使用 SQK-NBD114.24 进行简化甲基化测序(RRMS) (RRMS_9209_v114_revI_21Oct2025)
PromethION: Protocol
使用 SQK-NBD114.24 进行简化甲基化测序(RRMS) V RRMS_9209_v114_revI_21Oct2025
仅供研究使用。
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
概览
仅供研究使用。
1. 实验方案概览
“试剂盒14”中的适应性采样
本工作流程在 Kit 14 试剂体系下经过优化,可通过适应性采样富集特定目标区域,从而获得更高的数据产出与更优的测序结果。
如需了解有关适应性采样实验设计的更多背景信息,请参阅适应性采样最佳实践文档。
简化甲基化测序(RRMS)
采用纳米孔测序,用户无需对样本进行亚硫酸氢盐转化,即可直接检测甲基化胞嘧啶(如CpG位点)。CpG 位点常在基因组中以高密度簇集形式出现,称为 CpG 岛(CGI)。大多数脊椎动物基因的启动子区域都位于 CpG 岛内。
启动子区域甲基化模式的变化与基因表达变化密切相关,并与多种疾病状态(如癌症)有关。通过比较肿瘤样本与正常样本之间的甲基化差异,可以帮助揭示与肿瘤形成和发展相关的分子机制。
借助Oxford Nanopore的适应性采样(AS),样本无需前期处理,只需在测序过程中消耗非靶向区域,即可实现对目标基因区域(如CGI)的富集。该方法快速、灵活、准确。
请参阅我们的简化甲基化测序入门,了解有关此方法的详细工作原理,及与其它甲基化分析技术(如EPIC甲基化芯片、亚硫酸氢盐)的比较情况。
RRMS 可在 GridION 以及 PromethION P2S、P24 和 P48 设备上运行。
在 GridION 平台上运行时,我们建议每张芯片仅测序一个样本,并采用实验指南: 使用 SQK-LSK114 试剂盒对细胞进行简化甲基化测序。
人类样本测序
人类样本测序
简化甲基化测序 (RRMS)方案能够靶向人类基因组中约 310 Mb 的高 CpG 富集区域,覆盖所有已注释的 CpG 岛、岛岸、岛架及超过 90% 的启动子区域(其中含4个以上 CpG 的启动子覆盖率达100%),同时还包括基因组中其他富含 CpG 的区域。相应的 BED 文件共包含约 718 万个 CpG 位点。
为衡量 RRMS 的甲基化识别表现,我们为源自一男性个体的正常和癌性转移性黑色素瘤细胞系对(COLO829/COLO829_BL),及三阴性乳腺癌细胞系对(HCC1395/HCC1935_BL)构建文库,并进行简化甲基化测序(重复次数=5)。每个样本分别上样至一张 MinION/GridION 测序芯片。RRMS 可从每个样本中识别出七百三十万至八百五十万个高置信度(每个位点由超过 10 条序列片段覆盖)的 CpG 甲基化位点。
为便于比较,我们同时使用亚硫酸氢盐法对样本进行简化甲基化测序(RRBS)。该方法可从每个样本中识别出一百七十万至二百五十万个高置信度的甲基化位点。有关二者比较的更多信息,请参阅我们的 RRMS 甲基化识别表现文档 及 海报 。
小鼠样本测序
RRMS 方案及其新设计的 BED 文件同样适用于小鼠基因组,目标区域约 308 Mb,涵盖全部 CpG 岛和启动子区域,以及其他富含 CpG 的基因组区域。
我们在胚泡来源的胚胎干细胞系(ES-E14TG2a)和白血病细胞系(BALB/c AMuLV A.3R.1)上进行了重复实验,以评估 RRMS 方法在小鼠样本中的性能,并以非 RRMS 文库作为对照。每个样本均在单独的一张 MinION 测序芯片上进行测序。结果显示,RRMS 在小鼠基因组中可实现每个位点覆盖深度超过 10× 的高置信度甲基化检测,单个样本可检测到约 500–580 万个 CpG 位点,而对照文库仅检测到约 40 万个 CpG 位点。
RRMS 方案结合定制的 BED 文件亦可用于其他脊椎动物基因组的测序。
但请注意,Oxford Nanopore Technologies 目前仅验证了该方法在人类和小鼠样本中的适用性。
RRMS DNA 提取与多样本测序实验流程简介
本实验指南详细介绍了采用免扩增条形码试剂盒(SQK-NBD 114.24)和 MinKNOW 软件中的适应性采样功能,对样本进行 DNA 提取,并在单张 PromethION 测序芯片上同时完成最多 4 个样本的简化甲基化测序(RRMS) 的操作流程,以及常见问题的解决方法。
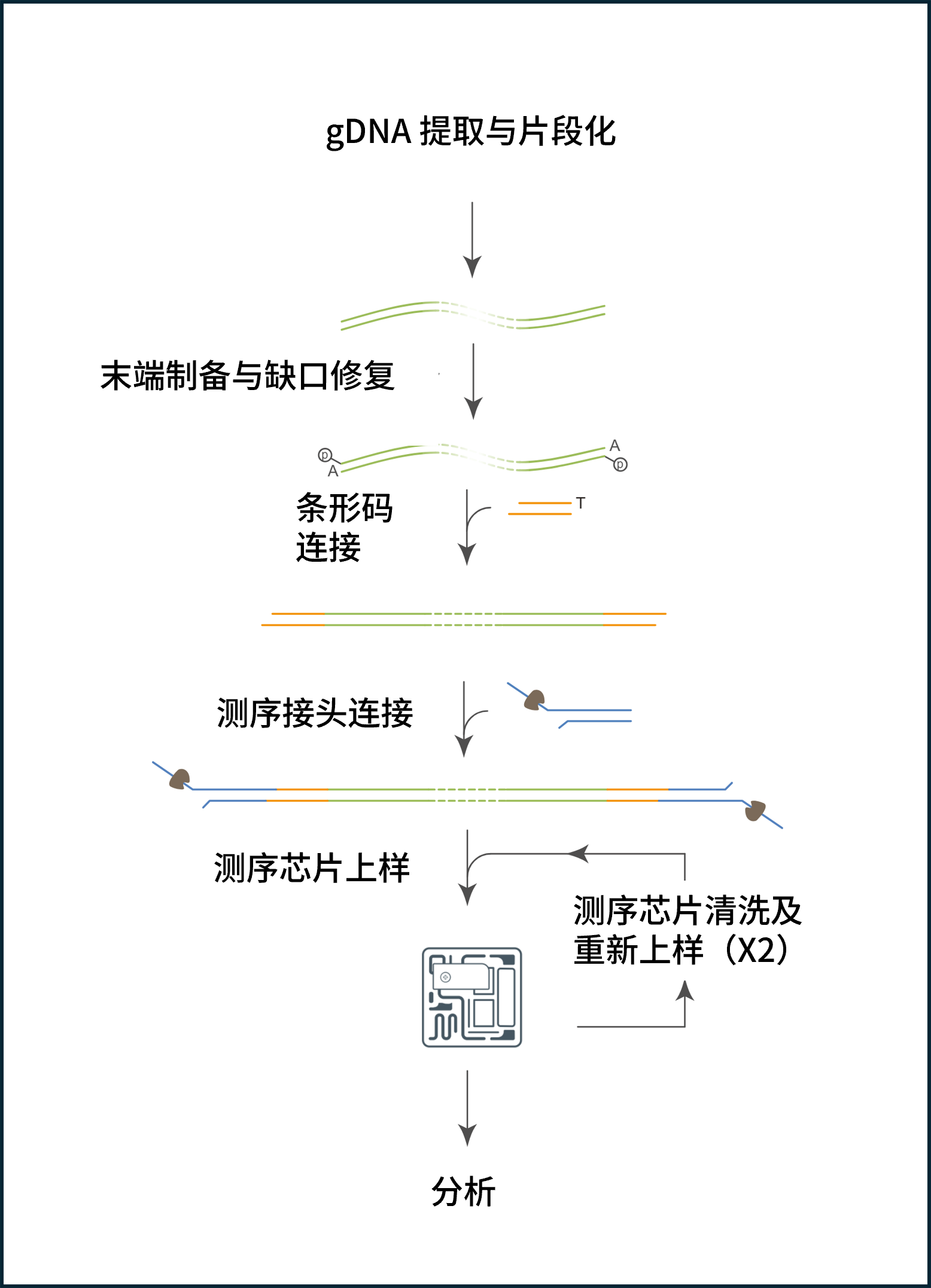
测序工作流程:
实验准备
您将需要:
- 确保您已准备好测序试剂盒、正确的仪器以及第三方试剂。
- 下载数据收集和分析软件。
- 请确保所使用的 BED 文件适用于适应性采样
- 检查您的测序芯片上有足够的活性纳米孔,以确保测序良好运行。
样本制备
- 采用 QIAGEN Puregene 细胞试剂盒提取 DNA
- 使用 Covaris g-TUBE 片段化 DNA,并评估其长度、浓度和纯度。 质量评估步骤对确保实验成功至关重要。
文库制备
下表概述了文库制备所需的步骤,包括时间安排和可以中止的节点。
| 文库制备 | 流程 | 时间 | 中止节点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNA 损伤及末端修复 | 修复片段化的 DNA,并对其末端进行处理,以便与条形码连接。 | 35 分钟 | 4°C 过夜 |
| 免扩增条码连接 | 将免扩增条形码连接至 DNA 末端。 | 60 分钟 | 4°C 过夜 |
| 接头连接及纯化 | 将测序接头连接到带条形码的 DNA 末端 | 50 分钟 | 若需短期保存或重复使用(如芯片清洗后再次上样),建议置于 4 °C; 若为长期保存且一次性使用,建议置于 –80 °C。 我们强烈建议在连接测序接头后即对文库进行测序。 |
| 测序芯片的预处理及上样 | 对测序芯片进行预处理,然后将制备好的文库加至芯片中进行测序。 | 10 分钟 | |
| 清洗测序芯片并重新上样(x2) | 暂停测序实验。使用核酸酶清洗测序芯片,去除之前的文库并疏通纳米孔。对测序芯片进行预处理,然后重新上样文库以继续测序。 | 60 分钟(x2) |
测序和分析
您将需要:
使用 MinKNOW 软件开始测序。该软件会通过测序仪收集原始数据,并将其识别成碱基序列。在实验配置阶段,开启适应性采样功能,并导入事先准备好的 BED 文件(包含感兴趣的目标区域)以及相应的 FASTA 参考序列文件。
样品测序总时长为 96 小时。当可用孔数下降至初始孔数的约 40% 时(通常分别在测序约 24 小时 和 48 小时 后),各进行一次芯片清洗操作,共两次。
使用 Dorado 进行修饰碱基识别;有关详细信息,请参阅 Dorado GitHub 页面。
使用本指南后文提供的命令,对检测到的修饰碱基进行整合与统计分析,并开展 CpG 岛注释分析。
实验方案适用性
本实验方案只适用于与以下产品搭配使用:
- 免扩增条码测序试剂盒-24 V14(SQK-NBD114.24)
- R10.4.1 测序芯片(FLO-PRO114M)
- 测序芯片清洗试剂盒 (EXP-WSH004)
- 测序辅助扩展包 V14(EXP-AUX003)
- 免扩增条形码扩展包 V14 (EXP-NBA114)
- PromethION 24/48 测序设备 - PromethION IT 配置要求文件
- PromethION 2 Solo 测序设备 - PromethION 2 Solo IT 配置要求文件
2. 实验器材及耗材
材料
- 每个样本需 5 × 10⁶ 个细胞(用于提取)
- 每个样本需 2 µg 片段化 gDNA(用于建库)
- 免扩增条形码测序试剂盒-24 V14(SQK-NBD114.24)
- 测序芯片清洗剂盒(EXP-WSH004)
耗材
- PromethION 测序芯片
- Puregene 细胞试剂盒(QIAGEN,158043)
- TE 缓冲液(10 mM Tris-HCl、1 mM EDTA、pH 8.0)(Fisher scientific,10224683)
- 1 x 磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)
- 异丙醇
- g-TUBE™(Covaris,520079)
- NEBNext FFPE修复混合液(NEB,M6630)
- NEBNext Ultra II 末端修复/ dA尾添加模块(NEB,E7546)
- NEB Blunt/TA 连接酶预混液(NEB,M0367)
- NEBNext®快速连接模块(NEB,E6056)
- 新制备的70%乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- 新制备的 80% 乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- 15 ml Falcon离心管
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- 0.2 ml 薄壁PCR管
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(Invitrogen, Q32851)
- Qubit dsDNA BR Assay(双链DNA宽范围检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher ,Q32850)
仪器
- PromethION 测序设备
- PromethION 测序芯片遮光片
- 适用于 15 ml Falcon 管的离心机及转子
- 设定为 37°C 和 50°C 的培养箱或水浴锅
- 用于提取沉淀 DNA 的接种环或一次性镊子
- Eppendorf 5424 离心机(或等效器材)
- Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)
- 适用于1.5ml Eppendorf 离心管的磁力架
- 迷你离心机
- 涡旋混匀仪
- 热循环仪
- 宽口移液枪头
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- P2 移液枪和枪头
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- 计时器
可选仪器
- Agilent Femto Pulse 系统(或用于读长质控的等效仪器)
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
上文列出的材料、耗材和器材清单适用于实验指南中的样本制备部分(DNA 提取)和文库制备部分。若样本已完成 DNA 提取,则仅需准备文库制备步骤所需的材料。
本实验方案的起始量要求如下:
对于 DNA 提取,起始量要求为:
- 每个样本需 500 万个细胞
对于文库制备,每个样本的起始量要求为:
- 2 µg 经 g-TUBE 打断的 gDNA
起始DNA
DNA质控
选择符合质量和浓度要求的起始DNA至关重要。使用过少或过多的DNA,或者质量较差的DNA(如,高度碎片化、含有RNA或化学污染物的DNA)都会影响文库制备。
有关如何对DNA样品进行质控,请参考起始DNA/RNA质控实验指南。
化学污染物
