Reduced representation methylation sequencing (RRMS) from cells using SQK-LSK114 (RRMS_9180_v114_revM_19Sep2025)
GridION: Protocol
V RRMS_9180_v114_revM_19Sep2025
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
Sample preparation
Library preparation
- 6. DNA repair and end-prep
- 7. Adapter ligation and clean-up
- 8. Priming and loading the MinION and GridION Flow Cell
- 9. Washing and reloading a MinION and GridION Flow Cell
Sequencing and data analysis
Troubleshooting
1. Overview of the protocol
Adaptive sampling in Kit 14 chemistry
While using Kit 14 chemistry, this workflow has been optimised to enrich specific regions of interest (ROIs) with Adaptive sampling, ensuring highest output and the best sequencing results.
For more background information about designing an adaptive sampling experiment, please refer to the Adaptive sampling best practice document: Adaptive sampling best practice
Reduced representation methylation sequencing (RRMS)
Nanopore sequencing enables direct detection of methylated cytosines (e.g. at CpG sites), without the need for bisulphite conversion. CpG sites frequently occur in high density clusters called CpG islands (CGI) and most vertebrate genes have their promoters embedded within CGIs.
Changes in methylation patterns within promoters is associated with changes in gene expression and disease states such as cancer. Exploring methylation differences between tumour samples and normal samples can help to uncover mechanisms associated with tumour formation and development.
Adaptive sampling (AS) offers a fast, flexible and precise method to enrich for regions of interest (e.g. CGIs) by depleting off-target regions during sequencing itself with no requirement for upfront sample manipulation.
To read more about how the method works, and how it compares to other techniques for analysing methylation (e.g. EPIC arrays, bisulfite), please see our Introduction to Reduced-Representation Methylation Sequencing.
RRMS can be deployed on a GridION and PromethION P2S, P24 and P48 devices.
When running on a GridION, we recommend running a single sample per flow cell using this protocol.
Alternatively, it is possible to multiplex up to 4 samples on a single PromethION Flow Cell, using our Reduced representation methylation multiplex sequencing (RRMS) from cells using SQK-NBD114.24 protocol.
Human sample sequencing
The RRMS protocol enables users to target 310 Mb of the human genome which are highly enriched for CpGs including all annotated CpG islands, shores, shelves and >90% of promoter regions (100% of promoter with more than 4 CpGs). As well as other rich CpG regions in the genome. The total number of CpG sites in the BED file is 7.18 million.
For benchmarking purposes, we performed RRMS on five replicates of a metastatic melanoma cell line and its normal pair for a male individual (COLO829/COLO829_BL) and a triple negative breast cancer cell line pair (HCC1395/HCC1935_BL). Each sample was run on a single MinION Flow Cell. RRMS resulted in high confidence methylation calls (>10 overlapping reads) for 7.3–8.5 million CpGs per sample.
For comparison, we also performed Reduced Representation Bisulphite Sequencing (RRBS), which typically yields 1.7–2.5 high confidence calls per sample. More information on this comparison can be accessed in our RRMS performance document and poster.
Mouse sample sequencing
The RRMS protocol and a new BED file have also been developed to target 308 Mb of the mouse genome, covering 100% of CpG island and promoter regions, as well as other CpG rich regions in the genome.
The performance of RRMS for mouse samples was characterised on replicates of a blastocyst-derived, embryonic stem cell line (ES-E14TG2a) and a leukaemia cell line (BALB/c AMuLV A.3R.1). A non-RRMS library was also run as a control. Each sample was run on a single MinION Flow Cell and RRMS resulted in high confidence methylation calls (>10X reads per site) for 5.0–5.8 million CpGs per sample in the mouse genome, compared with ~400,000 CpGs in the control library.
Alternative vertebrate genomes could be sequenced using the RRMS protocol and a bespoke BED file.
However, please note Oxford Nanopore Technologies has only validated this method using human and mouse samples.
Introduction to the DNA extraction and ligation sequencing protocol for RRMS
This protocol describes how to carry out DNA extraction and reduced representation methylation sequencing (RRMS) using the Ligation Sequencing Kit V14 (SQK-LSK114) and the Adaptive Sampling feature in MinKNOW.
Steps in the sequencing workflow:
Prepare for your experiment
You will need to:
- Extract your DNA, fragment it using the Covaris g-TUBE, and check its length, quantity and purity. The quality checks performed during the protocol are essential in ensuring experimental success.
- Ensure you have your sequencing kit, the correct equipment and third-party reagents.
- Download the software for acquiring and analysing your data.
- Ensure that you have the correct BED file for Adaptive Sampling.
- Check your flow cell to ensure it has enough pores for a good sequencing run.
Library preparation
The Table below is an overview of the steps required in the library preparation, including timings and optional stopping points.
| Library preparation | Process | Time | Stop option |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNA repair and end-prep | Repair the fragmented DNA and prepare the DNA ends for adapter attachment. | 35 minutes | 4°C overnight |
| Adapter ligation and clean-up | Attach the sequencing adapters to the DNA ends. | 30 minutes | 4°C short-term storage or for repeated use, such as re-loading your flow cell -80°C for single-use, long-term storage. We strongly recommend sequencing your library as soon as it is adapted. |
| Priming and loading the flow cell | Prime the flow cell and load the prepared library for sequencing. | 10 minutes |
Sequencing and analysis
You will need to:
- Start a sequencing run using the MinKNOW software, which will collect raw data from the device and convert it into basecalled reads. While configuring the run, turn on the Adaptive Sampling setting and import a pre-prepared BED file with your regions of interest, along with a FASTA reference file.
- Sequence the sample for a total of 96 hours, with two flow cell washes when the available pore count drops to around 40% of the starting pore count (typically after ~24 hours and the second time after ~48 hours).
- Use Dorado to call modified bases, for more information please refer to the Dorado Github page.
- Use the commands recommended at the end of this protocol to aggregate the modified bases and perform CpG island annotation.
Compatibility of this protocol
This protocol should only be used in combination with:
- Ligation Sequencing Kit V14 (SQK-LSK114)
- R10.4.1 flow cells (FLO-MIN114)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
- GridION - GridION IT requirements document
2. Equipment and consumables
材料
- 2 μg extracted genomic DNA (e.g. from cell culture or tissue sample)
- 连接测序试剂盒V14(SQK-LSK114)
- 测序芯片清洗剂盒(EXP-WSH004)
耗材
- 供 Oxford Nanopore Technologies® 连接测序使用的 NEBNext® 配套模块 v2(NEB, E7672S 或 E7672L)
- 新制备的 80% 乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- 0.2 ml 薄壁PCR管
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(Invitrogen, Q32851)
- MinION/GridION Flow Cell R10.4.1 (Oxford Nanopore, FLO-MIN114)
仪器
- GridION device
- Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)
- 适用于1.5ml Eppendorf 离心管的磁力架
- 迷你离心机
- 涡旋混匀仪
- 热循环仪
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- P2 移液枪和枪头
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- 计时器
可选仪器
- Agilent 生物分析仪(或等效仪器)
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
- Eppendorf 5424 离心机(或等效器材)
After performing DNA extraction and DNA fragmentation, you will need 2 µg genomic DNA to take forward into the library preparation.
Input DNA
How to QC your input DNA
It is important that the input DNA meets the quantity and quality requirements. Using too little or too much DNA, or DNA of poor quality (e.g. highly fragmented or containing RNA or chemical contaminants) can affect your library preparation.
For instructions on how to perform quality control of your DNA sample, please read the Input DNA/RNA QC protocol.
Chemical contaminants
Depending on how the DNA is extracted from the raw sample, certain chemical contaminants may remain in the purified DNA, which can affect library preparation efficiency and sequencing quality. Read more about contaminants on the Contaminants page of the Community.
