Ligation sequencing DNA V14 - automated Hamilton NGS STAR 96 (SQK-LSK114-XL) (GDA_9167_v114_revK_02Oct2025)
PromethION: Protocol
V GDA_9167_v114_revK_02Oct2025
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
Automated library preparation
- 3. DNA repair and end-prep
- 4. Adapter ligation and clean-up
- 5. Priming and loading the PromethION flow cell
Sequencing and data analysis
Troubleshooting
1. Overview of the protocol
Ligation Sequencing Kit XL V14 features
This kit is recommended for:
- Processing multiple samples simultaneously, either with a multichannel pipette or a liquid-handling robot
- Achieving raw read sequencing modal accuracy of Q20+ (99%) or above
- Controlling read length
- Upstream processes such as size selection, whole genome amplification, or enrichment for long reads
Optional fragmentation and size selection
By default, the protocol contains no DNA fragmentation step, however in some cases it may be advantageous to fragment your sample. For example, when working with lower amounts of input gDNA (100 ng – 500 ng), fragmentation will increase the number of DNA molecules and therefore increase throughput. Instructions are available in the DNA Fragmentation section of Extraction methods.
Additionally, we offer several options for size-selecting your DNA sample to enrich for long fragments - instructions are available in the Size Selection section of Extraction methods.
Introduction to the automated Ligation Sequencing protocol for DNA
This protocol describes how to carry out sequencing of a DNA sample using the Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-LSK114-XL).
We have developed this automated protocol on the Hamilton NGS STAR 96 liquid handling robot. The majority of the process is automated with minimal hands-on time which is required for sample quantification and deck re-loading.
It is highly recommended that a Lambda control experiment is completed first to become familiar with the technology.
To efficiently load multiple PromethION Flow Cells, we recommend using the Loading multiple PromethION Flow Cells protocol as a guideline.
Steps in the sequencing workflow:
Prepare for your experiment
You will need to:
- Extract your DNA and check its length, quantity and purity. The quality checks performed during the protocol are essential in ensuring experimental success.
- Ensure you have your sequencing kit, the correct equipment, primed liquid-handling robot and third-party reagents.
- Download the software for acquiring and analysing your data.
- Check your flow cells to ensure they have enough pores for a good sequencing run.
Library preparation
You will need to:
- Repair the DNA and prepare the DNA ends for adapter attachment.
- Attach sequencing adapters supplied in the kit to the DNA ends.
- Prime the flow cell and load your DNA library into the flow cell.
Sequencing and analysis
You will need to:
- Start a sequencing run using the MinKNOW software which will collect raw data from the device and convert it into basecalled reads.
Compatibility of this protocol
This protocol should only be used in combination with:
- Ligation Sequencing Kit XL V14 (SQK-LSK114-XL)
- R10.4.1 flow cells (FLO-PRO114M)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit XL (EXP-WSH004-XL)
- PromethION 24/48 device - PromethION IT requirements document
- PromethION 2 Solo device - PromethION 2 Solo IT requirements document
2. Equipment and consumables
Material
- 1 µg (o 100-200 fmol) de ADN genómico de alto peso molecular
- o 100+ ng de ADN genómico de alto peso molecular (si se fragmenta el ADN).
- Ligation Sequencing Kit XL V14 (SQK-LSK114-XL)
Consumibles
- NEBNext® Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB E7180S or E7180L) (módulo de acompañamiento NEBNext de secuenciación por ligación para Oxford Nanopore Technologies®) Como alternativa, se pueden utilizar los siguientes productos de NEBNext®:
- NEBNext FFPE Repair Mix (NEB M6630)
- NEBNext Ultra II End Repair/dA-tailing Module (NEB E7546)
- NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (NEB E6056)
- Microesferas Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter™, A63881)
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Etanol al 80 % recién preparado con agua sin nucleasas
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid (Cat# 56694-01)
- Hamilton PCR ComfortLid (Cat# 814300)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
- Hamilton 20 ml Reagent Reservoirs (Cat# 96424-02)
- Sarstedt Inc Screw Cap Micro tube 2 ml, PP 1000/case (e.g. FisherScientific, Cat# NC0418367)
- Thermo Scientific™ Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8 ml Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate (Thermo Scientific™, cat # AB0859)
Instrumental
- Ice bucket with ice
- Vortex mixer
- Centrifugadora de microplacas
- Hamilton NGS STAR 96 (NGS STAR with Multi-Probe Head 96)
- Hamilton On-Deck Thermal Cycler (ODTC)
Equipo opcional
- Bioanalizador Agilent (o equivalente)
- Qubit fluorometer plate reader (or equivalent for QC check)
Adjust your sample input quantity depending on your initial DNA sample length:
| Fragment library length | Starting input |
|---|---|
| Very short (<1 kb) | 200 fmol |
| Short (1-10 kb) | 100–200 fmol |
| Long (>10 kb) | 1 µg |
For more information on sample input and flow cell loading amounts for our ligation sequencing protocols please visit our know-how document.
Input DNA
How to QC your input DNA
It is important to use a plate reader to ensure the input DNA meets the quantity and quality requirements. Using too little or too much DNA, or DNA of poor quality (e.g. highly fragmented or containing RNA or chemical contaminants) can affect your library preparation.
For instructions on how to perform quality control of your DNA sample, please read the Input DNA/RNA QC protocol.
Input file worklist
A worklist input Excel file is required prior to running the protocol on the Hamilton NGS STAR 96. These contain information regarding the appropriate number of samples and well identifiers.
Example:
Source_SampleID | Source_Well | Target_Well |
|---|---|---|
| Sample_01 | A1 | A1 |
| Sample_02 | B1 | B2 |
| Sample_03 | C1 | C1 |
Hamilton NGS STAR 96
This method has been tested and validated using the Hamilton NGS STAR 96 (with 8 channels and MPH96) including an on deck thermal cycler (ODTC). An option to not use the ODTC is available in the method. The protocol may require some fine tuning for the NGS STAR 96 setup and the temperature/humidity of the customer laboratory.
Please contact your Hamilton representative for further details.
Deck layout 
- ODTC: On-Deck Thermal Cycler Module
- MIDI plates: Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8mL Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate
- Troughs: Hamilton 20 ml Reagent Reservoirs
- HSP plates: Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates
- Hamilton ComfortLid: Hamilton PCR ComfortLid
NEBNext® Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing
For customers new to nanopore sequencing, we recommend buying the NEBNext® Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180S or E7180L), which contains all the NEB reagents needed for use with the Ligation Sequencing Kit.
Please note, for our amplicon protocols, NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix and NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Buffer are not required.
Third-party reagents
We have validated and recommend the use of all the third-party reagents used in this protocol. Alternatives have not been tested by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
For all third-party reagents, we recommend following the manufacturer's instructions to prepare the reagents for use.
Check your flow cell
We highly recommend that you check the number of pores in your flow cell prior to starting a sequencing experiment. This should be done within 12 weeks of purchasing your PromethION Flow Cells. Oxford Nanopore Technologies will replace any unused flow cell with fewer than the number of pores listed in the Table below, when the result is reported within two days of performing the flow cell check, and when the storage recommendations have been followed. To do the flow cell check, please follow the instructions in the Flow Cell Check document.
