be used with any remaining barcodes to load another six sequencing libraries.
| Reagent | Acronym | Cap colour | No. of vials | Fill volume per vial (µl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Adapter | RAP | Green | 1 | 10 |
| Sequencing Tether | SQT | Purple | 1 | 10 |
| Loading Beads | LB | Pink | 1 | 360 |
| Sequencing Buffer | SQB | Red | 1 | 300 |
3. Computer requirements and software
MinION Mk1B IT requirements
Sequencing on a MinION Mk1B requires a high-spec computer or laptop to keep up with the rate of data acquisition. For more information, refer to the MinION Mk1B IT requirements document.
MinION Mk1C IT requirements
The MinION Mk1C contains fully-integrated compute and screen, removing the need for any accessories to generate and analyse nanopore data. For more information refer to the MinION Mk1C IT requirements document.
MinION Mk1D IT requirements
Sequencing on a MinION Mk1D requires a high-spec computer or laptop to keep up with the rate of data acquisition. For more information, refer to the MinION Mk1D IT requirements document.
Software for nanopore sequencing
MinKNOW
The MinKNOW software controls the nanopore sequencing device, collects sequencing data and basecalls in real time. You will be using MinKNOW for every sequencing experiment to sequence, basecall and demultiplex if your samples were barcoded.
For instructions on how to run the MinKNOW software, please refer to the MinKNOW protocol.
EPI2ME (optional)
The EPI2ME cloud-based platform performs further analysis of basecalled data, for example alignment to the Lambda genome, barcoding, or taxonomic classification. You will use the EPI2ME platform only if you would like further analysis of your data post-basecalling.
For instructions on how to create an EPI2ME account and install the EPI2ME Desktop Agent, please refer to this link.
Check your flow cell
We highly recommend that you check the number of pores in your flow cell prior to starting a sequencing experiment. This should be done within 12 weeks of purchasing for MinION/GridION/PromethION or within four weeks of purchasing Flongle Flow Cells. Oxford Nanopore Technologies will replace any flow cell with fewer than the number of pores in the table below, when the result is reported within two days of performing the flow cell check, and when the storage recommendations have been followed. To do the flow cell check, please follow the instructions in the Flow Cell Check document.
| Flow cell | Minimum number of active pores covered by warranty |
|---|---|
| Flongle Flow Cell | 50 |
| MinION/GridION Flow Cell | 800 |
| PromethION Flow Cell | 5000 |
4. Library preparation
材料
- 10 ng high molecular weight genomic DNA
- 16S Barcodes in 96-well plate, at 1 μM each
- Rapid Adapter (RAP)
消耗品
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. ThermoFisher, AM9937)
- LongAmp Hot Start Taq 2X Master Mix (NEB, M0533)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Freshly prepared 70% ethanol in nuclease-free water
- 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0 with 50 mM NaCl
- 0.2 ml 薄壁のPCRチューブ
装置
- サーマルサイクラー
- Hula mixer(緩やかに回転するミキサー)
- 1.5 mlエッペンドルフチューブに最適のマグネット式ラック
- アイスバケツ(氷入り)
- 小型遠心機
- Multichannel pipette and tips
- P1000 ピペット及びチップ
- P200 ピペットとチップ
- P100 ピペットとチップ
- P20 ピペットとチップ
- P10 ピペットとチップ
- P2 ピペットとチップ
Take one 96-well plate containing 16S barcodes. Break one set of barcodes (1-24, or as desired) away from the plate and return the rest to storage.
The 96-well plates are designed to break in one direction only. Strips, or multiple strips, of eight wells/barcodes can be removed from the plate at any one time.
Thaw the desired barcodes, make sure the liquid is at the bottom of the tubes, and place on ice.
Thaw the LongAmp Hot Start Taq 2X Master Mix, spin down briefly, mix well by pipetting and place on ice.
Prepare the DNA in nuclease-free water.
- Transfer 10 ng genomic DNA into a DNA LoBind tube
- Adjust the volume to 10 μl with nuclease-free water
- Mix thoroughly by flicking the tube, to avoid unwanted shearing
- Spin down briefly in a microfuge
For each sample to be tested, prepare the following mixture in separate 0.2 ml thin-walled PCR tubes.