NEBNext® Companion Module v2 for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing
We recommend buying the NEBNext® Companion Module v2 for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7672S or E7672L), which contains all the NEB reagents needed for use with the Ligation Sequencing Kit.
The previous version, NEBNext® Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180S or E7180L) is compatible, but the recommended v2 module offers more efficient dA-tailing and ligation, a result of the FFPEv2 DNA Repair Buffer and Salt-T4 DNA Ligase, respectively. A marked cost saving per sample preparation is also realised when using the v2 module.
Note: for our amplicon protocols, NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix is not required and purchasing the required reagents separately is more cost effective.
Third-party reagents
We have validated and recommend the use of all the third-party reagents used in this protocol. Alternatives have not been tested by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
For all third-party reagents, we recommend following the manufacturer's instructions to prepare the reagents for use.
Check your flow cell
We highly recommend that you check the number of pores in your flow cell prior to starting a sequencing experiment. This should be done within 12 weeks of purchasing your MinION/GridION Flow Cells. Oxford Nanopore Technologies will replace any unused flow cell with fewer than the number of pores listed in the Table below, when the result is reported within two days of performing the flow cell check, and when the storage recommendations have been followed. To do the flow cell check, please follow the instructions in the Flow Cell Check document.
| Flow cell | Minimum number of active pores covered by warranty |
|---|---|
| MinION/GridION Flow Cell | 800 |
We strongly recommend using the Ligation Buffer (LNB) supplied in the Ligation Sequencing Kit V14 rather than any third-party ligase buffers to ensure high ligation efficiency of the Ligation Adapter (LA).
Ligation Adapter (LA) included in this kit and protocol is not interchangeable with other sequencing adapters.
Ligation Sequencing Kit V14 (SQK-LSK114) contents
Note: This product contains AMPure XP reagent manufactured by Beckman Coulter, Inc. and can be stored at -20°C with the kit without detriment to reagent stability.
Note: The DNA Control Sample (DCS) is a 3.6 kb standard amplicon mapping the 3' end of the Lambda genome.
3. BED file
Download the BED file from the Adaptive Sampling catalogue.
The Adaptive Sampling catalogue provides a way for both the Oxford Nanopore team and Community members to share BED files with genomic target regions used for Adaptive Sampling experiments. The BED files along with a reference genome can be uploaded into MinKNOW.
For human genome RRMS experiments, download the Human reduced representation methylation sequencing (RRMS) file.
For mouse genome RRMS experiments, download the Mouse reduced representation methylation sequencing (RRMS) file.
(Optional): For alternative vertebrate genomes, please use a bespoke BED file for the desired organism.
4. DNA extraction
材料
- 5 × 10⁶ 个细胞
耗材
- Puregene 细胞试剂盒(QIAGEN,158043)
- 新制备的70%乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- TE 缓冲液(10 mM Tris-HCl、1 mM EDTA、pH 8.0)(Fisher scientific,10224683)
- 1 x 磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)
- 异丙醇
- Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher,Q32851)
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- 15 ml Falcon离心管
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- 适用于 15 ml Falcon 管的离心机及转子
- 设定为 37°C 和 50°C 的培养箱或水浴锅
- 涡旋混匀仪
- 用于提取沉淀 DNA 的接种环或一次性镊子
- 宽口移液枪头
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
Extraction from cultured cell lines:
Extract DNA from your sample(s) using one of our recommended extraction protocols.
For the benchmarking of this method, the Oxford Nanopore team extracted DNA from ~5 million cells using the protocol: Human cell line DNA – QIAGEN Puregene Cell Kit. The steps for this method are outlined below.
Note: this method is also suitable for mouse cell line DNA.
We also offer multiple mammalian sample extraction protocols, which you can use for other sample types.
Harvest and pellet 5 x 10^6 cells by centrifugation at 300 x g for 3 minutes. If any liquid remains associated with the pellet, spin down the cells again and aspirate the remaining supernatant.
Add 200 µl of 1x PBS to the pelleted cells and centrifuge at 300 x g for 3 minutes. Aspirate and discard the supernatant.
Add 2 ml of Cell Lysis Solution to the washed cell pellet. Using a wide-bore pipette tip, resuspend the cells and transfer them to a 15 ml Falcon tube. If clumps of cells remain, gently invert the tube.
Incubate the sample at 37°C for 30 minutes.
Add 700 µl of the Protein Precipitation Solution to the lysed cells and mix by vortexing for three pulses of 5 seconds.
Centrifuge the sample at 2000 x g for 5 minutes.
Transfer the supernatant to a new tube and add 2.5 ml of room temperature isopropanol. Discard the pellet.
Mix by gently inverting the tube 50 times.
Spool the DNA using an inoculation loop or disposable tweezers.
Dip the spooled DNA in an Eppendorf tube containing 70% cold ethanol.
Remove the inoculation loop or tweezers with the spooled DNA from the ethanol tube, and allow it to air-dry for a few seconds.
Dip the DNA in a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube containing 250 µl TE (1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) and allow the DNA to gently dislodge from the loop/tweezers.
Incubate the tube for 2 hours at 50°C, occasionally pipette mixing the whole volume tube contents (200 μl) with a wide-bore pipette tip.
Note: The DNA pellet may take some time to solubilise. Please ensure the solution is homogenous before quantifying.
Optional: Alternatively, this incubation can be performed at room temperature overnight.
Quantify 1 µl of each eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer.
Take forward 2 µg of extracted gDNA, for each sample, into the fragmentation of extracted DNA stage of the protcol.
5. DNA fragmentation
材料
- 2 µg 上一步骤中提取得到的 gDNA
耗材
- g-TUBE™(Covaris,520079)
- TE 缓冲液(10 mM Tris-HCl、1 mM EDTA、pH 8.0)(Fisher scientific,10224683)
- Qubit dsDNA BR Assay(双链DNA宽范围检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher ,Q32850)
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- Eppendorf 5424 离心机(或等效器材)
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P2 移液枪和枪头
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
可选仪器
- Agilent Femto Pulse 系统(或用于读长质控的等效仪器)
Fragmentation of extracted DNA using Covaris g-TUBE:
To prepare fragmented gDNA for the library prep protocol, mechanical fragmentation is performed using a g-TUBE (Covaris) to shear DNA to a fragment length of approximately 6kb.
Prepare the DNA in TE buffer:
- Ensure you have 2 µg of extracted gDNA from the sample extraction, and transfer this into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube.
- Adjust the volume to 50 μl with TE buffer.
- Mix thoroughly by pipetting up and down.
- Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Load the 50 µl of the sample into the top of the g-TUBE. Screw the cap firmly and centrifuge at 11,000 rpm (~11,300 RCF) for 30 seconds.
After centrifugation, spin the tube again at 11,000 rpm (~11,300 RCF) for 10 seconds to ensure complete passage of all gDNA through the constriction.
Visually inspect to confirm the entire sample has passed through the upper chamber to the lower chamber of the g-TUBE.
Invert the g-TUBE and spin it again at the same speed and duration as above: 11,000rpm (~11,300 RCF) for 30 seconds.
Repeat the centrifugation at 11,000 rpm (~11,300 RCF) for 10 seconds to ensure thorough passage of all gDNA through the constriction.
Unscrew the tube body, leaving the screw-cap containing the sample. Retrieve the sample from the g-TUBE screw-cap and transfer it into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendof tube.
Quantify 1 µl of the fragmented gDNA using the Qubit dsDNA Broad Range Assay Kit.
Sample concentration after g-TUBE shearing, is expected to be within the range of 25–35 ng/µl.
The fragmented gDNA should also be assessed using Femto-Pulse (Agilent) to evaluate the size and quality of the DNA.