| Flow cell | Minimum number of active pores covered by warranty |
|---|---|
| PromethION Flow Cell | 5000 |
We strongly recommend using the Ligation Buffer (LNB) supplied in the Ligation Sequencing Kit V14 rather than any third-party ligase buffers to ensure high ligation efficiency of the Ligation Adapter (LA).
Ligation Adapter (LA) included in this kit and protocol is not interchangeable with other sequencing adapters.
Consumables and reagent quantities required:
| Consumables | X24 samples | X48 samples | X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 216 | 432 | 768 |
| Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 451 | 694 | 1176 |
| Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Hamilton PCR ComfortLid | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plate | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Hamilton 20 ml Reagent Reservoirs | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Sarstedt Inc Screw Cap Micro Tube 2ml | 2 | 4 | 5 |
| Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8mL Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Reagents/kits | X24 samples | X48 samples | X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 16.5 ml | 28 ml | 51 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 6.8 ml | 9.7 ml | 15.5 ml |
| Ligation Sequencing Kit XL V14 (SQK-LSK114-XL) | 1 kit | 1 kit | 2 kits |
| NEBNext Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Sequencing (Cat# E7180L) | 1 kits | 1 kits | 1 kits |
| NEBNext Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Sequencing (Cat# E7180S) | - | 1 kits | 1 kits |
| Alternatively: | - | - | - |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix (Cat# M6630L) | 1 kit | 1 kit | 2 kits |
| NEBNext Ultra II End Repair/dA-Tailing Module (Cat# E7546L) | 1 kit | 2 kits | 3 kits |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (Cat# E6056L) | 1 kit | 2 kits | 3 kits |
Note: These are the number of kits required for one run through for the selected number of samples.
Ligation Sequencing Kit XL V14 (SQK-LSK114-XL) contents
| Name | Acronym | Vial colour | Number of vials | Fill volume per vial (µl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA Control Strand | DCS | Yellow | 1 | 100 |
| Ligation Adapter | LA | Green | 1 | 320 |
| Ligation Buffer | LNB | White | 1 | 1,500 |
| Elution Buffer | EB | White cap, black strip label | 1 | 10,000 |
| Long Fragment Buffer | LFB | White cap, orange strip label | 2 | 20,000 |
| Short Fragment Buffer | SFB | White cap, blue strip label | 2 | 25,000 |
| Library Beads | LIB | Pink | 2 | 1,800 |
| Library Solution | LIS | White cap, pink label | 2 | 1,800 |
| Sequencing Buffer | SB | Red | 3 | 1,700 |
| Flow Cell Flush | FCF | Clear | 4 | 15,500 |
| Flow Cell Tether | FCT | Purple | 1 | 1,600 |
Note: The DNA Control Sample (DCS) is a 3.6 kb standard amplicon mapping the 3' end of the Lambda genome.
3. DNA repair and end-prep
Material
- 1 µg (o 100-200 fmol) de ADN genómico de alto peso molecular
Consumibles
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix (NEB M6630)
- Módulo NEBNext® Ultra™ II End Repair/dA-Tailing (NEB, E7546)
- Microesferas Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter™, A63881)
- Etanol al 80 % recién preparado con agua sin nucleasas
- Thermo Scientific™ Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8 ml Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate (Thermo Scientific™, cat # AB0859)
- Sarstedt Inc Screw Cap Micro tube 2 ml, PP 1000/case (e.g. FisherScientific, Cat# NC0418367)
- Hamilton 20 ml Reagent Reservoirs (Cat# 96424-02)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
- Hamilton PCR ComfortLid (Cat# 814300)
- Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid (Cat# 56694-01)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
Instrumental
- Ice bucket with ice
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P10 pipette and tips
- Centrifugadora de microplacas
- Vortex mixer
Consumables and equipment quantities:
| Consumable/equipment | X24 samples | X48 samples | X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 96 | 192 | 384 |
| Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 201 | 298 | 490 |
| Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid | 2 (1 EtOH & H20) | 2 (1 EtOH & H20) | 2 (1 EtOH & H20) |
| Hamilton PCR ComfortLid | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plate | 1 (1 input sample & 1 end prepped sample) | 1 (1 input sample & 1 end prepped sample) | 1 (1 input sample & 1 end prepped sample) |
| Hamilton 20 ml Reagent Reservoirs | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sarstedt Inc Screw Cap Micro Tube 2 ml | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8 ml Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Reagents quantities:
| Reagents | X24 samples | X48 samples | X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 16.5 ml | 28 ml | 51 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 3.7 ml | 5.4 ml | 8.9 ml |
| NEBNext Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180L) regarding the reagents below | 1 tubes | 1 tubes | 1 tubes |
| NEBNext Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180S) regarding the reagents below | - | 1 tubes | 1 tubes |
| Alternatively: | - | - | - |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Buffer | 1 tube | 1 tube | 1 tube |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 1 tube | 1 tube | 2 tubes |
| Ultra II End-prep Reaction Buffer | 1 tube | 2 tubes | 3 tubes |
| Ultra II End-prep Enzyme Mix | 1 tube | 1 tube | 2 tubes |
Note: Dead volumes are included.
Please note, all screenshots are representative of X96 samples.
Optional fragmentation and size selection
By default, the protocol contains no DNA fragmentation step, however in some cases it may be advantageous to fragment your sample. For example, when working with lower amounts of input gDNA (100 ng – 500 ng), fragmentation will increase the number of DNA molecules and therefore increase throughput. Instructions are available in the DNA Fragmentation section of Extraction methods.
Additionally, we offer several options for size-selecting your DNA sample to enrich for long fragments - instructions are available in the Size Selection section of Extraction methods.
Prepare the NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix and NEBNext Ultra II End Repair / dA-tailing Module reagents in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions, and place on ice.
For optimal performance, NEB recommend the following:
Thaw all reagents on ice.
Flick and/or invert the reagent tubes to ensure they are well mixed.
Note: Do not vortex the FFPE DNA Repair Mix or Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix.Always spin down tubes before opening for the first time each day.
The Ultra II End Prep Buffer and FFPE DNA Repair Buffer may have a little precipitate. Allow the mixtures to come to room temperature and pipette the buffer up and down several times to break up the precipitate, followed by vortexing the tube for 30 seconds to solubilise any precipitate.
Note: It is important the buffers are mixed well by vortexing.The FFPE DNA Repair Buffer may have a yellow tinge and is fine to use if yellow.
Prepare each DNA sample per well with nuclease-free water in the input plate.
- Per sample, transfer 1 μg (or 100-200 fmol) of input DNA into a well of the input plate
- Adjust the volume to 48 μl with nuclease-free water
- Mix thoroughly by pipetting
- Spin down briefly in a microfuge
Quantify 1 µl of each eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer plate reader off deck.
Switch on the Hamilton NGS STAR 96 robot and open 'Hamilton Run Control' on the computer by clicking the icon:
![]()
Click 'File' and 'Open' to choose the method to run on the liquid handling robot.
Click 'Process01: DNA repair and end-prep' to start.