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Nuclease-free water | 5 µl |
| Input DNA (10 ng) | 10 µl |
| LongAmp Hot Start Taq 2X Master Mix | 25 µl |
| Total | 40 µl |
If the amount of input material is altered, the number of PCR cycles may need to be adjusted to produce the same yield.
Ensure the components are thoroughly mixed by pipetting, and spin down.
Using clean pipette tips, carefully pierce the foil surface of the required barcodes. Use a new tip for each barcode to avoid cross-contamination. Make a note of which barcode numbers will be run for each sample.
Using a multichannel pipette, mix the 16S barcodes by pipetting up and down 10 times. Transfer 10 μl of each 16S Barcode into respective sample-containing tubes.
The layout of the barcodes in the plate are as follows:
Mix thoroughly by pipetting up and down ten times.
Amplify using the following cycling conditions:
| Cycle step | Temperature | Time | No. of cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial denaturation | 95 °C | 1 min | 1 |
| Denaturation | 95 °C | 20 secs | 25 |
| Annealing | 55 °C | 30 secs | 25 |
| Extension | 65 °C | 2 mins | 25 |
| Final extension | 65 °C | 5 mins | 1 |
| Hold | 4 °C | ∞ |
Transfer each sample to a separate 1.5 ml DNA LoBind Eppendorf tube. Carry out steps 11-21 for each sample, before pooling the samples at step 22.
Resuspend the AMPure XP beads by vortexing.
Add 30 µl of resuspended AMPure XP beads to the reaction and mix by pipetting.
Incubate on a Hula mixer (rotator mixer) for 5 minutes at room temperature.
Prepare 500 μl of fresh 70% ethanol in nuclease-free water.
Spin down the sample and pellet on a magnet. Keep the tube on the magnet, and pipette off the supernatant when clear and colourless.
Keep the tube on the magnet and wash the beads with 200 µl of freshly prepared 70% ethanol without disturbing the pellet. Remove the ethanol using a pipette and discard.
Repeat the previous step.
Spin down and place the tube back on the magnet. Pipette off any residual ethanol. Allow to dry for ~30 seconds, but do not dry the pellet to the point of cracking.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack and resuspend pellet in 10 µl of 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0 with 50 mM NaCl. Incubate for 2 minutes at room temperature.
Pellet the beads on a magnet until the eluate is clear and colourless.
Remove and retain 10 µl of eluate into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
- Dispose of the pelleted beads
Quantify 1 µl of eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer.
Pool all barcoded libraries in the desired ratios to a total of 50-100 fmoles in 10 μl of 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0 with 50 mM NaCl. For 16S amplicons of ~1500 bp, 50-100 fmoles equates to ~50-100 ng.
Add 1 μl of RAP to the barcoded DNA.
Mix gently by flicking the tube, and spin down.
Incubate the reaction for 5 minutes at room temperature.
The prepared library is used for loading into the flow cell. Store the library on ice until ready to load.
If quantities allow, the libraries may be diluted in Elution Buffer (EB) for splitting across multiple flow cells.
Additional Elution Buffer (EB) for doing this can be found in the Sequencing Auxiliary Vials expansion (EXP-AUX001), available to purchase separately.
5. Priming and loading the SpotON flow cell
材料
- Flow Cell Priming Kit (EXP-FLP002)
- Sequencing Buffer (SQB)
- Loading Beads (LB)
消耗品
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. ThermoFisher, AM9937)
装置
- MinION Mk1B or Mk1C
- SpotON Flow Cell
- MinIONとGridIONのFlow Cell ライトシールド
- P1000 ピペット及びチップ
- P100 ピペットとチップ
- P20 ピペットとチップ
- P10 ピペットとチップ
Thaw the Sequencing Buffer (SQB), Loading Beads (LB), Flush Tether (FLT) and one tube of Flush Buffer (FB) at room temperature before mixing the reagents by vortexing, and spin down at room temperature.
To prepare the flow cell priming mix, add 30 µl of thawed and mixed Flush Tether (FLT) directly to the tube of thawed and mixed Flush Buffer (FB), and mix by vortexing at room temperature.
Open the MinION device lid and slide the flow cell under the clip.
Press down firmly on the flow cell to ensure correct thermal and electrical
Complete a flow cell check to assess the number of pores available before loading the library.
This step can be omitted if the flow cell has been checked previously.