Example DNA fragment distribution after g-TUBE fragmentation, analysed using an Agilent 165 kb Femto-Pulse Assay. Note the single prominent peak ~6 kb.
Take forward 2 µg of fragmented gDNA in 48 µl, for each sample, into the library preparation section of the protcol.
6. DNA repair and end-prep
材料
- gDNA in 48 μl nuclease-free water
- AMPure XP 磁珠(AXP)
耗材
- NEBNext®配套模块v2(NEB,E7672S或E7672L)中的NEBNext® FFPE DNA修复混合液
- NEBNext®配套模块v2(NEB,E7672S或E7672L)中的NEBNext® Ultra II 末端修复酶混合物
- NEBNext®配套模块v2(NEB,E7672S或E7672L)中的NEBNext® FFPE DNA修复缓冲液v2
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- 新制备的 80% 乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- 0.2 ml 薄壁PCR管
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher,Q32851)
仪器
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- 热循环仪
- 迷你离心机
- Hula混匀仪(低速旋转式混匀仪)
- 磁力架
- 盛有冰的冰桶
可选仪器
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
Check your flow cell.
We recommend performing a flow cell check before starting your library prep to ensure you have a flow cell with enough pores for a good sequencing run.
See the flow cell check document for more information.
We recommend using the NEBNext® Companion Module v2 for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7672S or E7672L), which contains all the NEB reagents needed for use with the Ligation Sequencing Kit.
The previous version, NEBNext® Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180S or E7180L) is also compatible, but the recommended v2 module offers more efficient dA-tailing and ligation.
Prepare the NEB reagents in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions, and place on ice.
For optimal performance, NEB recommend the following:
Thaw all reagents on ice.
Flick and/or invert the reagent tubes to ensure they are well mixed.
Note: Do not vortex the FFPE DNA Repair Mix or Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix.Always spin down tubes before opening for the first time each day.
Vortex the FFPE DNA Repair Buffer v2 to ensure it is well mixed.
Note: This buffer may contain a white precipitate. If this occurs, allow the mixture to come to room temperature and pipette the buffer several times to break up the precipitate, followed by a quick vortex to mix.The FFPE DNA Repair Buffer v2 may have a yellow tinge and is fine to use if yellow.
Prepare the DNA in nuclease-free water.
- Transfer 2 μg of the fragmented DNA into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube
- Adjust the volume to 48 μl with nuclease-free water
- Mix thoroughly by flicking the tube
- Spin down briefly in a microfuge
In a 0.2 ml thin-walled PCR tube, mix the following:
Between each addition, pipette mix 10-20 times.
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| DNA from the previous step | 48 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Buffer v2 | 7 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 2 µl |
| Ultra II End-prep Enzyme Mix | 3 µl |
| Total | 60 µl |
Ensure the components are thoroughly mixed by pipetting, and spin down.
Using a thermal cycler, incubate at 20°C for 5 minutes and 65°C for 5 minutes and hold at 4°C.
AMPure XP bead clean-up
It is recommended that the repaired/end-prepped DNA sample is subjected to the following clean-up with AMPure XP beads. This clean-up can be omitted for simplicity and to reduce library preparation time. However, it has been observed that omission of this clean-up can: reduce subsequent adapter ligation efficiency, increase the prevalence of chimeric reads, and lead to an increase in pores being unavailable for sequencing. If omitting the clean-up step, proceed to the next section.
Resuspend the AMPure XP Beads (AXP) by vortexing.
Transfer the DNA sample to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Add 60 µl of resuspended the AMPure XP Beads (AXP) to the end-prep reaction and mix by flicking the tube.
Incubate on a Hula mixer (rotator mixer) for 5 minutes at room temperature.
Prepare 500 μl of fresh 80% ethanol in nuclease-free water.
Spin down the sample and pellet on a magnet until supernatant is clear and colourless. Keep the tube on the magnet, and pipette off the supernatant.
Keep the tube on the magnet and wash the beads with 200 µl of freshly prepared 80% ethanol without disturbing the pellet. Remove the ethanol using a pipette and discard.