Click 'Process02: DNA repair and end-prep clean-up' to stop the automated library preparation and quantify the samples before the adapter ligation step.

It is mandatory for users to have an MPH module installed and we recommend the use of an ODTC module.
Select whether an ODTC module is available to use in the run and select Yes to use the MPH (96 Head) module.

Click 'Browse' to choose the Input File Worklist for the specific number of samples in the run and click 'OK'.

An input file worklist for the number of samples in the run must be generated before the run.
Prepare the End Prep Mastermix with the following reagents according to the Hamilton user interface. Click either 'Yes' or 'No' to continue.
Note: It is user preference whether to print and save the instructions.
Reagent volumes for all sample numbers:
| Reagent | Volume X24 samples | Volume X48 samples | Volume X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Buffer | 106.6 µl | 213.3 µl | 414.8 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 60.9 µl | 121.8 µl | 237 µl |
| Ultra II End-prep Reaction Buffer | 106.6 µl | 213.3 µl | 414.8 µl |
| Ultra II End-prep Enzyme Mix | 91.4 µl | 182.8 µl | 355.6 µl |
| Total | 365.6 µl | 731.2 µl | 1422.2 µl |

Insert the ComfortLid position as displayed on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Insert plates to their corresponding positions. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Load a full deck of 50 µl tips into the positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Highlight the 50 µl tips available to use on the 'Edit Tip Count' window and click 'Ok' to continue.