从原始样本中提取DNA的方法不同,可能会导致经纯化的DNA中所残留的化学污染物不同。这会影响文库的制备效率和测序质量。请参阅牛津纳米孔社区的污染物 页面了解更多信息。
第三方试剂
Oxford Nanopore Technologies 推荐您使用本实验指南中列出的所有第三方试剂,并已对其进行验证。我们尚未对其它替代试剂进行测试。
我们建议您按制造商说明准备待用的第三方试剂。
测序芯片质检
我们强烈建议您在开始测序实验前,对测序芯片的活性纳米孔数进行质检。质检需在您收到 PromethION 测序芯片 12 周内进行。Oxford Nanopore Technologies 会对活性孔数量少于以下标准,且尚未投入测序的芯片进行替换*:请您按照测序芯片质检文档中的说明进行芯片质检。
| 测序芯片 | 芯片上的活性孔数确保不少于 |
|---|---|
| PromethION 测序芯片 | 5000 |
*(请注意:自收到之日起,芯片须一直贮存于 Oxford Nanopore Technologies 推荐的条件下。且质检结果须在质检后的两日内递交给我们。)
本试剂盒及其实验指南中使用的免扩增接头(NA)不可与其他测序接头互换使用。
免扩增条形码试剂盒-24 V14(SQK-NBD114.24)内容物
请注意: 我们正在更新免扩增条形码试剂盒,新版将加大短片段缓冲液(SFB)的体积。如果您使用的是旧版试剂盒,或需要额外的短片段缓冲液(SFB),可通过购买 SFB 扩展包(EXP-SFB001) 获取。
新版试剂盒:加大体积的短片段缓冲液(SFB)
| 名称 | 缩写 | 管盖颜色 | 管数 | 每管溶液体积 (μl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 免扩增条形码 | NB01-24 | - | 两板,每板三套条形码组合 | 每孔 5 µl |
| DNA 参照 | DCS | 黄色 | 2 | 35 |
| 免扩增接头 | NA | 绿色 | 1 | 40 |
| 测序缓冲液 | SB | 红色 | 1 | 700 |
| 文库颗粒 | LIB | 粉色 | 1 | 600 |
| 文库溶液 | LIS | 白色管盖,粉色标签 | 1 | 600 |
| 洗脱缓冲液 | EB | 黑色 | 2 | 500 |
| AMPure XP 磁珠 | AXP | 透明管盖,浅青绿色标签 | 1 | 6000 |
| 长片段缓冲液 | LFB | 橙色 | 1 | 1800 |
| 短片段缓冲液 | SFB | 透明 | 1 | 13000 |
| EDTA | EDTA | 蓝色 | 1 | 700 |
| 测序芯片冲洗液 | FCF | 透明管盖,浅蓝色标签 | 1 | 8000 |
| 测序芯片系绳 | FCT | 紫色 | 1 | 200 |
旧版试剂盒:较低体积的短片段缓冲液(SFB)
| 名称 | 缩写 | 管盖颜色 | 管数 | 每管溶液体积 (μl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 免扩增条形码 | NB01-24 | - | 两板,每板三套条形码组合 | 每孔 5 µl |
| DNA 参照 | DCS | 黄色 | 2 | 35 |
| 免扩增接头 | NA | 绿色 | 1 | 40 |
| 测序缓冲液 | SB | 红色 | 1 | 700 |
| 文库颗粒 | LIB | 粉色 | 1 | 600 |
| 文库溶液 | LIS | 白色管盖,粉色标签 | 1 | 600 |
| 洗脱缓冲液 | EB | 黑色 | 2 | 500 |
| AMPure XP 磁珠 | AXP | 透明管盖,浅青绿色标签 | 1 | 6000 |
| 长片段缓冲液 | LFB | 橙色 | 1 | 1800 |
| 短片段缓冲液 | SFB | 透明 | 1 | 1800 |
| EDTA | EDTA | 蓝色 | 1 | 700 |
| 测序芯片冲洗液 | FCF | 透明管盖,浅蓝色标签 | 1 | 8000 |
| 测序芯片系绳 | FCT | 紫色 | 1 | 200 |
请注意: 本产品包含由贝克曼库尔特公司(Beckman Coulter, Inc)生产的 AMPure XP 试剂,并可与试剂盒一起于-20℃下储存(试剂稳定性将不受损害)。
请注意: DNA参照(DCS)是一段可比对到Lambda基因组的3'端、长度为3.6 kb 的标准扩增子。
3. BED 文件
从适应性采样目录下载 BED 文件。
适应性采样目录为 Oxford Nanopore 团队和社区成员提供了一个共享平台,用于上传和下载在适应性采样实验中使用的基因组目标区域 BED 文件。下载的 BED 文件可与参考基因组一同导入 MinKNOW 软件。
对于人类基因组 RRMS 实验,请下载人类简化甲基化测序(RRMS)文件。
对于小鼠基因组 RRMS 实验,请下载小鼠简化甲基化测序(RRMS)文件。
(可选格式):如使用其他脊椎动物基因组,请根据目标物种自定义相应的 BED 文件。
4. DNA 提取
材料
- 5 × 10⁶ 个细胞
耗材
- Puregene 细胞试剂盒(QIAGEN,158043)
- 新制备的70%乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- TE 缓冲液(10 mM Tris-HCl、1 mM EDTA、pH 8.0)(Fisher scientific,10224683)
- 1 x 磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)
- 异丙醇
- Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher,Q32851)
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- 15 ml Falcon离心管
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- 适用于 15 ml Falcon 管的离心机及转子
- 设定为 37°C 和 50°C 的培养箱或水浴锅
- 涡旋混匀仪
- 用于提取沉淀 DNA 的接种环或一次性镊子
- 宽口移液枪头
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
从培养的细胞系中提取 DNA:
请按需使用我们推荐的任一 提取方案,从样本中提取 DNA。
在评估本方法性能时,Oxford Nanopore 团队使用约 500 万个细胞,并采用以下方案进行 DNA 提取:人类细胞系 DNA – QIAGEN Puregene 细胞试剂盒。该方法的具体步骤如下所示。
注意: 此方法同样适用于小鼠细胞系 DNA 的提取。
此外,我们还提供多种 哺乳动物样本 DNA 提取方案,可用于其他类型的样本。
取约 5 × 10⁶ 个细胞:以 300 × g 离心 3 分钟,收集细胞沉淀。若沉淀中仍残留液体,可再次瞬时离心,并吸去剩余上清。
向细胞沉淀中加入 200 µl 1× PBS 溶液,再以 300 × g 离心 3 分钟。吸出清液并丢弃。
向洗涤后的细胞沉淀中加入 2 ml 细胞裂解液(Cell Lysis Solution)。使用宽口枪头将细胞重悬后,转移至 15 ml Falcon 离心管 中。若仍有细胞团存在,可轻轻倒转离心管以混匀。
37℃ 下孵育 30 分钟。
向裂解后的细胞中加入 700 µl 蛋白沉淀液(Protein Precipitation Solution),涡旋振荡混匀(振荡 3 次,每次 5 秒)。
2000 x g 离心 5 分钟。
将上清液转移至新的离心管中,加入 2.5 mL 室温异丙醇。弃去沉淀。
轻轻颠倒离心管 50 次,混匀溶液。
使用接种环或一次性镊子卷取沉淀的 DNA。
将收集到的 DNA 浸入含有 70% 冰冷乙醇的 Eppendorf 管中。
然后取出带 DNA 的接种环或镊子,让 DNA 在空气中自然风干数秒。
将 DNA 浸入含有 250 µl TE 缓冲液(1 mM EDTA,pH 8.0) 的 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管中。DNA 会在缓冲液中自然脱离接种环或镊子。
将离心管置于 50°C 下孵育 2 小时,期间可间歇性使用宽口枪头吹打混匀管内溶液。
注意: DNA 沉淀可能需要一定时间才能完全溶解。 请确保溶液在定量前已充分混匀。
可选: 您也可选择在室温下进行过夜孵育。
取1 µl 洗脱样品,用Qubit定量。
每个样品取 2 µg 提取的 gDNA,用于后续的 DNA 片段化步骤。
5. DNA片段化
材料
- 2 µg 上一步骤中提取得到的 gDNA
耗材
- g-TUBE™(Covaris,520079)
- TE 缓冲液(10 mM Tris-HCl、1 mM EDTA、pH 8.0)(Fisher scientific,10224683)
- Qubit dsDNA BR Assay(双链DNA宽范围检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher ,Q32850)
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- Eppendorf 5424 离心机(或等效器材)
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P2 移液枪和枪头
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
可选仪器
- Agilent Femto Pulse 系统(或用于读长质控的等效仪器)
使用 Covaris g-TUBE 管片段化已提取的 DNA:
使用 g-TUBE(Covaris) 对 gDNA 进行机械剪切,将 DNA 打断为约 6 kb 的片段,用于后续文库构建。
在 TE 缓冲液中制备 DNA:
1.将 2 µg 提取的 gDNA 转移至 1.5 ml Eppendorf 离心管中。
2.如不足 50 μl,请加入 TE 缓冲液补足。
3.吹打以充分混匀。
4.使用迷你离心机瞬时离心。
将 50 µl 样品加入 g-TUBE 上端。旋紧管盖后,以 11000 rpm(~11300 RCF) 离心 30 秒。
离心结束后,再以 11000 rpm(~11300 RCF) 离心 10 秒,以确保全部 gDNA 通过狭窄的剪切通道。
目视检查,确认样品已完全从 g-TUBE 上腔流入下腔。
将 g-TUBE 倒置,然后再次按上述条件离心:11000 rpm(~11300 RCF)离心 30 秒。
再次以 11000 rpm(~11300 RCF) 离心 10 秒,以确保全部 gDNA 通过狭窄的剪切通道。
拧下 g-TUBE 管体,保留含样品的旋盖部分。从旋盖中吸出样品,转移至洁净的 1.5 ml Eppendorf 离心管中。
取 1 µl 片段化 gDNA,使用 Qubit dsDNA Broad Range 检测试剂盒 进行定量。
g-TUBE 剪切后的样品浓度预计约为 40 ng/µl。
我们建议您使用 Femto-Pulse(Agilent)评估片段化 DNA 的长度和质量。