Repeat the previous step.
Spin down and place the tube back on the magnet. Pipette off any residual ethanol. Allow to dry for ~30 seconds, but do not dry the pellet to the point of cracking.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack and resuspend the pellet in 61 µl nuclease-free water by gently pipetting up and down or by flicking the tube. Incubate for 2 minutes at room temperature.
Pellet the beads on a magnet until the eluate is clear and colourless, for at least 1 minute.
Remove and retain 61 µl of eluate into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Quantify 1 µl of eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer.
Take forward the repaired and end-prepped DNA into the adapter ligation step. However, at this point it is also possible to store the sample at 4°C overnight.
7. Adapter ligation and clean-up
材料
- 连接接头(LA)
- 连接测序试剂盒内的连接缓冲液(LNB)
- 长片段缓冲液(LFB)
- AMPure XP 磁珠(AXP)
- 洗脱缓冲液(EB)
耗材
- 耐盐T4 DNA连接酶(NEB, M0467)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Qubit™ dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(ThermoFisher,Q32851)
仪器
- 磁力架
- 迷你离心机
- 涡旋混匀仪
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
We recommend using the Salt-T4® DNA Ligase (NEB, M0467).
Salt-T4® DNA Ligase (NEB, M0467) can be bought separately or is provided in the NEBNext® Companion Module v2 for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7672S or E7672L).
The Quick T4 DNA Ligase (NEB, E6057) available in the previous version NEBNext® Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies® Ligation Sequencing (NEB, E7180S or E7180L) is also compatible, but the new recommended reagent offers more efficient and ligation.
Although third-party ligase products may be supplied with their own buffer, the ligation efficiency of the Ligation Adapter (LA) is higher when using the Ligation Buffer (LNB) supplied in the Ligation Sequencing Kit.
Spin down the Ligation Adapter (LA) and Salt-T4® DNA Ligase, and place on ice.
Thaw Ligation Buffer (LNB) at room temperature, spin down and mix by pipetting. Due to viscosity, vortexing this buffer is ineffective. Place on ice immediately after thawing and mixing.
Thaw the Elution Buffer (EB) at room temperature and mix by vortexing. Then spin down and place on ice.
Thaw the Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) at room temperature and mix by vortexing. Then spin down and place on ice.
In a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, mix in the following order:
Between each addition, pipette mix 10-20 times.
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| DNA sample from the previous step | 60 µl |
| Ligation Adapter (LA) | 5 µl |
| Ligation Buffer (LNB) | 25 µl |
| Salt-T4® DNA Ligase | 10 µl |
| Total | 100 µl |
Ensure the components are thoroughly mixed by pipetting, and spin down.
Incubate the reaction for 10 minutes at room temperature.
If you have omitted the AMPure purification step after DNA repair and end-prep, do not incubate the reaction for longer than 10 minutes.
Resuspend the AMPure XP Beads (AXP) by vortexing.
Add 40 µl of resuspended AMPure XP Beads (AXP) to the reaction and mix by flicking the tube.
Incubate on a Hula mixer (rotator mixer) for 5 minutes at room temperature.
Spin down the sample and pellet on a magnet. Keep the tube on the magnet, and pipette off the supernatant when clear and colourless.
Wash the beads by adding 250 μl Long Fragment Buffer (LFB). Flick the beads to resuspend, spin down, then return the tube to the magnetic rack and allow the beads to pellet. Remove the supernatant using a pipette and discard.
Repeat the previous step.
Spin down and place the tube back on the magnet. Pipette off any residual supernatant. Allow to dry for ~30 seconds, but do not dry the pellet to the point of cracking.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack and resuspend the pellet in 38 µl Elution Buffer (EB). Spin down and incubate for 10 minutes at room temperature. For high molecular weight DNA, incubating at 37°C can improve the recovery of long fragments.
Pellet the beads on a magnet until the eluate is clear and colourless, for at least 1 minute.
Remove and retain 38 µl of eluate containing the DNA library into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Dispose of the pelleted beads