Load a full deck of 300 µl tips in the positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Highlight the 300 µl tips available to use on the 'Edit Tip Count' window and click 'Ok' to continue.

Freshly prepare 80% ethanol in nuclease-free water in a trough.
| Reagents | Volume X24 samples | Volume X48 samples | Volume X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 16.5 ml | 28 ml | 51 ml |
Insert the trough of 80% ethanol in the position on screen and click 'Ok' to continue.

If the consumables used for troughs are not barcoded, click 'Exclude' on all the selected troughs inserted in the robot and click 'Execute' to continue.

Prepare the AMPure XP beads by vortexing and load the 20 ml trough with the volume required:
| Reagents | Volume X24 samples | Volume X48 samples | Volume X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beads | 3.7 ml | 5.4 ml | 8.9 ml |
Ensure the AMPure XP beads are well mixed before use by vortexing.
Insert the trough of AMPure XP beads and nuclease-free water in their positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

If the consumables used for troughs are not barcoded, click 'Exclude' on all the selected troughs inserted in the robot and click 'Execute' to continue.

Load 1000 µl tips and insert the input plate of DNA samples into the position on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Highlight the 1000 µl tips available to use on the 'Edit Tip Count' window and click 'Ok' to continue.

Ensure the mastermix is well mixed and homogenous before loading the 2 ml Sarstedt tubes. Mixing in the robot is not effective.
Mix and insert the prepared End Prep Mastermix into the positions on screen.

Click 'Ok' to start the DNA repair and end-prep automation process.
Once the automation process has finished, there will be an on screen prompt to unload the plate. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Quantify 1 µl of each eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer plate reader off deck.
Take forward the repaired and end repaired DNA into the adapter ligation and clean-up step.
4. Adapter ligation and clean-up
Material
- Ligation Adapter (LA)
- Ligation Buffer (LNB)
- Long Fragment Buffer (LFB)
- Short Fragment Buffer (SFB)
- Elution Buffer (EB)
Consumibles
- NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (NEB E6056)
- Microesferas Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter™, A63881)
- Thermo Scientific™ Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8 ml Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate (Thermo Scientific™, cat # AB0859)
- Sarstedt Inc Screw Cap Micro tube 2 ml, PP 1000/case (e.g. FisherScientific, Cat# NC0418367)
- Hamilton 20 ml Reagent Reservoirs (Cat# 96424-02)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
- Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid (Cat# 56694-01)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
Instrumental
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P10 pipette and tips
- Vortex mixer
- Centrifugadora de microplacas
Although third-party ligase products may be supplied with their own buffer, the ligation efficiency of the Ligation Adapter (LA) is higher when using the Ligation Buffer (LNB) supplied in the Ligation Sequencing Kit.
Consumables and equipment quantities:
| Consumable/equipment | X24 samples | X48 samples | X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 120 | 240 | 384 |
| Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 250 | 396 | 686 |
| Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 32 | 32 | 32 |
| Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid | 2 (1 L/SFB & 1 EB) | 2 (1 L/SFB & 1 EB) | 2 (1 L/SFB & 1 EB) |
| Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plate | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Hamilton 20 ml Reagent Reservoirs | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sarstedt Inc Screw Cap Micro Tube 2 ml | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8 ml Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Reagents quantities:
| Reagents | X24 samples | X48 samples | X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligation adapter (LA) | 2 tubes | 4 tubes | 8 tubes |
| Ligation Buffer (LNB) | 2 tubes | 4 tubes | 8 tubes |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle | 1 bottle | 1 bottle |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles | 4 bottles | 8 bottles |
| Short Fragment Buffer (SFB) | 2 bottles | 4 bottles | 8 bottles |
| AMPure XP Beads | 3.1 ml | 4.3 ml | 6.6 ml |
| NEBNext Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180L) regarding the reagent below: | 1 tubes | 1 tubes | 1 tubes |
| NEBNext Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180S) regarding the reagent below: | - | 1 tubes | 1 tubes |
| Alternatively: | - | - | - |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 1 tube | 2 tubes | 3 tubes |
Note: Dead volumes are included.
Please note, all screenshots are representative of X96 samples.
Spin down the Ligation Adapter (LA) and Quick T4 Ligase, and place on ice.
Thaw the Ligation Buffer (LNB) at room temperature, spin down and combine all the required tubes. Place on ice immediately after thawing and mixing.
Thaw a bottle of Elution Buffer (EB) at room temperature, mix by vortexing and place on ice.
Depending on the wash buffer (LFB or SFB) used, the clean-up step after adapter ligation is designed to either enrich for DNA fragments of >3 kb, or purify all fragments equally.
- To enrich for DNA fragments of 3 kb or longer, use Long Fragment Buffer (LFB)
- To retain DNA fragments of all sizes, use Short Fragment Buffer (SFB)
To enrich for DNA fragments of 3 kb or longer, thaw the Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) at room temperature, mix by vortexing and combine all the required bottles before storing on ice.
To retain DNA fragments of all sizes, thaw the Short Fragment Buffer (SFB) at room temperature, mix by vortexing and combine all the required bottles before storing on ice.
Click 'Process03: Adapter ligation' to start.