上图展示了 g-TUBE 剪切后 DNA 的片段分布(通过 Agilent 165 kb Femto-Pulse Assay 分析获得),结果显示片段在约 6 kb 处出现单一主峰。
每个样品取 48 µl 片段化 gDNA(约 2 µg DNA),用于后续文库构建。
6. DNA损伤及末端修复
材料
- 每个样品需 48 µl 片段化 gDNA(2 µg)(共 4 个样品)
- AMPure XP 磁珠(AXP)
耗材
- NEBNext FFPE DNA 修复混合液(NEB,M6630)
- NEBNext® Ultra II 末端修复/ dA尾添加模块(NEB,E7546)
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(Invitrogen, Q32851)
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- 新制备的 80% 乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- 0.2 ml 薄壁PCR管
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- 迷你离心机
- 热循环仪
- Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)
- 磁力架
- 盛有冰的冰桶
可选仪器
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
根据生产厂家的说明准备 NEBNext FFPE DNA 修复混合液及 NEBNext Ultra II 末端修复/ dA 尾添加模块,并置于冰上。
为获得最优表现,NEB建议如下:
1.于冰上解冻所有试剂。
2.轻弹或倒转试剂管,使其充分混匀。
注意: 请勿涡旋振荡 FFPE DNA 修复混合液 或 Ultra II 末端修复酶混合物。
3.每日首次打开一管试剂前,请务必先瞬时离心。
4.Ultra II 末端修复反应缓冲液 及 FFPE DNA 修复缓冲液中可能会含有少量沉淀。请待液体回复至室温后,使用移液枪上下吹打数次,打散沉淀;随后涡旋振荡30秒,至沉淀完全溶解。
注意: 通过涡旋振荡充分混合缓冲液至关重要。
5.NEBNext FFPE 修复缓冲液可能呈淡黄色,此属正常现象,不影响其使用。
使用无核酸酶水配制 DNA 样本:
1.确认每个样品已按要求准备约 2 µg 的已提取并片段化的 DNA,并分别置于独立的 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管中。。
2.如不足 48 μl,请加入无核酸酶水补足。
3.吹打或轻弹离心管,充分混匀。
4.使用迷你离心机瞬时离心。
向上述含片段化 DNA 样本的各1.5 ml Eppendorf LoBind DNA 管中加入以下试剂:
| 试剂 | 体积 |
|---|---|
| 前一步骤所得 ~2 µg 片段化 DNA | 48 µl |
| Ultra II 末端修复反应缓冲液 | 3.5 µl |
| Ultra II 末端修复酶混合物 | 3 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA 修复缓冲液 | 3.5 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA 修复混合液 | 2 µl |
| 总体积 | 60 µl |
轻轻吹打以充分混匀,并瞬时离心。
使用带加热盖的热循环仪,在 20°C 下孵育 5 分钟,再于 65°C 下孵育 5 分钟,随后在 4°C 保持。
将样本从热循环仪中取出,置于冰上。
涡旋振荡以重悬AMPure XP磁珠(AXP)。
将等体积(60µl)的重悬 AMPure XP磁珠(AXP)加入各管 DNA 末端修复反应体系中,轻弹试管以混匀。
将离心管置于Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)上室温孵育5分钟。
准备3 ml新制备的80%乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)。
将样品瞬时离心后置于磁力架上,待磁珠与液相分离,且液相澄清无色。保持离心管在磁力架上不动,用移液枪吸去清液并丢弃。
保持试管在磁力架上不动,以200µl新鲜制备的80%乙醇洗涤磁珠。小心不要扰动磁珠。用移液枪将乙醇吸走并弃掉。
如果沉淀被扰动,请等待磁珠重新沉降后再吸走乙醇。
重复上述步骤。
将离心管瞬时离心后置于磁力架上。用移液枪吸走残留的乙醇。让磁珠在空气中干燥约30秒,但不要干至表面开裂。
将各离心管从磁力架上移开。将磁珠重悬于 20 µl 无核酸酶水中。室温下孵育2分钟。
将离心管静置于磁力架上至少1分钟,直到磁珠和液相分离,且洗脱液澄清无色。
将每个样本的 20 μl 洗脱产物分别转移至新的 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 管中。
注意: 请确保分别处理各个样品。此阶段尚未为样本添加条形码。
使用 Qubit 荧光计 对每个洗脱后的样品进行定量。
注意: 为了获得更准确的定量结果,我们建议您对每个样品进行多次 Qubit 测定(三次重复测量)。该数据对于后续在添加条形码前对样品浓度进行标准化处理至关重要。
在末端修复步骤后,每个样品的回收量应在 1000–1600 ng 之间。
根据测定结果,将各样品的 DNA 量统一至产量最低样品的水平。
1.取产量最低的样品 15 µl,转移至洁净的 0.2 ml 薄壁 PCR 管中。
2.对其余样品,分别取与上述样品等量的 DNA,转移至相应洁净的 0.2 ml 薄壁 PCR 管 中。
3.使用无核酸酶水将各样品总体积补足至 15 µl。
将所得等摩尔量且经末端修复的各 DNA 样品(15 µl)用于后续的免扩增条形码连接步骤。如需要,您也可以此时将样品置于 4°C 储存过夜。
7. 免扩增条码连接
材料
- 来自上一步的 15 µl 末端修复 DNA(4 个样品,已按产量最低样品统一至相同 DNA 量)
- 免扩增条形码(NB01-24)
- AMPure XP 磁珠(AXP)
- EDTA(EDTA)
- 短片段缓冲液(SFB)
耗材
- NEB Blunt/TA 连接酶预混液(NEB,M0367)
- 新制备的 80% 乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- Eppendorf 低吸附 twin.tec® 96 孔 PCR 板,半裙边(Eppendorf™,0030129504)带热封
- 或 0.2ml 薄壁PCR管
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher,Q32851)
仪器
- 磁力架
- 涡旋混匀仪
- Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)
- 迷你离心机
- 热循环仪
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- 多通道移液枪和枪头
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- P2 移液枪和枪头
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
按照生产商说明制备 Blunt/TA 连接酶预混液,并置于冰上:
1.在室温下解冻试剂。
2.将各试剂管瞬时离心5秒。
3.用移液枪全量吹打试剂 10 次,确保充分混匀。
将 EDTA 于室温下解冻,涡旋振荡混匀后,瞬时离心,并置于冰上。
在室温下解冻免扩增条形码(NB01–24),瞬时离心后,根据样品数量,分别用移液枪吹打混匀所需的每一种条形码,然后置于冰上。
条形码板孔仅限一次使用。使用前请确认所选孔密封完好;一旦刺穿或开启,不得再次使用。
为计划上样于同一测序芯片的各个样本选择不同的条形码。各样本在添加条形码后,应合并在同一实验中测序。
请注意: 每个样本应仅对应一种条形码。
在各支装有已调整至相同 DNA 量样品的 0.2 ml PCR 管中,按下列顺序加入试剂:
| 试剂 | 体积 |
|---|---|
| 经过末端修复的 DNA | 15 µl |
| 免扩增条形码(NB01-24) | 5 µl |
| Blunt/TA 连接酶预混液 | 20 µl |
| 总体积 | 40 µl |