Quantify 1 µl of eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer.
We recommend loading 150 ng of the final prepared library onto the flow cell.
The loading recommendation has been optimised for the sample preparation and sequencing output of this protocol. The loading quantity differs from the standard Kit 14 ligation protocols due to a higher input requirement in the adaptive sampling.
Take forward 12 µl of the final prepared library.
Store the remaining prepared library for flow cell washing and reloading.
The prepared library is used for loading into the flow cell. Store the library on ice or at 4°C until ready to load.
Library storage recommendations
We recommend storing libraries in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes at 4°C for short term storage or repeated use, for example, reloading flow cells between washes. For single use and long-term storage of more than 3 months, we recommend storing libraries at -80°C in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes.
Sequencing and flow cell washes
Sequence the sample for a total of 96 hours, with two flow cell washes. After ~24 hours, or when the pore count drops to 40-50% of the initial number at the start of the experiment, pause the run and wash the flow cell using the Flow Cell Wash Kit. Load another 12 µl of eluted DNA library and sequence for another ~24 hours. After this, repeat the flow cell wash for the second time, load another 12 µl of eluted DNA library and sequence for the remaining ~48 hours.
Note: To avoid pore numbers falling too low before performing the flow cell wash, it may be necessary to pause the experiment overnight.
8. Priming and loading the MinION and GridION Flow Cell
材料
- 12 µl of adapted DNA library (from previous step)
- 测序芯片冲洗液(FCF)
- 测序芯片系绳(FCT)
- 文库溶液(LIS)
- 文库颗粒(LIB)
- 测序缓冲液(SB)
耗材
- MinION/GridION测序芯片
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
仪器
- GridION device
- MinION 及GridION 测序芯片遮光片
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
Please note, this kit is only compatible with R10.4.1 flow cells (FLO-MIN114).
Take the flow cell out of the fridge and leave it at room temperature for 20 minutes. This will improve visibility of the array during priming and sample loading.
Priming and loading a flow cell
We recommend all new users watch the 'Priming and loading your flow cell' video before your first run.
Thaw the Sequencing Buffer (SB), Library Beads (LIB) or Library Solution (LIS, if using), Flow Cell Tether (FCT) and Flow Cell Flush (FCF) at room temperature before mixing by vortexing. Then spin down and store on ice.
To prepare the flow cell priming mix, combine the Flow Cell Flush (FCF) and Flow Cell Tether (FCT), as directed below. Mix by pipetting at room temperature.
In a suitable tube for the number of flow cells, combine the following reagents:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Flow Cell Flush (FCF) | 1,170 µl |
| Flow Cell Tether (FCT) | 30 µl |
| Total volume | 1,200 µl |
Open the GridION device lid and slide the flow cell under the clip. Press down firmly on the priming port cover to ensure correct thermal and electrical contact.
Complete a flow cell check to assess the number of pores available before loading the library.
This step can be omitted if the flow cell has been checked previously.
See the flow cell check document for more information.
Slide the flow cell priming port cover clockwise to open the priming port.
Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back a small volume to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl
- Insert the tip into the priming port
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, to draw back 20-30 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip
Note: Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the priming port across the sensor array.
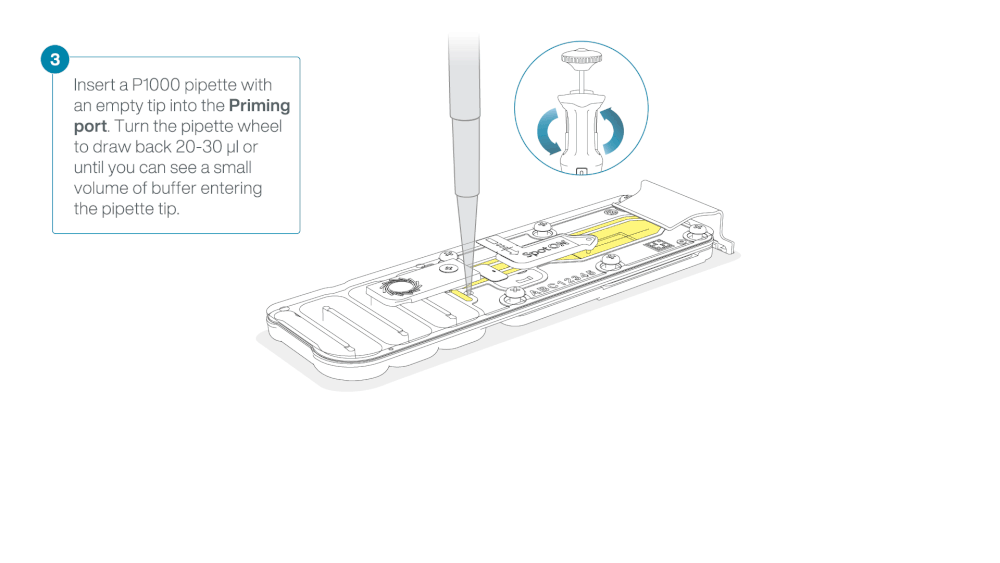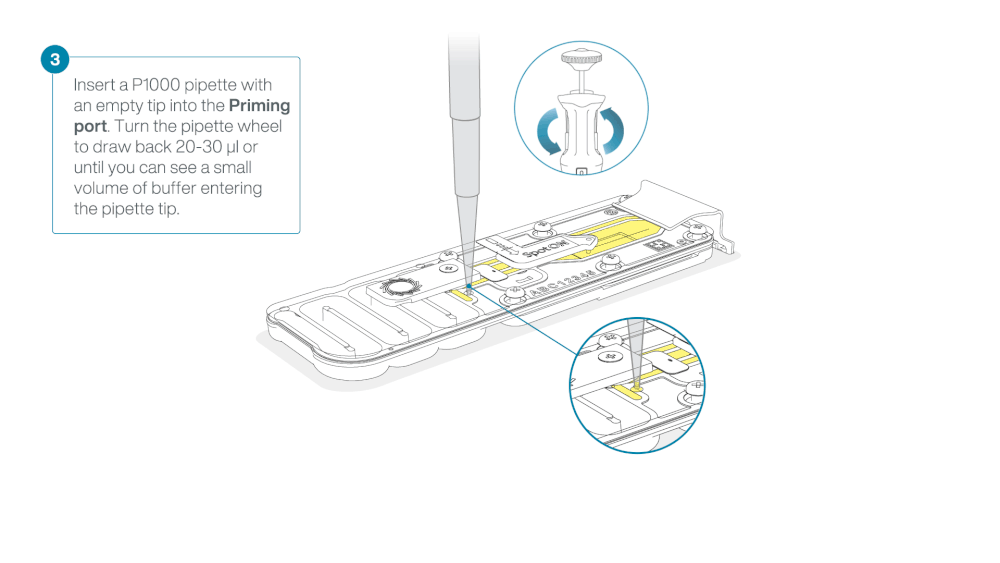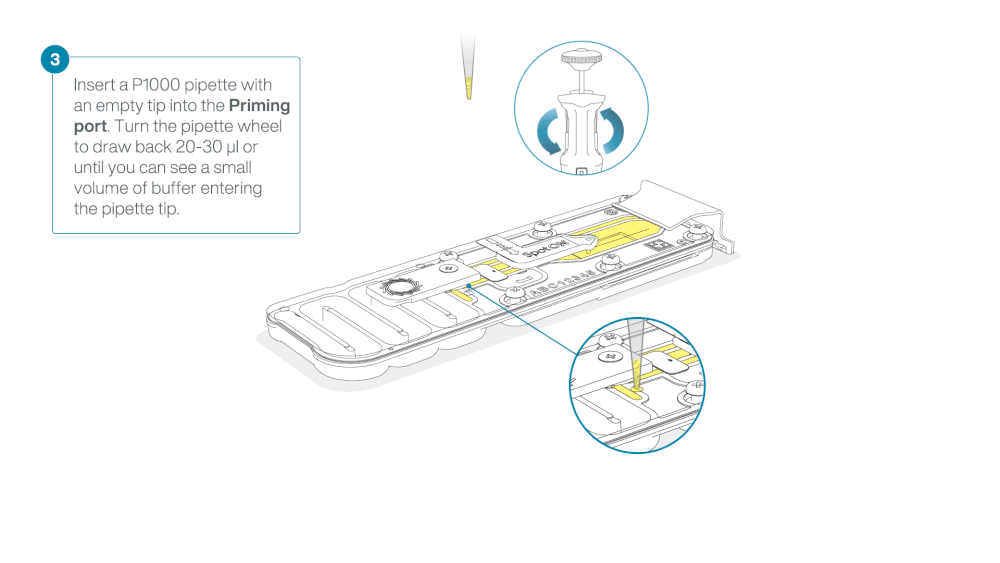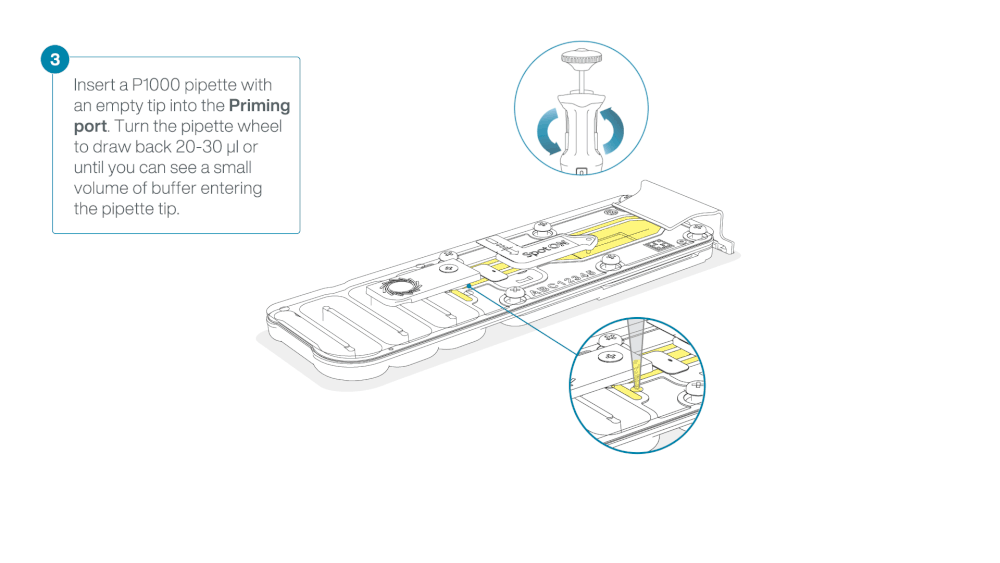
Load 800 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the priming port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait for five minutes. During this time, prepare the library for loading by following the steps below.