Click 'Process04: Adapter ligation and clean-up' to stop the automated library preparation and quantify the samples before sequencing.

It is mandatory for the MPH module to be installed on the liquid handling robot. Select 'Yes' to use the MPH (96 Head) module.

Click 'Browse' to choose the Input File Worklist used during DNA repair and end-prep.

Prepare the Adapter Ligation Mastermix with the following reagents according to the Hamilton user interface. Select either 'Yes' or 'No' to continue.
Note: It is user preference whether to print and save the instructions.
Reagent volumes for all sample numbers:
| Reagent | Volume X24 samples | Volume X48 samples | Volume X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligation Adapter (LA) | 140.5 µl | 281 µl | 559.5 µl |
| Ligation Buffer (LNB) | 702.5 µl | 1405 µl | 2797.5 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 281 µl | 562 µl | 1119 µl |

Ensure the mastermix is well mixed and homogenous before loading the 2 ml Sarstedt tubes. Mixing in the robot is not effective.
Insert plates to their corresponding positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Load a full deck of 50 µl tips into the positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Highlight the 50 µl tips available to use on the 'Edit Tip Count' window. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Load a full deck of 300 µl tips in the positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Highlight the 300 µl tips available to use on the 'Edit Tip Count' window. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Prepare the AMPure XP beads by vortexing and load the 20 ml trough with the volume required:
| Reagents | Volume X24 samples | Volume X48 samples | Volume X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beads | 3.1 ml | 4.3 ml | 6.6 ml |
Ensure the AMPure XP beads are well mixed before use by vortexing.
Insert troughs of AMPure XP beads, LFB/SFB and EB in the positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.
| Reagent | Volume X24 samples | Volume X48 samples | Volume X96 samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long/Short Fragment Buffer | 2 bottles | 4 bottles | 8 bottles |
| Elution Buffer | 1 bottle | 1 bottle | 1 bottle |

If the troughs are not barcoded, click 'Exclude' on all the selected troughs inserted in the robot and click 'Execute' to continue.

Insert 1000 µl tips and the Clean End Prep Plate to the correct positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Highlight the 1000 µl tips available to use on the 'Edit Tip Count' window. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Insert the prepared Adapter Ligation Mastermix into the positions on screen. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Ensure the mastermix is well mixed and homogenous before loading the 2 ml Sarstedt tubes. Mixing in the robot is not effective.
Once the automation process has finished, there will be an on screen prompt to unload the plate. Click 'Ok' to continue.

Quantify 1 µl of each eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer plate reader off deck.
Seal the plate once the library is prepared and store on ice until ready to load onto the flow cell.
We do not recommend running the liquid handling robot overnight as the plate must be sealed and stored on ice as soon as the library preparation is completed.
Depending on your DNA library fragment size, prepare your final library in 32 µl of Elution Buffer (EB).
| Fragment library length | Flow cell loading amount |
|---|---|
| Very short (<1 kb) | 100 fmol |
| Short (1-10 kb) | 35–50 fmol |
| Long (>10 kb) | 300 ng |
Note: If the library yields are below the input recommendations, load the entire library.
If required, we recommend using a mass to mol calculator such as the NEB calculator.
We recommend loading the following amount of prepared library onto the R10.4.1 flow cell:
For high output, load 35-50 fmol of final library. This is to ensure high pore occupancy of >95% is reached.
Library storage recommendations
We recommend storing libraries at 4°C for short term storage or repeated use, for example, re-loading flow cells between washes. For single use and long term storage of more than 3 months, we recommend storing libraries at -80°C. For further information, please refer to the Library Stability Know-How document.
If quantities allow, the library may be diluted in Elution Buffer (EB) for splitting across multiple flow cells.
Depending on how many flow cells the library will be split across, more Elution Buffer (EB) than what is supplied in the kit will be required.
5. Priming and loading the PromethION flow cell
Material
- Flow Cell Flush (FCF)
- Flow Cell Tether (FCT)
- Library Solution (LIS)
- Library Beads (LIB)
- Sequencing Buffer (SB)
Consumibles
- Celdas de flujo PromethION
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Instrumental
- Dispositivo PromethION 24/48 o PromethION 2 Solo
- Dispositivo PromethION
- Pantalla protectora celdas de flujo PromethION
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
This kit is only compatible with R10.4.1 flow cells (FLO-PRO114M).
After taking the flow cell out of the fridge, wait 20 minutes for the flow cell to reach room temperature, before inserting it into the PromethION. Condensation can form on the flow cell in humid environments. Inspect the gold connector pins on the top and underside of the flow cell for condensation and wipe off with a lint-free wipe if any is observed. Ensure the heat pad (black pad) is present on the underside of the flow cell.
Using the Library Solution
For most sequencing experiments, use the Library Beads (LIB) for loading your library onto the flow cell. However, for viscous libraries it may be difficult to load with the beads and may be appropriate to load using the Library Solution (LIS).
Thaw the Sequencing Buffer (SB), Library Beads (LIB) or Library Solution (LIS, if using), Flow Cell Tether (FCT) and Flow Cell Flush (FCF) at room temperature before mixing by vortexing. Then spin down and store on ice.
Prepare the flow cell priming mix in a suitable tube for the number of flow cells to flush. Once combined, mix well by briefly vortexing.
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Flow Cell Tether (FCT) | 30 µl |
| Flow Cell Flush (FCF) | 1170 µl |
| Total volume | 1,200 µl |
For PromethION 2 Solo, load the flow cell(s) as follows:
Place the flow cell flat on the metal plate.
Slide the flow cell into the docking port until the gold pins or green board cannot be seen.