轻轻吹打以充分混匀,并瞬时离心。
室温下孵育20分钟。
向每管中加入4 µl EDTA(蓝盖),充分吹打混匀后,瞬时离心。
加入 EDTA 的目的是终止反应。
将各带条形码样本合并至一支1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管中。
| . | 对4个样本 |
|---|---|
| 包含 EDTA(蓝盖) 在内的总反应体系体积 | 176 µl |
我们建议您在样品合并前后,分别检查各 PCR 管(或板孔)底部液体体积是否相同,以确保所有样品的液体都已完全转移。
涡旋振荡以重悬AMPure XP磁珠(AXP)。
向混合样本中加入0.65 倍体积的 AMPure XP 磁珠(AXP),吹打混匀。
| . | 对4个样本 |
|---|---|
| 使用 EDTA(蓝盖)体系所需的 AXP 体积 | 115 µl |
将离心管置于Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)上室温孵育10分钟。
以下纯化步骤中使用短片段缓冲液(SFB)而非80%的乙醇来洗涤磁珠。使用乙醇会严重破坏测序反应。
将样本瞬时离心,并于磁力架上静置5分钟。将离心管静置于磁力架上,直到磁珠和液相分离,且洗脱液澄清无色,吸出上清。
加入500 μl短片段缓冲液(SFB)洗涤磁珠。轻弹离心管将磁珠混匀后,将离心管瞬时离心,再放回磁力架,静置待磁珠和液相分离。保持试管在磁力架上不动,用移液枪吸去清液。
重复上述步骤。
将离心管瞬时离心后置于磁力架上。用移液枪吸去残留的短片段缓冲液(SFB)。让磁珠在空气中干燥约 30 秒,但不要干至表面开裂。
将离心管从磁力架上移开。轻弹离心管,将磁珠重悬于32 µl 无核酸酶水中。
在 37°C 下孵育 15 分钟。每隔两分钟,轻弹含样品的离心管 10 秒,以促进 DNA 的洗脱。
将离心管置于磁力架上,直到磁珠和液相分离,且洗脱液澄清无色。
将 32µl 洗脱液转移至一支新的 1.5ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 管中。
取 1µl 洗脱样品,用 Qubit 定量。
注意: 在条形码连接步骤完成后,预期可回收约 2200–3200 ng 的 DNA。
带条形码的 DNA 样本将用于稍后的接头连接及纯化步骤。如需要,您也可以此时将样品置于4°C储存过夜。
8. 接头连接及纯化
材料
- 长片段缓冲液(LFB)
- 洗脱缓冲液(EB)
- 免扩增接头(NA)
- AMPure XP 磁珠(AXP)
耗材
- NEBNext®快速连接模块(NEB,E6056)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher,Q32851)
仪器
- 迷你离心机
- 磁力架
- 涡旋混匀仪
- Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)
- 热循环仪
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
本试剂盒及其实验指南中使用的免扩增接头(NA)不可与其他测序接头互换使用。
测序芯片质检
我们强烈建议在接头连接及纯化前,对测序芯片的活性纳米孔数量进行质检,以确保其足够支持实验的顺利进行。
详情请参阅 MinKNOW 实验指南中的 测序芯片质检说明。
请根据厂家的说明准备 NEBNext 快速连接反应模块,并置于冰上。
1.室温下解冻
2.将各试剂管瞬时离心5秒。
3.用移液枪全量吹打试剂 10 次,确保充分混匀。 注意: 请勿涡旋振荡快速 T4 DNA 连接酶。
NEBNext 快速连接反应缓冲液(5X)可能会出现少量沉淀。请待液体回复至室温后,使用移液枪上下吹打数次,打散沉淀;然后涡旋振荡数秒,确保充分混匀。
请勿涡旋震荡快速 T4 DNA 连接酶。
瞬时离心免扩增接头(NA)和快速 T4 DNA 连接酶,吹打混匀后置于冰上。
于室温下解冻洗脱缓冲液(EB),涡旋振荡混匀,瞬时离心后置于冰上。
于室温下解冻长片段缓冲液(LFB),涡旋振荡混匀,瞬时离心后置于冰上。
在一支 1.5ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管内,将所有试剂按以下顺序混合:
每添加一样试剂后,请吹打混匀10-20次,再添加下一样试剂。
| 试剂 | 体积 |
|---|---|
| 合并后的带条码样本 | 30 µl |
| 免扩增接头(NA) | 5 µl |
| NEBNext 快速连接反应缓冲液(5X) | 10 µl |
| 快速 T4 DNA 连接酶 | 5 µl |
| 总体积 | 50 µl |
轻轻吹打以充分混匀,并瞬时离心。
室温下孵育20分钟。
以下纯化步骤中使用长片段缓冲液(LFB)而非80%的乙醇来洗涤磁珠。使用乙醇会严重破坏测序反应。
涡旋振荡以重悬AMPure XP磁珠(AXP)。
将 25 µl(0.5x)重悬的 AMPure XP 磁珠(AXP)加入反应体系中,吹打混匀。
将离心管置于Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)上室温孵育10分钟。
将样品瞬时离心后置于磁力架上,待磁珠与液相完全分离。保持离心管在磁力架上不动,用移液枪吸去清液。
加入 250 μl 长片段缓冲液(LFB)洗涤磁珠。轻弹离心管将磁珠混匀后,瞬时离心,再放回磁力架,静置不少于 5 分钟,待磁珠和液相分离。保持离心管在磁力架上不动,用移液枪吸去清液。
请注意: 吸取上清液时请谨慎操作,由于缓冲液黏度较高,可能会将磁珠一同吸出。
重复上述步骤。
将离心管瞬时离心后置于磁力架上。用移液枪吸走残留的上清液。让磁珠在空气中干燥约30秒,但不要干至表面开裂。
将离心管从磁力架上移开。将磁珠重悬于 97 µl 洗脱缓冲液(EB)中。
瞬时离心后,于 37 °C 下孵育 20 分钟。每隔两分钟轻弹样品 10 秒,以促进 DNA 洗脱。
将离心管静置于磁力架上至少1分钟,直到磁珠和液相分离,且洗脱液澄清无色。
将此97 µl洗脱液转移至一支新的1.5ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind管中。
将磁珠丢弃。
取1µl洗脱样品,用Qubit定量。
注意: 在接头连接及纯化步骤完成后,预期可在 96 µl 的体积中回收约 1000–1200 ng 的 DNA。
构建好的文库即可用于测序芯片上样。在上样前,请将文库置于冰上或4℃条件下保存。
文库保存建议
若为 短期 保存或重复使用(例如在清洗芯片后再次上样),我们建议将文库置于Eppendorf LoBind 离心管中 4℃ 保存。 若为一次性使用且储存时长 超过3个月 ,我们建议将文库置于Eppendorf LoBind 离心管中 -80℃ 保存。
9. PromethION测序芯片的预处理及上样
材料
- 测序缓冲液(SB)
- 文库颗粒(LIB)
- 测序芯片系绳(FCT)
- 测序芯片冲洗液(FCF)
耗材
- PromethION 测序芯片
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- PromethION 2 Solo 测序设备
- PromethION 测序设备
- PromethION 测序芯片遮光片
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
本试剂盒仅兼容R10.4.1测序芯片(FLO-PRO114M)。
将芯片从冰箱中取出后,请将其置于室温环境孵育 20 分钟再插入 PromethION 测序仪。潮湿环境下的测序芯片上可能会形成冷凝水。因此,请检查测序芯片顶部和底部的金色连接器引脚处是否有水凝结。如有,请使用无绒布擦干。请确保测序芯片的底部有热垫(黑色)覆盖。
于室温下解冻测序缓冲液(SB)、文库颗粒(LIB)、测序芯片系绳(FCT)和测序芯片冲洗液(FCF)。完全解冻后,涡旋振荡混匀。然后瞬时离心,置于冰上。
按下文制备测序芯片的预处理液,室温下涡旋振荡混匀。
请根据待上样测序芯片的数量,另拿一支适当体积的洁净离心管,按下表制备测序芯片预处理液。
| 试剂 | 体积(每张芯片) |
|---|---|
| 测序芯片冲洗液 (FCF) | 1,170 µl |
| 测序芯片系绳(FCT) | 30 µl |
| 总体积 | 1,200 µl |
对 PromethION 2 Solo,请按以下步骤为测序芯片上样:
1.将测序芯片平放在金属板上。
2.将测序芯片推入对接端口,直至金色引脚或绿色电路板不可见。