See the flow cell check instructions in the MinKNOW protocol for more information.
Slide the priming port cover clockwise to open the priming port.
Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back a small volume to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl
- Insert the tip into the priming port
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, to draw back 20-30 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip
Note: Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the priming port across the sensor array.
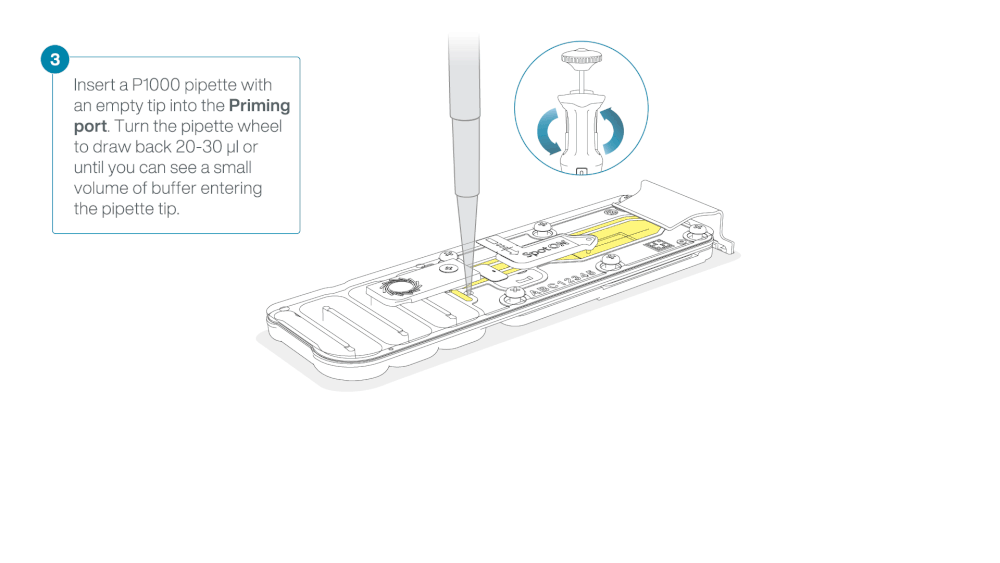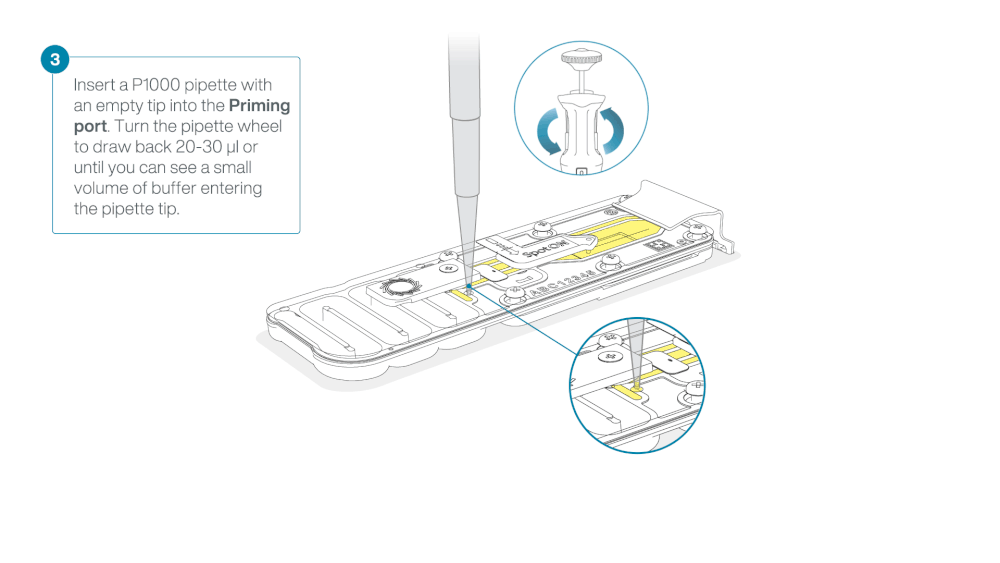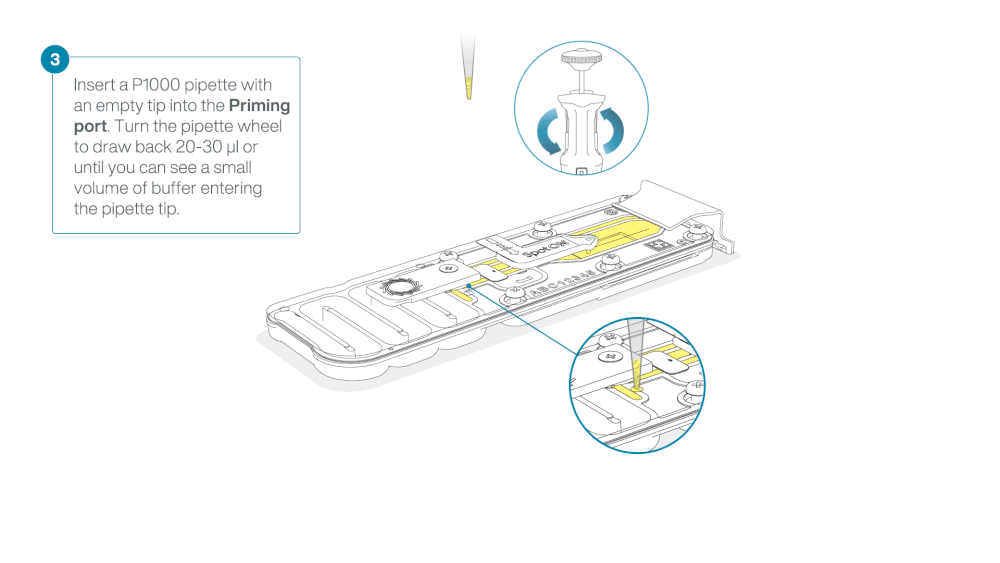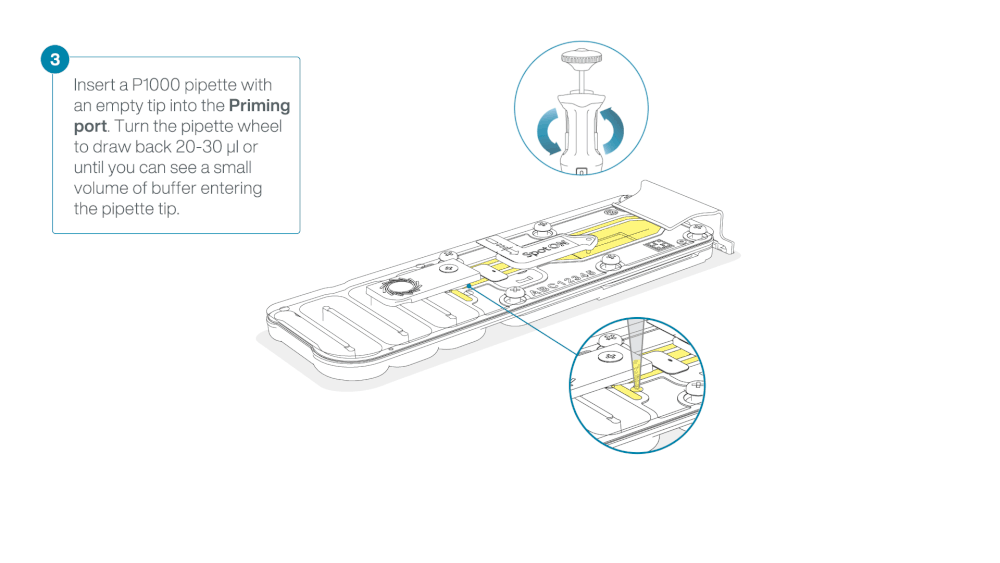
Load 800 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the priming port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait for five minutes. During this time, prepare the library for loading by following the steps below.

Thoroughly mix the contents of the Loading Beads (LB) tubes by vortexing.
The Loading Beads (LB) tube contains a suspension of beads. These beads settle very quickly. It is vital that they are mixed immediately before use.
In a new tube, prepare the library for loading as follows:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer (SQB) | 34 µl |
| Loading Beads (LB), mixed immediately before use | 25.5 µl |
| Nuclease-free water | 4.5 µl |
| DNA library | 11 µl |
| Total | 75 µl |
Note: Load the library onto the flow cell immediately after adding the Sequencing Buffer (SQB) and Loading Beads (LB) because the fuel in the buffer will start to be consumed by the adapter.