For the PromethION 24/48, load the flow cell(s) into the docking ports:
- Line up the flow cell with the connector horizontally and vertically before smoothly inserting into position.
- Press down firmly onto the flow cell and ensure the latch engages and clicks into place.


Insertion of the flow cells at the wrong angle can cause damage to the pins on the PromethION and affect your sequencing results. If you find the pins on a PromethION position are damaged, please contact support@nanoporetech.com for assistance.

Antes de cargar la biblioteca, realizar una comprobación de la celda de flujo a fin de evaluar el número de poros disponible.
Este paso puede omitirse si la celda de flujo se ha comprobado con anterioridad.
Para más información, consultar el documento de comprobación de celdas de flujo en el protocolo de MinKNOW.
Slide the inlet port cover clockwise to open.

Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the inlet port, draw back a small volume to remove any air bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette tip to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the inlet port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip.

Load 500 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the inlet port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait five minutes. During this time, prepare the library for loading using the next steps in the protocol.

Thoroughly mix the contents of the Library Beads (LIB) by pipetting.
The Library Beads (LIB) tube contains a suspension of beads. These beads settle very quickly. It is vital that they are mixed immediately before use.
We recommend using the Library Beads (LIB) for most sequencing experiments. However, the Library Solution (LIS) is available for more viscous libraries.
In a new 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, prepare the library for loading as follows:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer (SB) | 100 µl |
| Library Beads (LIB) thoroughly mixed before use, or Library Solution (LIS) | 68 µl |
| DNA library | 32 µl |
| Total | 200 µl |
Note: Library loading volume has been increased to improve array coverage.
Complete the flow cell priming by slowly loading 500 µl of the priming mix into the inlet port.

Mix the prepared library gently by pipetting up and down just prior to loading.
Load 200 µl of library into the inlet port using a P1000 pipette.

Close the valve to seal the inlet port.
For optimal sequencing output, install the light shield on your flow cell as soon as the library has been loaded.
We recommend leaving the light shield on the flow cell when library is loaded, including during any washing and reloading steps. The shield can be removed when the library has been removed from the flow cell.
If the light shield has been removed from the flow cell, install the light shield as follows:
- Align the inlet port cut out of the light shield with the inlet port cover on the flow cell. The leading edge of the light shield should sit above the flow cell ID.
- Firmly press the light shield around the inlet port cover. The inlet port clip will click into place underneath the inlet port cover.