对PromethION 24/48,将测序芯片插入相应卡槽的对接端口:
1.将测序芯片与连接器横竖对齐,以便顺利卡入。
2.用力下压芯片至卡槽,并确认卡夹位置归位。


如插入配置测试芯片的角度出现偏差,可能会损坏PromethION上的引脚并影响测序结果。如您发现 PromethION测序仪芯片位置上的引脚损坏,请通过电子邮件(support@nanoporetech.com)联系我们的技术支持团队。

请在文库上样前完成测序芯片质检,评估可用的活性纳米孔数量。
若该测序芯片此前已完成质检,则可跳过此步骤。
详细操作说明请参阅 MinKNOW 实验指南中的测序芯片质检说明部分。
顺时针滑动加液孔孔盖,将其打开。

小心地从测序芯片中反旋吸出缓冲液。请勿吸出超过 20-30 µl的缓冲液,并确保芯片上的纳米孔阵列一直有缓冲液覆盖。将气泡引入阵列会对纳米孔造成不可逆转地损害。
在加液孔打开的状态下,按下述步骤吸取少量液体,同时避免引入气泡:
1.将P1000移液枪转至200µl刻度。
2.将枪头垂直插入加液孔中。
3.反向转动移液枪量程调节转纽,直至移液枪刻度在 220-230 µl之间,或直至您看到有少量缓冲液进入移液枪枪头。

向芯片的加液孔中加入 500 µl 芯片预处理液。加入过程中,请避免引入气泡。等待5分钟。与此同时,您可按以下步骤准备上样文库。

将含有文库颗粒的LIB管用移液枪吹打混匀。
LIB管内的文库颗粒分散于悬浮液中。由于颗粒沉降速度非常快,因此请在混匀颗粒后立即使用。
对于大多数测序实验,我们建议您使用文库颗粒(LIB)。但如文库较为粘稠,您可考虑使用文库溶液(LIS)。
在一支新的1.5ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind离心管内,将所有试剂按以下顺序混合:
| 试剂 | 每张测序芯片的上样体积 |
|---|---|
| 测序缓冲液(SB) | 100 µl |
| 文库颗粒 (LIB),使用前充分混匀 | 68 µl |
| DNA 文库 | 32 µl |
| 总体积 | 200 µl |
请注意: 此处制备的文库用于后续的芯片上样。在上样前,请将文库置于冰上或4℃条件下保存。
缓慢向芯片的加液口中加入 500 µl 预处理液,完成芯片的预处理。

临上样前,用移液枪轻轻吹打混匀制备好的文库。
使用 P1000 移液枪向加液孔中加入 200 µl 文库。

合上加液孔孔盖。

为获得最佳测序产出,在文库样本上样后,请立即在测序芯片上安装遮光片。
我们建议在清洗芯片并重新上样时,将遮光片保留在测序芯片上。一旦文库从测序芯片中吸出,即可取下遮光片。
如遮光片不在测序芯片上,请您按照以下步骤安装:
1.将遮光片的中空部分(空槽)与测序芯片的加液孔孔盖对齐。确保遮光片的前沿位于测序芯片ID的上方。
2.用力下压遮光片的卡垫部分,遮光片空槽边缘会随卡垫卡入加液孔孔盖下方。


准备就绪后,合上 PromethION 设备上盖。
请在为 PromethION 芯片上样后,等待至少 10 分钟再启动实验,以提高芯片产出。
有关如何设置测序实验的说明,请参阅本指南中“数据采集与碱基识别”一节。
注意: 本实验指南建议在测序运行约 24 小时后,对测序芯片进行清洗并重新上样,以保持较高的数据采集效率。
请按照本指南中 “PromethION 从测序芯片的清洗与重新上样” 一节的说明进行操作。
10. PromethION 测序芯片的清洗与重新上样
材料
- 之前步骤获得的已连接接头的 DNA 文库
- 测序芯片清洗剂盒(EXP-WSH004)
- 测序辅助扩展包 V14(EXP-AUX003)
耗材
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- 涡旋混匀仪
我们建议在测序约 24 小时后对测序芯片进行清洗并重新上样。
本方法建议在测序约 24 小时后对芯片进行首次清洗,以恢复纳米孔活性并维持高效的数据采集。再经过约 24 小时测序后,应进行第二次清洗并重新上样。接头连接步骤中已预先制备足够的文库,以满足三次芯片上样的需求。
- 此清洗步骤旨在去除测序芯片内现存的大部分文库并疏通纳米孔,为芯片的下一次上样做好准备。
- 请在清洗及上样过程中 暂停 MinKNOW 的数据采集。
- 测序芯片经清洗后,即可用于下一文库的上样。
您可以在“纳米孔活动状态”(Pore Activity) 或“孔扫描结果”(Pore Scan Results) 图中查看纳米孔的可用情况。
下图展示了测序芯片在清洗前后纳米孔状态的示例数据, 以及包含清洗和重新上样步骤的累计测序数据产出示例。 红色星号标示了执行测序芯片清洗与重新上样的时间点。

图 1. 96 小时测序过程中的通道状态变化。通过对测序芯片进行清洗,可恢复被堵塞的纳米孔,从而实现连续高效的数据采集。红色星号表示执行冲洗的时间点。

图 2. 96 小时运行期间的累计测序数据产出。红色星号表示执行冲洗的时间点。
PromethION 测序芯片的清洗与重新上样视频
以下视频演示了如何在测序运行结束后清洗测序芯片并上样新的文库。
如您计划在清洗后立即进行下一次文库上样,建议在清洗过程中保留测序芯片的遮光片。
若芯片在清洗后需暂时保存,则可将遮光片移除。
将清洗混合液(WMX)置于冰上。请勿涡旋振荡该离心管。
于室温下解冻一管清洗稀释液(DIL)。
涡旋振荡混匀清洗稀释液(DIL),瞬时离心,置于冰上。
在一支洁净的1.5ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind离心管内,按下表制备测序芯片清洗混合液:
| 试剂 | 每张测序芯片所需体积 |
|---|---|
| 清洗混合液(WMX) | 2 μl |
| 清洗稀释液(DIL) | 398 μl |
| 总体积 | 400 μl |
吹打混匀,然后置于冰上。请勿涡旋振荡该离心管。
在 MinKNOW 中暂停测序实验,保持测序芯片于测序仪内。
在吸出废液前,请确保加液孔已关闭,以避免气泡进入传感器阵列,造成大量测序通道损失。
吸出废液的步骤如下:
1.合上加液孔孔盖。
2.将 P1000 移液枪插入废液口,吸出废液。
注意: 由于加液孔已关闭,因此传感器阵列内的液体不会流失。
顺时针转动加液孔孔盖,使加液孔显露出来。