Complete the flow cell priming:
- Gently lift the SpotON sample port cover to make the SpotON sample port accessible.
- Load 200 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell priming port (not the SpotON sample port), avoiding the introduction of air bubbles.

Mix the prepared library gently by pipetting up and down just prior to loading.
Add 75 μl of the prepared library to the flow cell via the SpotON sample port in a dropwise fashion. Ensure each drop flows into the port before adding the next.

6. Data acquisition and basecalling
How to start sequencing
Once you have loaded your flow cell, the sequencing run can be started on MinKNOW, our sequencing software that controls the device, data acquisition and real-time basecalling. For more detailed information on setting up and using MinKNOW, please see the MinKNOW protocol.
MinKNOW can be used and set up to sequence in multiple ways:
- On a computer either directly or remotely connected to a sequencing device.
- Directly on a GridION or PromethION 24/48 sequencing device.
For more information on using MinKNOW on a sequencing device, please see the device user manuals:
To start a sequencing run on MinKNOW:
1. Navigate to the start page and click Start sequencing.
2. Fill in your experiment details, such as name and flow cell position and sample ID.
3. Select the sequencing kit used in the library preparation on the Kit page.
4. Configure the sequencing and output parameters for your sequencing run or keep to the default settings on the Run configuration tab.
Note: If basecalling was turned off when a sequencing run was set up, basecalling can be performed post-run on MinKNOW. For more information, please see the MinKNOW protocol.
5. Click Start to initiate the sequencing run.
Data analysis after sequencing
After sequencing has completed on MinKNOW, the flow cell can be reused or returned, as outlined in the Flow cell reuse and returns section.
After sequencing and basecalling, the data can be analysed. For further information about options for basecalling and post-basecalling analysis, please refer to the Data Analysis document.
In the Downstream analysis section, we outline further options for analysing your data.
7. Flow cell reuse and returns
材料
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
After your sequencing experiment is complete, if you would like to reuse the flow cell, please follow the Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol and store the washed flow cell at +2°C to +8°C.
The Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol is available on the Nanopore Community.
We recommend you to wash the flow cell as soon as possible after you stop the run. However, if this is not possible, leave the flow cell on the device and wash it the next day.
Alternatively, follow the returns procedure to send the flow cell back to Oxford Nanopore.
Instructions for returning flow cells can be found here.
If you encounter issues or have questions about your sequencing experiment, please refer to the Troubleshooting Guide that can be found in the online version of this protocol.
8. Downstream analysis
Post-basecalling analysis
There are several options for further analysing your basecalled data:
1. EPI2ME workflows
For in-depth data analysis, Oxford Nanopore Technologies offers a range of bioinformatics tutorials and workflows available in EPI2ME. The platform provides a vehicle where workflows deposited in GitHub by our Research and Applications teams can be showcased with descriptive texts, functional bioinformatics code and example data.
2. Research analysis tools
Oxford Nanopore Technologies' Research division has created a number of analysis tools, which are available in the Oxford Nanopore GitHub repository. The tools are aimed at advanced users, and contain instructions for how to install and run the software. They are provided as-is, with minimal support.
3. Community-developed analysis tools
If a data analysis method for your research question is not provided in any of the resources above, please refer to the resource centre and search for bioinformatics tools for your application. Numerous members of the Nanopore Community have developed their own tools and pipelines for analysing nanopore sequencing data, most of which are available on GitHub. Please be aware that these tools are not supported by Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and are not guaranteed to be compatible with the latest chemistry/software configuration.