Close the PromethION lid when ready to start a sequencing run on MinKNOW.
Wait a minimum of 10 minutes after loading the flow cells onto the PromethION before initiating any experiments. This will help to increase the sequencing output.
6. Data acquisition and basecalling
How to start sequencing
Once you have loaded your flow cell, the sequencing run can be started on MinKNOW, our sequencing software that controls the device, data acquisition and real-time basecalling. For more detailed information on setting up and using MinKNOW, please see the MinKNOW protocol.
MinKNOW can be used and set up to sequence in multiple ways:
- On a computer either direcly or remotely connected to a sequencing device.
- Directly on a GridION or PromethION 24/48 sequencing device.
For more information on using MinKNOW on a sequencing device, please see the device user manuals:
To start a sequencing run on MinKNOW:
1. Navigate to the start page and click Start sequencing.
2. Fill in your experiment details, such as name and flow cell position and sample ID.
3. Select the Ligation Sequencing Kit XL V14 (SQK-LSK114-XL) on the Kit page.
4. Configure the sequencing and output parameters for your sequencing run or keep to the default settings on the Run configuration tab.
Note: If basecalling was turned off when a sequencing run was set up, basecalling can be performed post-run on MinKNOW. For more information, please see the MinKNOW protocol.
5. Click Start to initiate the sequencing run.
Data analysis after sequencing
After sequencing has completed on MinKNOW, the flow cell can be reused or returned, as outlined in the Flow cell reuse and returns section.
After sequencing and basecalling, the data can be analysed. For further information about options for basecalling and post-basecalling analysis, please refer to the Data Analysis document.
In the Downstream analysis section, we outline further options for analysing your data.
7. Flow cell reuse and returns
Material
- Kit Flow Cell Wash (EXP-WSH004)
After your sequencing experiment is complete, if you would like to reuse the flow cell, please follow the Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol and store the washed flow cell at +2°C to +8°C.
The Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol is available on the Nanopore Community.
We recommend you to wash the flow cell as soon as possible after you stop the run. However, if this is not possible, leave the flow cell on the device and wash it the next day.
Alternatively, follow the returns procedure to send the flow cell back to Oxford Nanopore.
Instructions for returning flow cells can be found here.
If you encounter issues or have questions about your sequencing experiment, please refer to the Troubleshooting Guide that can be found in the online version of this protocol.
8. Downstream analysis
Post-basecalling analysis
There are several options for further analysing your basecalled data:
EPI2ME workflows
For in-depth data analysis, Oxford Nanopore Technologies offers a range of bioinformatics tutorials and workflows available in EPI2ME, which are available in the EPI2ME section of the Community. The platform provides a vehicle where workflows deposited in GitHub by our Research and Applications teams can be showcased with descriptive texts, functional bioinformatics code and example data.
Research analysis tools
Oxford Nanopore Technologies' Research division has created a number of analysis tools, that are available in the Oxford Nanopore GitHub repository. The tools are aimed at advanced users, and contain instructions for how to install and run the software. They are provided as-is, with minimal support.
Community-developed analysis tools
If a data analysis method for your research question is not provided in any of the resources above, please refer to the resource centre and search for bioinformatics tools for your application. Numerous members of the Nanopore Community have developed their own tools and pipelines for analysing nanopore sequencing data, most of which are available on GitHub. Please be aware that these tools are not supported by Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and are not guaranteed to be compatible with the latest chemistry/software configuration.
9. Issues during automation of library preparation
Please contact your automation vendor FAS and/or Nanopore FAS if you have any issues.
10. Issues during the sequencing run
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Fewer pores at the start of sequencing than after Flow Cell Check
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | An air bubble was introduced into the nanopore array | After the Flow Cell Check it is essential to remove any air bubbles near the priming port before priming the flow cell. If not removed, the air bubble can travel to the nanopore array and irreversibly damage the nanopores that have been exposed to air. The best practice to prevent this from happening is demonstrated in this video for [how to load a PromethION Flow Cell. |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | The flow cell is not correctly inserted into the device | Stop the sequencing run, remove the flow cell from the sequencing device and insert it again, checking that the flow cell is firmly seated in the device and that it has reached the target temperature. If applicable, try a different position on the device (GridION/PromethION). |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | Contaminations in the library damaged or blocked the pores | The pore count during the Flow Cell Check is performed using the QC DNA molecules present in the flow cell storage buffer. At the start of sequencing, the library itself is used to estimate the number of active pores. Because of this, variability of about 10% in the number of pores is expected. A significantly lower pore count reported at the start of sequencing can be due to contaminants in the library that have damaged the membranes or blocked the pores. Alternative DNA/RNA extraction or purification methods may be needed to improve the purity of the input material. The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