Thoroughly mix the contents of the Library Beads (LIB) by pipetting.
The Library Beads (LIB) tube contains a suspension of beads. These beads settle very quickly. It is vital that they are mixed immediately before use.
We recommend using the Library Beads (LIB) for most sequencing experiments. However, the Library Solution (LIS) is available for more viscous libraries.
In a new 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, prepare the library for loading as follows:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer (SB) | 37.5 µl |
| Library Beads (LIB) mixed immediately before use, or Library Solution (LIS), if using | 25.5 µl |
| DNA library | 12 µl |
| Total | 75 µl |
Complete the flow cell priming:
- Gently lift the SpotON sample port cover to make the SpotON sample port accessible.
- Load 200 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell priming port (not the SpotON sample port), avoiding the introduction of air bubbles.

Mix the prepared library gently by pipetting up and down just prior to loading.
Add 75 μl of the prepared library to the flow cell via the SpotON sample port in a dropwise fashion. Ensure each drop flows into the port before adding the next.

Gently replace the SpotON sample port cover, making sure the bung enters the SpotON port and close the priming port.

For optimal sequencing output, install the light shield on your flow cell as soon as the library has been loaded.
We recommend leaving the light shield on the flow cell when library is loaded, including during any washing and reloading steps. The shield can be removed when the library has been removed from the flow cell.
Place the light shield onto the flow cell, as follows:
Carefully place the leading edge of the light shield against the clip. Note: Do not force the light shield underneath the clip.
Gently lower the light shield onto the flow cell. The light shield should sit around the SpotON cover, covering the entire top section of the flow cell.

The MinION Flow Cell Light Shield is not secured to the flow cell therefore, careful handling is required after installation.
Close the device lid and set up a sequencing run on MinKNOW.
For instructions on setting up your sequencing run please visit the Data acquisition and basecalling section of this protocol.
Reminder: For this protocol, we recommend washing and reloading your flow cell with fresh library to maintain high data acquisition after ~24 hours of sequencing.
Follow the instructions in the Washing and reloading a MinION and GridION Flow Cell section of this protocol.
9. Washing and reloading a MinION and GridION Flow Cell
材料
- 12 µl of adapted DNA library (from previous step)
- 测序芯片清洗剂盒(EXP-WSH004)
- Flow cell priming reagents available in your sequencing kit or in the following kits:
- 测序辅助扩展包 V14(EXP-AUX003)
- Flow Cell Priming Kit V14 (EXP-FLP004)
耗材
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- 涡旋混匀仪
We recommend washing and reloading the flow cell after ~24 hours of sequencing.
We recommend washing and reloading the flow cell after ~24 hours of sequencing. For this method, the flow cell is washed after ~24 hours of sequencing to restore pores to ensure efficient data acquisition. After an additional 24 hours of sequencing, the flow cell is washed and reloaded a second time. For this reason, enough library was generated for 3 flow cell loads in the adapter ligation step of the protocol.
- This washing procedure aims to remove most of the initial library and unblock the pores to prepare the flow cell for the loading of a subsequent library.
- Data acquisition in MinKNOW should be paused during the wash procedure and library loading.
- After the flow cell has been washed, the next library can be loaded.
You can navigate to the Pore Activity or the Pore Scan Results plot to see pore availability.
Place the tube of Wash Mix (WMX) on ice. Do not vortex the tube.
Thaw one tube of Wash Diluent (DIL) at room temperature.
Mix the contents of Wash Diluent (DIL) thoroughly by vortexing, then spin down briefly and place on ice.
In a fresh 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, prepare the following Flow Cell Wash Mix:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Wash Mix (WMX) | 2 μl |
| Wash Diluent (DIL) | 398 μl |
| Total | 400 μl |
Mix well by pipetting, and place on ice. Do not vortex the tube.
Pause the sequencing experiment in MinKNOW, and leave the flow cell in the device.
Ensure that the flow cell priming port cover and SpotON sample port cover are closed, as indicated in the figure below.
It is vital that the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed before removing the waste buffer to prevent air from being drawn across the sensor array area, which would lead to a significant loss of sequencing channels.
Remove all fluid from the waste channel through waste port 1 using a P1000 pipette.
As both the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed, no fluid should leave the sensor array area.

Slide the flow cell priming port cover clockwise to open.
Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back a small volume to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the flow cell priming port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer/liquid entering the pipette tip.
- Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the flow cell priming port across the sensor array.

Slowly load 200 µl of the prepared flow cell wash mix into the priming port, as follows:
- Using a P1000 pipette, take 200 µl of the flow cell wash mix
- Insert the pipette tip into the priming port, ensuring there are no bubbles in the tip
- Slowly twist the pipette wheel down to load the flow cell (if possible with your pipette) or push down the plunger very slowly, leaving a small volume of buffer in the pipette tip.
- Set a timer for a 5 minute incubation.

Once the 5 minute incubation is complete, carefully load the remaining 200 µl of the prepared flow cell wash mix into the priming port, as follows:
- Using a P1000 pipette, take the remaining 200 µl of the flow cell wash mix
- Insert the pipette tip into the priming port, ensuring there are no bubbles in the tip
- Slowly twist the pipette wheel down to load the flow cell (if possible with your pipette) or push down the plunger very slowly, leaving a small volume of buffer in the pipette tip.

Close the priming port and wait for 1 hour.
Ensure that the flow cell priming port cover and SpotON sample port cover are closed, as indicated in the figure below.
It is vital that the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed before removing the waste buffer to prevent air from being drawn across the sensor array area, which would lead to a significant loss of sequencing channels.
Remove all fluid from the waste channel through waste port 1 using a P1000 pipette.
As both the flow cell priming port and SpotON sample port are closed, no fluid should leave the sensor array area.

The buffers used in this process are incompatible with conducting a Flow Cell Check step prior to loading the subsequent library.
Thaw the Sequencing Buffer (SB), Library Beads (LIB) or Library Solution (LIS, if using), Flow Cell Tether (FCT) and Flow Cell Flush (FCF) at room temperature, before mixing by vortexing. Then spin down before storing on ice.
To prepare the flow cell priming mix, combine the Flow Cell Flush (FCF) and Flow Cell Tether (FCT), as directed below. Mix by pipetting at room temperature.
In a suitable tube for the number of flow cells, combine the following reagents:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Flow Cell Flush (FCF) | 1,170 µl |
| Flow Cell Tether (FCT) | 30 µl |
| Total volume | 1,200 µl |
Slide the priming port cover clockwise to open the priming port.
Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back a small volume to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the flow cell priming port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer/liquid entering the pipette tip.
- Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the flow cell priming port across the sensor array.

Load 800 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the priming port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait for five minutes. During this time, prepare the library for loading by following the steps below.