9. Issues during DNA/RNA extraction and library preparation
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Low sample quality
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low DNA purity (Nanodrop reading for DNA OD 260/280 is <1.8 and OD 260/230 is <2.0–2.2) | The DNA extraction method does not provide the required purity | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants document. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. Consider performing an additional SPRI clean-up step. |
| Low RNA integrity (RNA integrity number <9.5 RIN, or the rRNA band is shown as a smear on the gel) | The RNA degraded during extraction | Try a different RNA extraction method. For more info on RIN, please see the RNA Integrity Number document. Further information can be found in the DNA/RNA Handling page. |
| RNA has a shorter than expected fragment length | The RNA degraded during extraction | Try a different RNA extraction method. For more info on RIN, please see the RNA Integrity Number document. Further information can be found in the DNA/RNA Handling page. We recommend working in an RNase-free environment, and to keep your lab equipment RNase-free when working with RNA. |
Low DNA recovery after AMPure bead clean-up
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low recovery | DNA loss due to a lower than intended AMPure beads-to-sample ratio | 1. AMPure beads settle quickly, so ensure they are well resuspended before adding them to the sample. 2. When the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio is lower than 0.4:1, DNA fragments of any size will be lost during the clean-up. |
| Low recovery | DNA fragments are shorter than expected | The lower the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio, the more stringent the selection against short fragments. Please always determine the input DNA length on an agarose gel (or other gel electrophoresis methods) and then calculate the appropriate amount of AMPure beads to use. 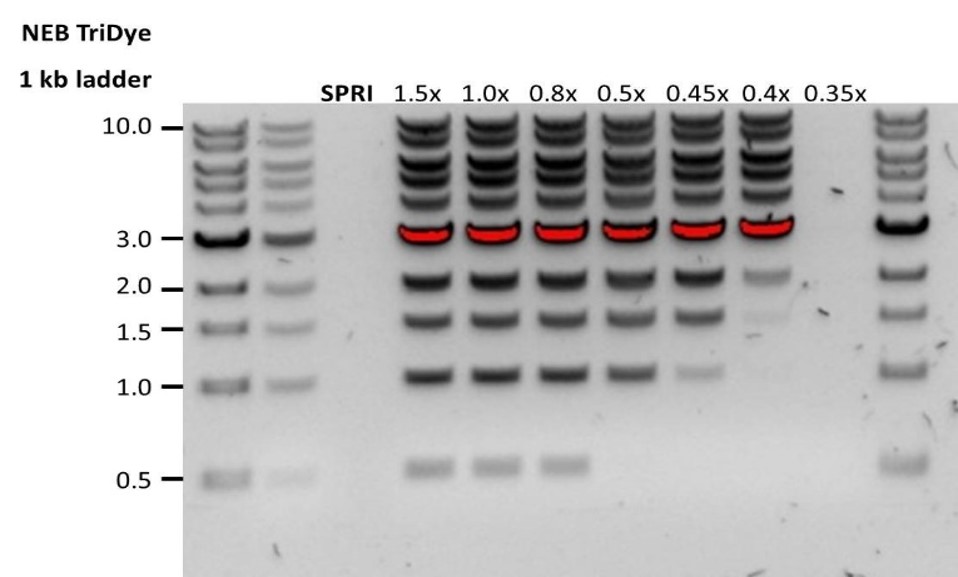 |
| Low recovery after end-prep | The wash step used ethanol <70% | DNA will be eluted from the beads when using ethanol <70%. Make sure to use the correct percentage. |
10. Issues during the sequencing run
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Fewer pores at the start of sequencing than after Flow Cell Check
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | An air bubble was introduced into the nanopore array | After the Flow Cell Check it is essential to remove any air bubbles near the priming port before priming the flow cell. If not removed, the air bubble can travel to the nanopore array and irreversibly damage the nanopores that have been exposed to air. The best practice to prevent this from happening is demonstrated in this video. |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | The flow cell is not correctly inserted into the device | Stop the sequencing run, remove the flow cell from the sequencing device and insert it again, checking that the flow cell is firmly seated in the device and that it has reached the target temperature. If applicable, try a different position on the device (GridION/PromethION). |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | Contaminations in the library damaged or blocked the pores | The pore count during the Flow Cell Check is performed using the QC DNA molecules present in the flow cell storage buffer. At the start of sequencing, the library itself is used to estimate the number of active pores. Because of this, variability of about 10% in the number of pores is expected. A significantly lower pore count reported at the start of sequencing can be due to contaminants in the library that have damaged the membranes or blocked the pores. Alternative DNA/RNA extraction or purification methods may be needed to improve the purity of the input material. The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