小心地从测序芯片中反旋吸出缓冲液。请勿吸出超过 20-30 µl的缓冲液,并确保芯片上的纳米孔阵列一直有缓冲液覆盖。将气泡引入阵列会对纳米孔造成不可逆转地损害。
将加液孔打开后,检查孔周围是否有小气泡。请按照以下方法,从孔中排出少量液体以清除气泡:
1.将 P1000 移液枪转至 200µl 刻度。
2.将枪头垂直插入加液孔中。
3.反向转动移液枪量程调节转纽,直至移液枪刻度在 220-230 µl 之间,或直至您看到有少量缓冲液进入移液枪枪头。

按以下步骤向测序芯片加液孔缓缓加入 200 µl 制备好的测序芯片清洗混合液:
1.使用 P1000 移液枪吸取 200 µl 测序芯片清洗混合液。
2.将移液枪枪头插入加液孔,请确保枪头没有气泡。
3.缓慢转动移液枪的量程调节齿轮(若移液枪具备该功能),将清洗混合液加入测序芯片;或 非常缓慢地 按压移液枪按钮,直至枪尖内剩余少量缓冲液。
4.设置计时器,孵育5分钟。
孵育5分钟后,按以下步骤小心地将余下的 200 µl测序芯片清洗混合液加入加液孔:
1.使用 P1000 移液枪吸取 200 µl测序芯片清洗混合液。
2.将移液枪枪头插入加液孔,请确保枪头没有气泡。
3.缓慢转动移液枪的量程调节齿轮(若移液枪具备该功能),将清洗混合液加入测序芯片;或 非常缓慢地 按压移液枪按钮,直至枪尖内剩余少量缓冲液。
合上加液孔并等待一小时。

在吸出废液前,请确保加液孔已关闭,以避免气泡进入传感器阵列,造成大量测序通道损失。
吸出废液的步骤如下:
1.请确保加液孔已关闭。
2.将 P1000 移液枪插入废液口,吸出废液
请注意: 由于加液孔已关闭,因此传感器阵列内的液体不会流失。
本过程所用的缓冲液不支持在下次上样前进行芯片质检;但在下一次孔扫描后,系统会报告可用的活性孔数量。
于室温下解冻测序缓冲液(SB)、文库颗粒(LIB)或文库溶液(LIS,按需)、测序芯片系绳(FCT)和测序芯片冲洗液(FCF)。完全解冻后,涡旋振荡混匀。然后瞬时离心,置于冰上。
根据待冲洗的测序芯片数量,在适当体积的离心管中配制芯片预处理混合液。混合后短时旋涡振荡混匀。
| 试剂 | 体积(每张芯片) |
|---|---|
| 测序芯片冲洗液 (FCF) | 1170 µl |
| 测序芯片系绳(FCT) | 30 µl |
| 总体积 | 1200 µl |
顺时针滑动加液孔孔盖,将其打开。

小心地从测序芯片中反旋吸出缓冲液。请勿吸出超过 20-30 µl的缓冲液,并确保芯片上的纳米孔阵列一直有缓冲液覆盖。将气泡引入阵列会对纳米孔造成不可逆转地损害。
在加液孔打开的状态下,按下述步骤吸取少量液体,同时避免引入气泡:
1.将P1000移液枪转至200µl刻度。
2.将枪头垂直插入加液孔中。
3.反向转动移液枪量程调节转纽,直至移液枪刻度在 220-230 µl之间,或直至您看到有少量缓冲液进入移液枪枪头。

待其恢复室温后,立即取 500 µl,并按以下步骤缓缓加入测序芯片加液孔:
1.使用 P1000 移液枪吸取 500μl 预处理液。
2.将移液枪枪头插入预处理孔,请确保枪头没有气泡。
3.缓慢转动移液枪的量程调节齿轮(若移液枪具备该功能),将预处理液加入测序芯片;或 非常缓慢地 按压移液枪按钮,直至枪尖内剩余少量缓冲液。

为确保充分清除核酸酶,两次预处理液冲洗之间请务必等待 5 分钟。
合上加液孔并等待5分钟。
与此同时,您可按以下步骤准备上样文库。
将含有文库颗粒的LIB管用移液枪吹打混匀。
LIB管内的文库颗粒分散于悬浮液中。由于颗粒沉降速度非常快,因此请在混匀颗粒后立即使用。
对于大多数测序实验,我们建议您使用文库颗粒(LIB)。但如文库较为粘稠,您可考虑使用文库溶液(LIS)。
在一支新的1.5ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind离心管内,将所有试剂按以下顺序混合:
| 试剂 | 每张测序芯片的上样体积 |
|---|---|
| 测序缓冲液(SB) | 100 µl |
| 文库颗粒 (LIB),使用前充分混匀;或文库溶液 (LIS) | 68 µl |
| DNA 文库 | 32 µl |
| 总体积 | 200 µl |
请注意: 此处增大了文库的上样量,以提升纳米孔阵列的覆盖度。
在吸出废液前,请确保加液孔已关闭,以避免气泡进入传感器阵列,造成大量测序通道损失。
吸出废液的步骤如下:
1.请确保加液孔已关闭。
2.将 P1000 移液枪插入废液口,吸出废液
请注意: 由于加液孔已关闭,因此传感器阵列内的液体不会流失。
顺时针滑动加液孔孔盖,将其打开。

小心地从测序芯片中反旋吸出缓冲液。请勿吸出超过 20-30 µl的缓冲液,并确保芯片上的纳米孔阵列一直有缓冲液覆盖。将气泡引入阵列会对纳米孔造成不可逆转地损害。
在加液孔打开的状态下,按下述步骤吸取少量液体,同时避免引入气泡:
1.将P1000移液枪转至200µl刻度。
2.将枪头垂直插入加液孔中。
3.反向转动移液枪量程调节转纽,直至移液枪刻度在 220-230 µl之间,或直至您看到有少量缓冲液进入移液枪枪头。

按以下步骤缓缓将 500 µl 预处理液加入测序芯片加液孔:
1.使用 P1000 移液枪吸取 500μl 预处理液。
2.将移液枪枪头插入预处理孔,请确保枪头没有气泡。
3.缓慢转动移液枪的量程调节齿轮(若移液枪具备该功能),将预处理液加入测序芯片;或 非常缓慢地 按压移液枪按钮,直至枪尖内剩余少量缓冲液。

在吸出废液前,请确保加液孔已关闭,以避免气泡进入传感器阵列,造成大量测序通道损失。
吸出废液的步骤如下:
1.合上加液孔孔盖。
2.将 P1000 移液枪插入废液口,吸出废液。
注意: 由于加液孔已关闭,因此传感器阵列内的液体不会流失。
顺时针滑动加液孔孔盖,将其打开。

小心地从测序芯片中反旋吸出缓冲液。请勿吸出超过 20-30 µl的缓冲液,并确保芯片上的纳米孔阵列一直有缓冲液覆盖。将气泡引入阵列会对纳米孔造成不可逆转地损害。
在加液孔打开的状态下,按下述步骤吸取少量液体,同时避免引入气泡:
1.将P1000移液枪转至200µl刻度。
2.将枪头垂直插入加液孔中。
3.反向转动移液枪量程调节转纽,直至移液枪刻度在 220-230 µl之间,或直至您看到有少量缓冲液进入移液枪枪头。

临上样前,用移液枪轻轻吹打混匀制备好的文库。
使用 P1000 移液枪向加液孔中加入 200 µl 文库。

合上加液孔孔盖。

为获得最佳测序产出,在文库样本上样后,请立即在测序芯片上安装遮光片。
我们建议在清洗芯片并重新上样时,将遮光片保留在测序芯片上。一旦文库从测序芯片中吸出,即可取下遮光片。
如遮光片不在测序芯片上,请您按照以下步骤安装:
1.将遮光片的中空部分(空槽)与测序芯片的加液孔孔盖对齐。确保遮光片的前沿位于测序芯片ID的上方。
2.用力下压遮光片的卡垫部分,遮光片空槽边缘会随卡垫卡入加液孔孔盖下方。