MinKNOW script failed
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Script failed" | Restart the computer and then restart MinKNOW. If the issue persists, please collect the MinKNOW log files and contact Technical Support. If you do not have another sequencing device available, we recommend storing the flow cell and the loaded library at 4°C and contact Technical Support for further storage guidance. |
Pore occupancy below 40%
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Pore occupancy <40% | Not enough library was loaded on the flow cell | Ensure you load the recommended amount of good quality library in the relevant library prep protocol onto your flow cell. Please quantify the library before loading and calculate mols using tools like the Promega Biomath Calculator, choosing "dsDNA: µg to pmol" |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and sequencing adapters did not ligate to the DNA | Make sure to use the NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (E6056) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Buffer (LNB, provided in the sequencing kit) at the sequencing adapter ligation step, and use the correct amount of each reagent. A Lambda control library can be prepared to test the integrity of the third-party reagents. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and ethanol was used instead of LFB or SFB at the wash step after sequencing adapter ligation | Ethanol can denature the motor protein on the sequencing adapters. Make sure the LFB or SFB buffer was used after ligation of sequencing adapters. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | No tether on the flow cell | Tethers are adding during flow cell priming (FLT/FCT tube). Make sure FLT/FCT was added to FB/FCF before priming. |
Shorter than expected read length
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Shorter than expected read length | Unwanted fragmentation of DNA sample | Read length reflects input DNA fragment length. Input DNA can be fragmented during extraction and library prep. 1. Please review the Extraction Methods in the Nanopore Community for best practice for extraction. 2. Visualise the input DNA fragment length distribution on an agarose gel before proceeding to the library prep. 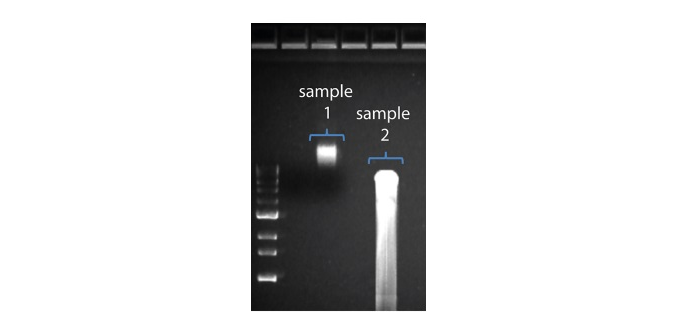 In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented. In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented.3. During library prep, avoid pipetting and vortexing when mixing reagents. Flicking or inverting the tube is sufficient. |
Large proportion of unavailable pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
Large proportion of unavailable pores (shown as blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot) 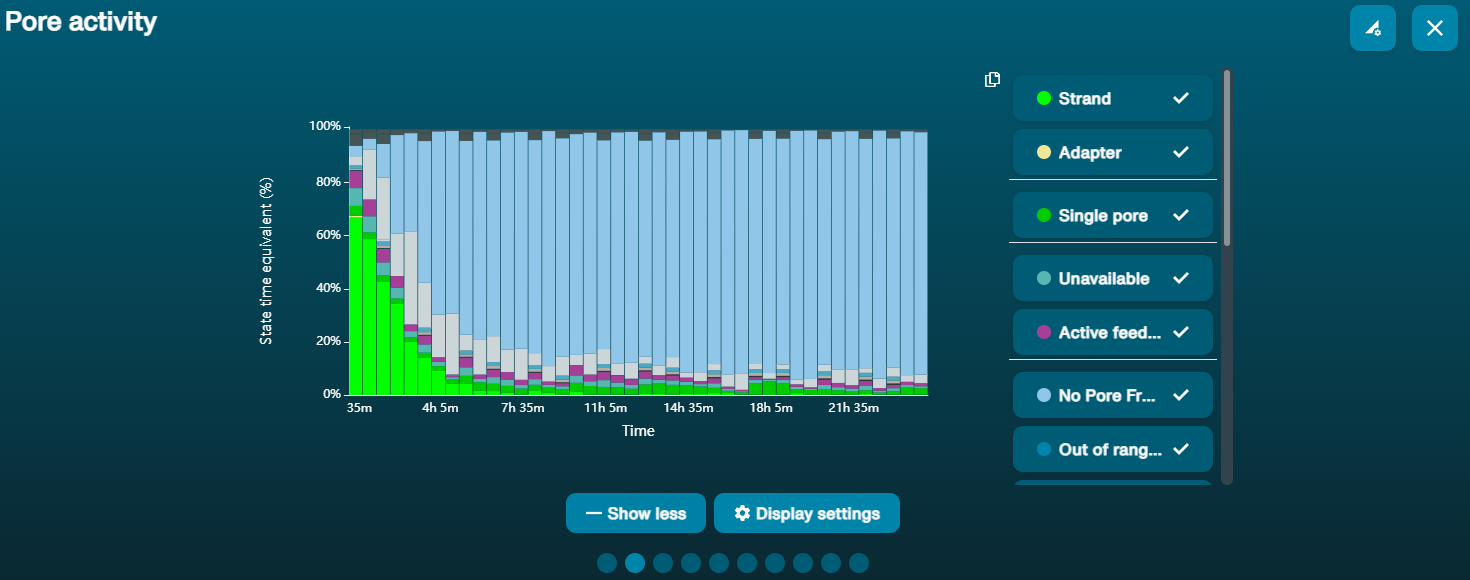 The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. | Contaminants are present in the sample | Some contaminants can be cleared from the pores by the unblocking function built into MinKNOW. If this is successful, the pore status will change to "sequencing pore". If the portion of unavailable pores stays large or increases: 1. A nuclease flush using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) can be performed, or 2. Run several cycles of PCR to try and dilute any contaminants that may be causing problems. |
Large proportion of inactive pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores (shown as light blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot. Pores or membranes are irreversibly damaged) | Air bubbles have been introduced into the flow cell | Air bubbles introduced through flow cell priming and library loading can irreversibly damage the pores. Watch the how to load a PromethION Flow Cell video for best practice. |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Certain compounds co-purified with DNA | Known compounds, include polysaccharides, typically associate with plant genomic DNA. 1. Please refer to the Plant leaf DNA extraction method. 2. Clean-up using the QIAGEN PowerClean Pro kit. 3. Perform a whole genome amplification with the original gDNA sample using the QIAGEN REPLI-g kit. |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Contaminants are present in the sample | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run | For Kit 9 chemistry (e.g. SQK-LSK109), fast fuel consumption is typically seen when the flow cell is overloaded with library (please see the appropriate protocol for your DNA library to see the recommendation). | Add more fuel to the flow cell by following the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol. In future experiments, load lower amounts of library to the flow cell. |
Temperature fluctuation
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature fluctuation | The flow cell has lost contact with the device | Check that there is a heat pad covering the metal plate on the back of the flow cell. Re-insert the flow cell and press it down to make sure the connector pins are firmly in contact with the device. If the problem persists, please contact Technical Services. |
Failed to reach target temperature
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Failed to reach target temperature" | The instrument was placed in a location that is colder than normal room temperature, or a location with poor ventilation (which leads to the flow cells overheating) | MinKNOW has a default timeframe for the flow cell to reach the target temperature. Once the timeframe is exceeded, an error message will appear and the sequencing experiment will continue. However, sequencing at an incorrect temperature may lead to a decrease in throughput and lower q-scores. Please adjust the location of the sequencing device to ensure that it is placed at room temperature with good ventilation, then re-start the process in MinKNOW. |