MinKNOW script failed
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Script failed" | Restart the computer and then restart MinKNOW. If the issue persists, please collect the MinKNOW log files and contact Technical Support. If you do not have another sequencing device available, we recommend storing the flow cell and the loaded library at 4°C and contact Technical Support for further storage guidance. |
Pore occupancy below 40%
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Pore occupancy <40% | Not enough library was loaded on the flow cell | Ensure you load the recommended amount of good quality library in the relevant library prep protocol onto your flow cell. Please quantify the library before loading and calculate mols using tools like the Promega Biomath Calculator, choosing "dsDNA: µg to pmol" |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and sequencing adapters did not ligate to the DNA | Make sure to use the NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (E6056) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Buffer (LNB, provided in the sequencing kit) at the sequencing adapter ligation step, and use the correct amount of each reagent. A Lambda control library can be prepared to test the integrity of the third-party reagents. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and ethanol was used instead of LFB or SFB at the wash step after sequencing adapter ligation | Ethanol can denature the motor protein on the sequencing adapters. Make sure the LFB or SFB buffer was used after ligation of sequencing adapters. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | No tether on the flow cell | Tethers are adding during flow cell priming (FLT/FCT tube). Make sure FLT/FCT was added to FB/FCF before priming. |
Shorter than expected read length
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Shorter than expected read length | Unwanted fragmentation of DNA sample | Read length reflects input DNA fragment length. Input DNA can be fragmented during extraction and library prep. 1. Please review the Extraction Methods in the Nanopore Community for best practice for extraction. 2. Visualise the input DNA fragment length distribution on an agarose gel before proceeding to the library prep. 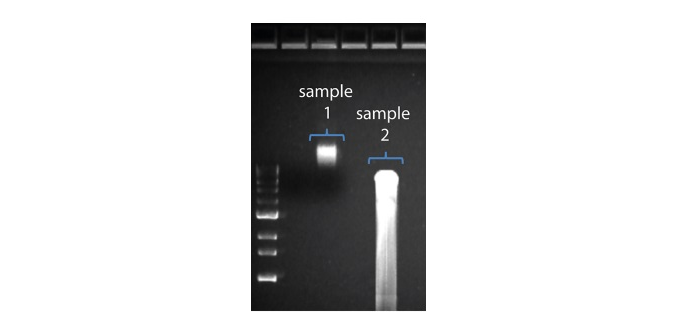 In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented. In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented.3. During library prep, avoid pipetting and vortexing when mixing reagents. Flicking or inverting the tube is sufficient. |
Large proportion of unavailable pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
Large proportion of unavailable pores (shown as blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot) 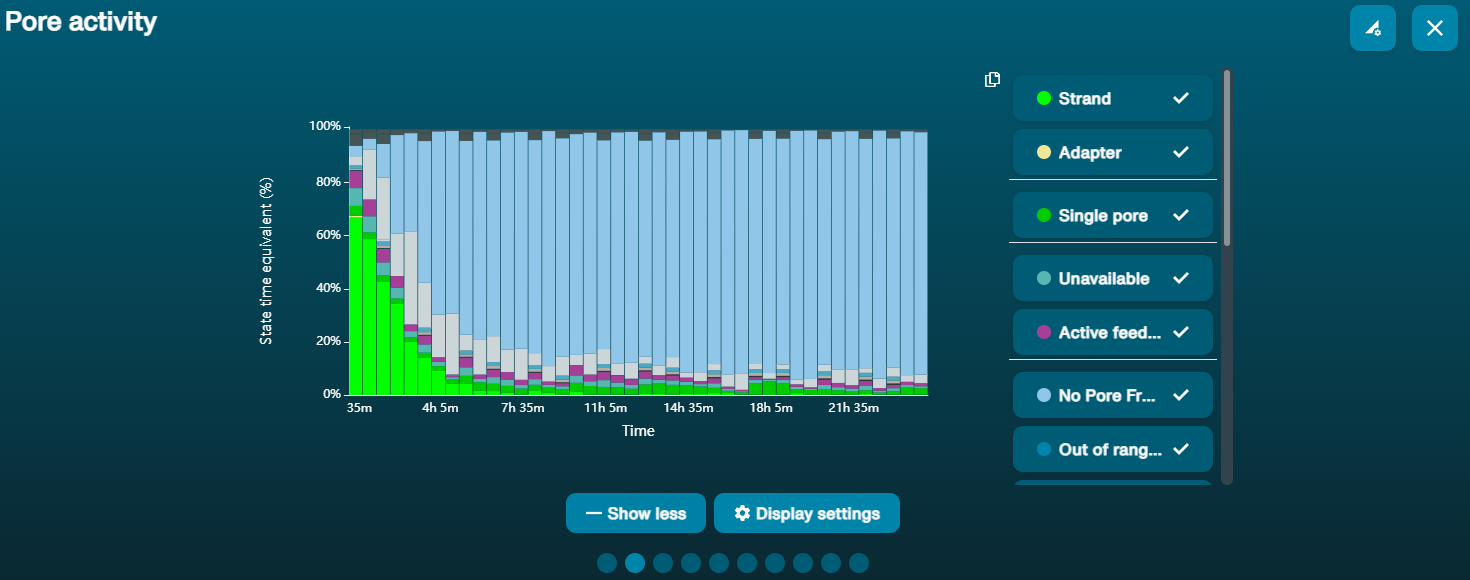 The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. | Contaminants are present in the sample | Some contaminants can be cleared from the pores by the unblocking function built into MinKNOW. If this is successful, the pore status will change to "sequencing pore". If the portion of unavailable pores stays large or increases: 1. A nuclease flush using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) can be performed, or 2. Run several cycles of PCR to try and dilute any contaminants that may be causing problems. |