Thoroughly mix the contents of the Library Beads (LIB) by pipetting.
The Library Beads (LIB) tube contains a suspension of beads. These beads settle very quickly. It is vital that they are mixed immediately before use.
We recommend using the Library Beads (LIB) for most sequencing experiments. However, the Library Solution (LIS) is available for more viscous libraries.
In a new 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, prepare the library for loading as follows:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer (SB) | 37.5 µl |
| Library Beads (LIB) mixed immediately before use, or Library Solution (LIS), if using | 25.5 µl |
| DNA library | 12 µl |
| Total | 75 µl |
Complete the flow cell priming:
- Gently lift the SpotON sample port cover to make the SpotON sample port accessible.
- Load 200 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the priming port (not the SpotON sample port), avoiding the introduction of air bubbles.

Mix the prepared library gently by pipetting up and down just prior to loading.
Add 75 μl of the prepared library to the flow cell via the SpotON sample port in a dropwise fashion. Ensure each drop flows into the port before adding the next.

Gently replace the SpotON sample port cover, making sure the bung enters the SpotON port, close the priming port and close the GridION device lid.
Select "Resume" to continue the sequencing run.
Repeat the "Washing and reloading a MinION Flow Cell" step up to two times, for a total of three library loads to maximise data acquisition.
10. Data acquisition and basecalling
Overview of nanopore data analysis
For a full overview of nanopore data analysis, which includes options for basecalling and post-basecalling analysis, please refer to the Data Analysis document.
How to start sequencing
The sequencing device control and data acquisition are carried out by the MinKNOW software. Please ensure MinKNOW is installed on your computer. Further instructions for setting up your sequencing run can be found in the MinKNOW protocol.
Sequencing settings for the reduced representation methylation sequencing (RRMS) protocol:
Select the Ligation Sequencing Kit (SQK-LSK114) in kit selection.
Turn basecalling OFF.
Note: Basecalling will be carried out post-sequencing in the downstream analysis section of the protocol.Turn Adaptive Sampling ON, and select Enrich.
Input the human reference file for alignment and the .bed file for enumerating regions (check online catalogue for the human RRMS .bed file).Set the run duration for a minimum of 96 hours.
Set up your desired output parameters.
To ensure the downstream analysis functions correctly, we recommend keeping the default options of the output file format (.POD5).Click Start to begin the sequencing run.
11. Downstream analysis
Software versions
See below the software versions used in this guide. Please note, newer versions of the software may not be compatible with commands shown in this guide.
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| dorado | v0.7.3 |
| modkit | v0.2.8 |
| wf-human-variation | v2.3.0 |
| mosdepth | v0.3.8 |
Basecalling
Dorado stand-alone can be used for basecalling using the Dorado basecaller. Open a terminal and enter the following commands:
dorado basecaller hac,5mCG_5hmCG \
--secondary “no” -Y \
--reference {reference_fasta} {input_pod5_folder} \
| samtools view -e '[qs] >= {qscore_filter}' \
--output {out_pass_bam} \
--unoutput {out_fail_bam}
Notes:
We recommend using the high accuracy model (hac) for RRMS sequencing runs. However, if using the super accurate model (sup), ensure you are utilising the correct model in the above command.
Alignment can be performed while basecalling by providing a reference FASTA file. The recommended human reference file can be downloaded.
Secondary alignments are discarded by using “--secondary no” and -Y option is enabled, to allow soft-clipping supplementary alignments.
We recommend setting the qscore filter to 10.
Please note, GPU compute is needed to perform basecalling with Dorado, more information on how to run Dorado can be found in the github repository.
Coverage analysis:
RRMS target bed file can be downloaded from the AS catalogue available here.
Mosdepth is used to check coverage on target regions for the barcodes of interest:
mosdepth -x -t 8 -n -b {target_bed} {out_prefix} {input_pass_bam}
Modification calling
Human variation pipeline is used to aggregate modifications per genomic positions using modkit.
The workflow is available in the following repository: wf-human-variation github.
The documentation can be found in the following space: wf-human-variation EPI2ME page
For most RRMS runs we recommend running the following command:
nextflow run https://github.com/epi2me-labs/wf-human-variation \
-profile singularity \
--mod \
--bam <bam> \
--bed RRMS_human_hg38.bed \
--ref GCA_000001405.15_GRCh38_no_alt_analysis_set.fasta \
--sample_name <sample> --out_dir <output_dir>
(Optional) For haplotype-specific methylation:
If haplotype-specific methylation is required, you can provide options “--snp –phased“ to aggregate modifications identified on each of the haplotypes (i.e. one bedmethyl file for each of the haplotypes will be generated):
nextflow run https://github.com/epi2me-labs/wf-human-variation \
-profile singularity \
--mod --snp --phased \
--bam <bam> \
--bed RRMS_human_hg38.bed \
--ref GCA_000001405.15_GRCh38_no_alt_analysis_set.fasta \
--sample_name <sample> --out_dir <output_dir>
Note: For this specific analysis, a sample coverage of >30X is recommended.
Differentially methylated regions detection:
For detection of differentially methylated regions across different samples “modkit dmr” can be used.
For more information check the modkit documentation.
Visualisation:
The BAM file(s) generated by Dorado contains canonical bases as well as per-read modifications stored in MM and ML BAM tags. To visualise the per-read modification calls, IGV can be used to load the BAM file and set "colour reads as" to “base modification 2-color (all)”.
If phasing was performed using wf-human-variation pipeline, the haplotagged BAM file can be uploaded in IGV and alignments can be grouped by haplotype using the IGV option “group by” and selecting “phase”.
Per-position methylation frequencies can also be visualised in IGV by using BIGWIG format. For this, modkit is used to generate BEDGRAPH files using the following command:
modkit pileup --cpg --combine-strands --bedgraph \
--threads 10 --prefix {out_prefix} \
--ref {reference_fasta} \
{out_folder} {input_pass_bam}
Please note, a different bedgraph file will be created for each of the modifications present, in this case 5mC and 5hmC.
Next, bedGraphToBigWig is used to generate bigwig files which can be uploaded together with your BAM file in IGV:
bedtools sort -i {out_folder}/{prefix}_m_CG0_combined.bedgraph | cut -f 1-4 > {out_folder}/{prefix}_m_CG0_combined_sort.bedgraph