准备就绪后,合上 PromethION 设备上盖。
请在为 PromethION 芯片上样后,等待10分钟再启动实验,以提高芯片产出。
执行两次“PromethION 测序芯片清洗与重新上样” 操作,共完成三次文库上样(即初始上样 + 两次清洗与重新上样),以最大化数据产出。
- 第一次清洗与重新上样应在测序约 24 小时时进行。
- 第二次清洗与重新上样应在测序约 48 小时时进行。
11. 数据采集和碱基识别
纳米孔数据分析概览
有关纳米孔数据分析的完整概述,包括碱基识别和次级分析,请参阅数据分析 文档。
如何开始测序
MinKNOW 软件负责仪器控制和数据采集。 请确保已在计算机上安装 MinKNOW。有关测序实验的详细设置说明,请参阅 MinKNOW 实验指南。
简化甲基化混样测序实验方案的测序设置:
在"试剂盒"页面上,选择 免扩增条形码测序试剂盒-24(SQK-NBD114.24) 。
将碱基识别设置为 关 (此操作将自动关闭条码拆分功能)。
注意: 碱基识别和条码拆分将在测序完成后,于下游分析步骤中进行。将适应性采样设为 开 ,并选择 富集 。
指定 人类参考基因组文件(用于比对) 以及 .bed 文件(用于定义富集区域) 。您可从在线目录中查找适用于人类 RRMS 的 .bed 文件。将运行时长设置为 至少 96 小时 。
根据实验需求设置输出参数。
为确保下游分析正常运行,建议保持默认输出格式(.POD5)。点击 开始 启动测序。
12. 下游分析
软件版本
以下列出了本指南使用的软件版本。请注意,更高版本的软件可能与本指南中的命令不完全兼容。
| 软件 | 版本 |
|---|---|
| dorado | v0.7.3 |
| modkit | v0.2.8 |
| wf-human-variation | v2.3.0 |
| mosdepth | v0.3.8 |
碱基识别及条形码拆分
碱基识别
独立版 Dorado 通过 Dorado 碱基识别工具(basecaller)进行碱基识别。 打开终端窗口,输入以下命令:
dorado basecaller hac,5mCG_5hmCG --kit-name SQK-NBD114-24 \
--secondary “no” -Y \
--reference {reference_fasta} {input_pod5_folder} \
| samtools view -e '[qs] >= {qscore_filter}' \
--output {out_pass_bam} \
--unoutput {out_fail_bam}
注意:
- 我们建议在 RRMS 测序实验中采用高精准(hac)模型。如选用超精准(sup)模型,请确保在上述命令中调用正确的模型。
- 如提供 FASTA 参考文件,则可在碱基识别过程中同时进行比对。您可点此下载推荐的人类参考基因组文件。
- 使用参数 --secondary no 可去除二级比对结果;启用 -Y 参数,可对补充比对结果进行软剪切。
- 通过添加参数 --kit-name SQK-NBD114-24,Dorado 会在生成的 BAM 文件中添加条形码标签,从而根据条形码对序列进行分类。
- 建议将质量分数(qscore)过滤阈值设置为 10。
- 请注意,使用 Dorado 进行碱基识别时需要 GPU 计算资源。 更多有关如何运行 Dorado 的详情,请参阅 github 资料库。
条形码拆分
Dorado demux 用于根据条形码对测序片段进行拆分。具体命令如下:
dorado demux --no-classify --sort-bam --output-dir <out_folder> {out_pass_bam}
注意:
- 此步骤会根据所使用的条形码试剂盒(例如 SQK-NBD114-24),为其中每个可识别的条形码分别生成一个已排序的 BAM 文件。
- Dorado 默认会自动剪切接头和条形码。一旦条形码被剪切,测序片段将无法再次进行条形码拆分。 如需了解更多信息,请参阅Dorado 文档。
覆盖度分析
您可以从 AS 目录下载 RRMS 实验所需的目标区域 BED 文件。
Mosdepth 用于评估感兴趣条形码所对应目标区域的覆盖度:
mosdepth -x -t 8 -n -b {target_bed} {out_prefix} {input_pass_bam}
修饰识别
Human variation (人类变异分析)流程使用 modkit 对基因组各位点的修饰信息进行汇总分析。
该工作流程可在以下仓库中获取:wf-human-variation github.
相关文档可在以下页面中查阅:wf-human-variation EPI2ME 页面
对于大多数 RRMS 实验,我们建议使用以下命令:
nextflow run https://github.com/epi2me-labs/wf-human-variation \
-profile singularity \
--mod \
--bam <bam> \
--bed RRMS_human_hg38.bed \
--ref GCA_000001405.15_GRCh38_no_alt_analysis_set.fasta \
--sample_name <sample> --out_dir <output_dir>
(可选)单倍型特异性甲基化分析:
如需进行单倍型特异性甲基化分析,可在命令中添加参数 --snp --phased。此操作将分别汇总各单倍型上的甲基化修饰(例如,为每个单倍型生成独立的 bedmethyl 文件):
nextflow run https://github.com/epi2me-labs/wf-human-variation \
-profile singularity \
--mod --snp --phased \
--bam <bam> \
--bed RRMS_human_hg38.bed \
--ref GCA_000001405.15_GRCh38_no_alt_analysis_set.fasta \
--sample_name <sample> --out_dir <output_dir>
注意: 对于此类特定分析,建议样本的测序覆盖度在 30X 以上。
差异甲基化区域检测:
“modkit dmr” 工具可用于检测不同样本间的差异甲基化区域。
详细说明请参阅 modkit 文档。
可视化:
由 Dorado 生成的 BAM 文件不仅包含标准碱基信息,还包括存储在 MM 和 ML 标签中的逐条序列(per-read)修饰信息。若需可视化单条序列的修饰碱基识别结果,可在 IGV 中加载 BAM 文件,并将 “colour reads as” 选项设置为 “base modification 2-color (all)”。
如果您使用 wf-human-variation 流程进行了分相(phasing)分析,则可以在 IGV 中加载带有单倍型标签的 BAM 文件。之后,在 IGV 的 “group by” 选项中选择 “phase”,即可根据单倍型(haplotype)信息将比对结果分组显示。
此外,您还可在 IGV 中通过 BIGWIG 格式查看各个位点的甲基化频率。 为此,您可首先使用 modkit 通过以下命令生成 BEDGRAPH 文件:
modkit pileup --cpg --combine-strands --bedgraph \
--threads 10 --prefix {out_prefix} \
--ref {reference_fasta} \
{out_folder} {input_pass_bam}
请注意,对于每种碱基修饰(如本例中 5mC 和 5hmC),都会分别生成一个独立的 BEDGRAPH 文件。
随后,可使用 bedGraphToBigWig 工具将 BEDGRAPH 文件转换为 BIGWIG 格式。转换后的 BIGWIG 文件可与 BAM 文件一同加载至 IGV:
bedtools sort -i {out_folder}/{prefix}_m_CG0_combined.bedgraph | cut -f 1-4 > {out_folder}/{prefix}_m_CG0_combined_sort.bedgraph
bedGraphToBigWig {out_folder}/{prefix}_m_CG0_combined_sort.bedgraph {reference_chrSize} {out_mod_bed_agg_filt_bigwig}
基准测试结果
有关 RRMS 在人类样本中的性能评估信息,请参阅我们的 RRMS 性能评估文档。
13. 测序芯片的重复利用及回收
本方法中不建议对测序芯片进行清洗或重复使用。
由于 RRMS 实验测序时间较长,并包含多次芯片清洗和文库重新上样,实验完成后不建议再次使用该测序芯片。
重复使用可能导致数据产出不足,无法满足分析需求。
请按照回收程序将测序芯片返还至 Oxford Nanopore。
您可在 此处找到回收测序芯片的说明。