Large proportion of inactive pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores (shown as light blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot. Pores or membranes are irreversibly damaged) | Air bubbles have been introduced into the flow cell | Air bubbles introduced through flow cell priming and library loading can irreversibly damage the pores. Watch the Priming and loading your flow cell video for best practice |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Certain compounds co-purified with DNA | Known compounds, include polysaccharides, typically associate with plant genomic DNA. 1. Please refer to the Plant leaf DNA extraction method. 2. Clean-up using the QIAGEN PowerClean Pro kit. 3. Perform a whole genome amplification with the original gDNA sample using the QIAGEN REPLI-g kit. |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Contaminants are present in the sample | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run | For Kit 9 chemistry (e.g. SQK-LSK109), fast fuel consumption is typically seen when the flow cell is overloaded with library (please see the appropriate protocol for your DNA library to see the recommendation). | Add more fuel to the flow cell by following the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol. In future experiments, load lower amounts of library to the flow cell. |
Temperature fluctuation
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature fluctuation | The flow cell has lost contact with the device | Check that there is a heat pad covering the metal plate on the back of the flow cell. Re-insert the flow cell and press it down to make sure the connector pins are firmly in contact with the device. If the problem persists, please contact Technical Services. |
Failed to reach target temperature
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Failed to reach target temperature" | The instrument was placed in a location that is colder than normal room temperature, or a location with poor ventilation (which leads to the flow cells overheating) | MinKNOW has a default timeframe for the flow cell to reach the target temperature. Once the timeframe is exceeded, an error message will appear and the sequencing experiment will continue. However, sequencing at an incorrect temperature may lead to a decrease in throughput and lower q-scores. Please adjust the location of the sequencing device to ensure that it is placed at room temperature with good ventilation, then re-start the process in MinKNOW. Please refer to this link for more information on MinION temperature control. |
Guppy – no input .fast5 was found or basecalled
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| No input .fast5 was found or basecalled | input_path did not point to the .fast5 file location | The --input_path has to be followed by the full file path to the .fast5 files to be basecalled, and the location has to be accessible either locally or remotely through SSH. |
| No input .fast5 was found or basecalled | The .fast5 files were in a subfolder at the input_path location | To allow Guppy to look into subfolders, add the --recursive flag to the command |
Guppy – no Pass or Fail folders were generated after basecalling
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| No Pass or Fail folders were generated after basecalling | The --qscore_filtering flag was not included in the command | The --qscore_filtering flag enables filtering of reads into Pass and Fail folders inside the output folder, based on their strand q-score. When performing live basecalling in MinKNOW, a q-score of 7 (corresponding to a basecall accuracy of ~80%) is used to separate reads into Pass and Fail folders. |
Guppy – unusually slow processing on a GPU computer
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Unusually slow processing on a GPU computer | The --device flag wasn't included in the command | The --device flag specifies a GPU device to use for accelerate basecalling. If not included in the command, GPU will not be used. GPUs are counted from zero. An example is --device cuda:0 cuda:1, when 2 GPUs are specified to use by the Guppy command. |