如果您遇到问题或对测序实验有疑问,请参阅本实验指南在线版本中的“疑难解答指南”一节。
14. DNA提取和文库制备过程中可能出现的问题
以下表格列出了提取和文库制备过程中的常见问题,以及可能的原因和解决方法。
我们还在 Nanopore 社区的Support板块提供了常见问题解答(FAQ)。
如果以下方案仍无法解决您的问题,请通过电邮(support@nanoporetech.com)或 纳米孔社区的在线支持(LiveChat)联系我们。
低质量样本
经AMPure磁珠纯化后的DNA回收率低
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 低回收率 | AMPure磁珠量与样品量的比例低于预期,导致DNA因未被捕获而丢失 | 1.AMPure 磁珠沉降速度较快,因此在将磁珠加入样品前,请务必充分重悬混匀。 2.当AMPure磁珠量与样品量的比值低于0.4:1时,所有的DNA片段都会在纯化过程中丢失。 |
| 低回收率 | DNA片段短于预期 | AMPure磁珠量与样品量的比值越低,针对短片段的筛选就越严格。每次实验时,请先使用琼脂糖凝胶(或其他凝胶电泳方法)确定起始DNA的长度,据此计算出合适的AMPure磁珠用量。 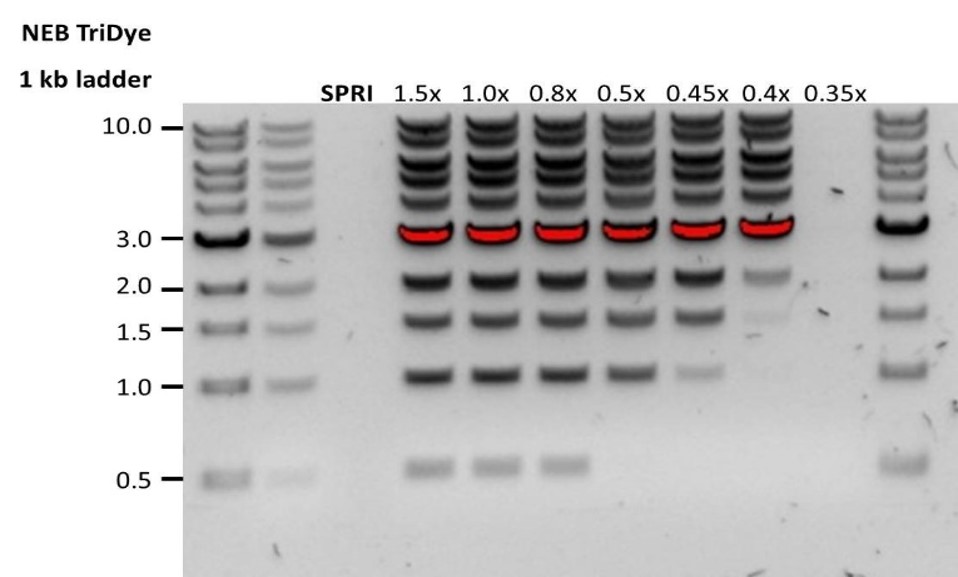 |
| 末端修复后的DNA回收率低 | 清洗步骤所用乙醇的浓度低于70% | 当乙醇浓度低于70%时,DNA会从磁珠上洗脱下来。请确保使用正确浓度的乙醇。请确保使用正确浓度的乙醇。 |
15. 测序过程中可能出现的问题
以下表格列出了提取和文库制备过程中的常见问题,以及可能的原因和解决方法。
我们还在 Nanopore 社区的Support板块提供了常见问题解答(FAQ)。
如果以下方案仍无法解决您的问题,请通过电邮(support@nanoporetech.com)或 纳米孔社区的在线支持(LiveChat)联系我们。
MinKNOW Mux 扫描在测序起始时报告的活性孔数少于芯片质检时报告的活性孔数
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW Mux 扫描在测序起始时报告的活性孔数少于芯片质检时报告的活性孔数 | 纳米孔阵列中引入了气泡 | 在对通过质控的芯片进行预处理之前,请务必排出预处理孔附近的气泡。否则,气泡会进入纳米孔阵列对其造成不可逆转地损害。 为 PromethION 测序芯片上样视频中演示了避免引入气泡的最佳操作方法 |
| MinKNOW Mux 扫描在测序起始时报告的活性孔数少于芯片质检时报告的活性孔数 | 测序芯片没有正确插入测序仪 | 停止测序,将芯片从测序仪中取出,再重新插入测序仪内。请确保测序芯片牢固嵌入测序仪中,并已到达目标温度。如用户使用的是GridION/PromethION测序仪,也可尝试将芯片插入仪器的其它芯片槽进行测序。 |
| MinKNOW Mux 扫描在测序起始时报告的活性孔数少于芯片质检时报告的活性孔数 | 文库中残留的污染物对纳米孔造成损害或堵塞 | 在测序芯片质检阶段,我们用芯片储存缓冲液中的质控DNA分子来评估活性纳米孔的数量。而在测序开始时,我们使用DNA文库本身来评估活性纳米孔的数量。因此,活性纳米孔的数量在这两次评估中会有约10%的浮动。如测序开始时报告的孔数明显降低,则可能是由于文库中的污染物对膜结构造成了损坏或将纳米孔堵塞。用户可能需要使用其它的DNA/RNA提取或纯化方法,以提高起始核酸的纯度。您可在 污染物专题技术文档中查看污染物对测序实验的影响。请尝试其它不会导致污染物残留的 提取方法。 |
MinKNOW脚本失败
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW显示 "Script failed”(脚本失败) | 重启计算机及MinKNOW。如问题仍未得到解决,请收集 MinKNOW日志文件并联系我们的技术支持。如您没有其他可用的测序设备,我们建议您先将装有文库的测序芯片置于4°C 储存,并联系我们的技术支持团队获取进一步储存上的建议。 |
纳米孔利用率低于40%
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 纳米孔利用率<40% | 测序芯片中的文库量不够 | 请确保您按照相应实验指南,向测序芯片中加入正确浓度和体积的测序文库。请在上样前对文库进行定量,并使用 Promega Biomath Calculator 等工具中的“dsDNA:µg to pmol”功能来计算DNA分子的摩尔量。 |
| 纳米孔利用率接近0 | 使用连接测序试剂盒,但接头并未与DNA成功连接 | 请确保您在“测序接头连接”步骤中使用的是NEBNext快速连接模块(E6056),以及SQK-LSK114试剂盒中的连接缓冲液(LNB)。同时,请确保每种试剂的用量正确。您可通过制备Lambda对照文库来检验第三方试剂的可用性。 |
| 纳米孔利用率接近0 | 使用连接测序试剂盒;但在接头连接后的纯化步骤中并未使用LFB 或SFB洗涤,而是使用了酒精 | 酒精可导致测序接头上的马达蛋白变性。请确保在测序接头连接后使用洗涤缓冲液(LFB或SFB)。 |
| 纳米孔利用率接近0 | 测序芯片中无系绳 | 系绳(FLT或FCT)随预处理液加至芯片。请确保在制备预处理液时,根据需求将 FLT 或 FCT 添加到相应的冲洗缓冲液 (FB) 或 测序芯片冲洗液 (FCF) 中。 |
读长短于预期
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 读长短于预期 | DNA样本降解 | 读长反映了起始DNA片段的长度。起始DNA在提取和文库制备过程中均有可能被打断。 1.请查阅纳米孔社区中的 提取方法 以获得最佳DNA提取方案. 2.在进行文库制备之前,请先跑电泳,查看起始DNA片段的长度分布。 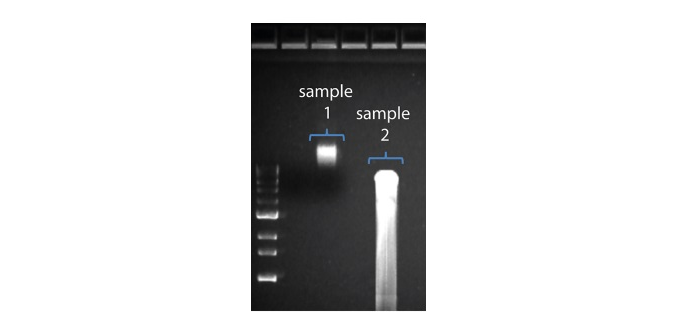 在上图中,样本1为高分子量DNA,而样本2为降解样本。 在上图中,样本1为高分子量DNA,而样本2为降解样本。3.在制备文库的过程中,请避免使用吹打或/和涡旋振荡的方式来混合试剂。轻弹或上下颠倒离心管即可。 |
大量纳米孔处于不可用状态
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
大量纳米孔处于不可用状态 (在通道面板和纳米孔活动状态图上以蓝色表示)  上方的纳米孔活动状态图显示:状态为不可用的纳米孔的比例随着测序进程而不断增加。 上方的纳米孔活动状态图显示:状态为不可用的纳米孔的比例随着测序进程而不断增加。 | 样本中含有污染物 | 使用MinKNOW中的“Unblocking”(疏通)功能,可对一些污染物进行清除。如疏通成功,纳米孔的状态会变为"测序孔"(sequencing pore)。若疏通后,状态为不可用的纳米孔的比例仍然很高甚至增加: 1.用户可使用 测序芯片冲洗试剂盒 (EXP-WSH004)进行核酸酶冲洗 操作,或 2.使用PCR扩增目标片段,以稀释可能导致问题的污染物。 |
大量纳米孔处于“失活”(Inactive)状态
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 大量纳米孔处于失活状态(在通道面板和纳米孔活动状态图上以浅蓝色表示。膜结构或纳米孔遭受不可逆转地损伤 | 测序芯片中引入了气泡 | 芯片预处理和文库上样过程中引入的气泡会对纳米孔带来不可逆转地损害。请观看如何为 PromethION 测序芯片上样 的视频了解最佳操作方法。 |
| 大量纳米孔处于失活状态 | 存在与 DNA 共纯化的化合物 | 已知的化合物包括多糖等。 1.使用 QIAGEN PowerClean Pro试剂盒进行纯化。 2.利用QIAGEN REPLI-g 试剂盒对原始 gDNA 样本进行全基因组扩增。 |
| 大量纳米孔处于失活/不可用状态 | 样本中含有污染物 | 您可在Contaminants 中查看污染物对测序实验的影响。请尝试其它不会导致污染物残留的提取方法。 |
温度波动
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 温度波动 | 测序芯片和仪器接触不良 | 检查芯片背面的金属板是否有热垫覆盖。重新插入测序芯片,用力向下按压,以确保芯片的连接器引脚与测序仪牢固接触。如问题仍未得到解决,请联系我们的技术支持。 |
未能达到目标温度
| 现象 | 可能原因 | 措施及备注 |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW显示“未能达到目标温度” | 测序仪所处环境低于标准室温,或通风不良(以致芯片过热) | MinKNOW会限定测序芯片达到目标温度的时间。当超过限定时间后,系统会显示出错信息,但测序实验仍会继续。值得注意的是,在错误温度下测序可能会导致通量和数据质量(Q值)的降低。请调整测序仪的摆放位置,确保将其置于室温下、通风良好的环境中,再在MinKNOW中重启进程。 |