bedGraphToBigWig {out_folder}/{prefix}_m_CG0_combined_sort.bedgraph {reference_chrSize} {out_mod_bed_agg_filt_bigwig}
Benchmarking results:
For information about benchmarking the performance of RRMS for human samples, please see our RRMS performance document.
12. Flow cell reuse and returns
We do not recommend washing and reusing your flow cells for this method.
Due to the extended sequencing time, and the multiple flow cell washes and library reloads, we do not recommend re-using the flow cells used in this method.
Re-using these flow cells for subsequent sequencing experiments may result in insufficient data generation for analysis.
Follow the returns procedure to send back flow cells to Oxford Nanopore for recycling.
Instructions for returning flow cells can be found here.
If you encounter issues or have questions about your sequencing experiment, please refer to the Troubleshooting Guide that can be found in the online version of this protocol.
13. Issues during DNA extraction and library preparation
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Low sample quality
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low DNA purity (Nanodrop reading for DNA OD 260/280 is <1.8 and OD 260/230 is <2.0–2.2) | The DNA extraction method does not provide the required purity | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants document. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. Consider performing an additional SPRI clean-up step. |
Low DNA recovery after AMPure bead clean-up
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low recovery | DNA loss due to a lower than intended AMPure beads-to-sample ratio | 1. AMPure beads settle quickly, so ensure they are well resuspended before adding them to the sample. 2. When the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio is lower than 0.4:1, DNA fragments of any size will be lost during the clean-up. |
| Low recovery | DNA fragments are shorter than expected | The lower the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio, the more stringent the selection against short fragments. Please always determine the input DNA length on an agarose gel (or other gel electrophoresis methods) and then calculate the appropriate amount of AMPure beads to use. 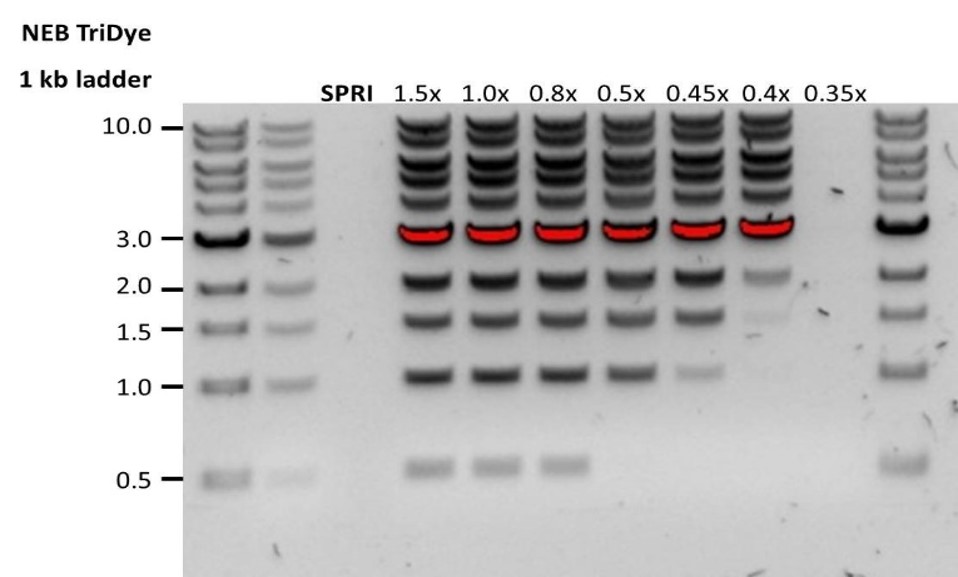 |
| Low recovery after end-prep | The wash step used ethanol <70% | DNA will be eluted from the beads when using ethanol <70%. Make sure to use the correct percentage. |
14. Issues during the sequencing run
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Fewer pores at the start of sequencing than after Flow Cell Check
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | An air bubble was introduced into the nanopore array | After the Flow Cell Check it is essential to remove any air bubbles near the priming port before priming the flow cell. If not removed, the air bubble can travel to the nanopore array and irreversibly damage the nanopores that have been exposed to air. The best practice to prevent this from happening is demonstrated in this video. |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | The flow cell is not correctly inserted into the device | Stop the sequencing run, remove the flow cell from the sequencing device and insert it again, checking that the flow cell is firmly seated in the device and that it has reached the target temperature. If applicable, try a different position on the device (GridION/PromethION). |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | Contaminations in the library damaged or blocked the pores | The pore count during the Flow Cell Check is performed using the QC DNA molecules present in the flow cell storage buffer. At the start of sequencing, the library itself is used to estimate the number of active pores. Because of this, variability of about 10% in the number of pores is expected. A significantly lower pore count reported at the start of sequencing can be due to contaminants in the library that have damaged the membranes or blocked the pores. Alternative DNA/RNA extraction or purification methods may be needed to improve the purity of the input material. The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
MinKNOW script failed
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Script failed" | Restart the computer and then restart MinKNOW. If the issue persists, please collect the MinKNOW log files and contact Technical Support. If you do not have another sequencing device available, we recommend storing the flow cell and the loaded library at 4°C and contact Technical Support for further storage guidance. |
Pore occupancy below 40%
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Pore occupancy <40% | Not enough library was loaded on the flow cell | Ensure you load the recommended amount of good quality library in the relevant library prep protocol onto your flow cell. Please quantify the library before loading and calculate mols using tools like the Promega Biomath Calculator, choosing "dsDNA: µg to pmol" |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and sequencing adapters did not ligate to the DNA | Make sure to use the NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (E6056) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Buffer (LNB, provided in the sequencing kit) at the sequencing adapter ligation step, and use the correct amount of each reagent. A Lambda control library can be prepared to test the integrity of the third-party reagents. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and ethanol was used instead of LFB or SFB at the wash step after sequencing adapter ligation | Ethanol can denature the motor protein on the sequencing adapters. Make sure the LFB or SFB buffer was used after ligation of sequencing adapters. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | No tether on the flow cell | Tethers are adding during flow cell priming (FLT/FCT tube). Make sure FLT/FCT was added to FB/FCF before priming. |
Shorter than expected read length
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Shorter than expected read length | Unwanted fragmentation of DNA sample | Read length reflects input DNA fragment length. Input DNA can be fragmented during extraction and library prep. 1. Please review the Extraction Methods in the Nanopore Community for best practice for extraction. 2. Visualise the input DNA fragment length distribution on an agarose gel before proceeding to the library prep. 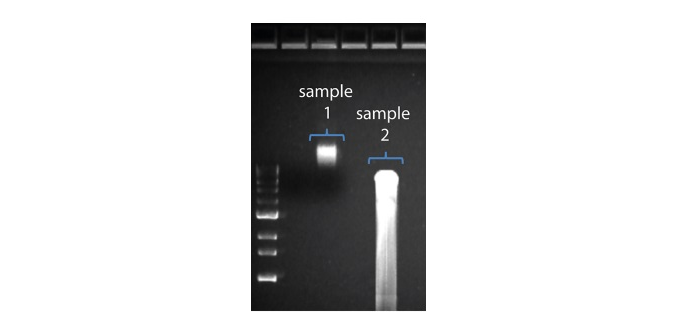 In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented. In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented.3. During library prep, avoid pipetting and vortexing when mixing reagents. Flicking or inverting the tube is sufficient. |
Large proportion of unavailable pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
Large proportion of unavailable pores (shown as blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot) 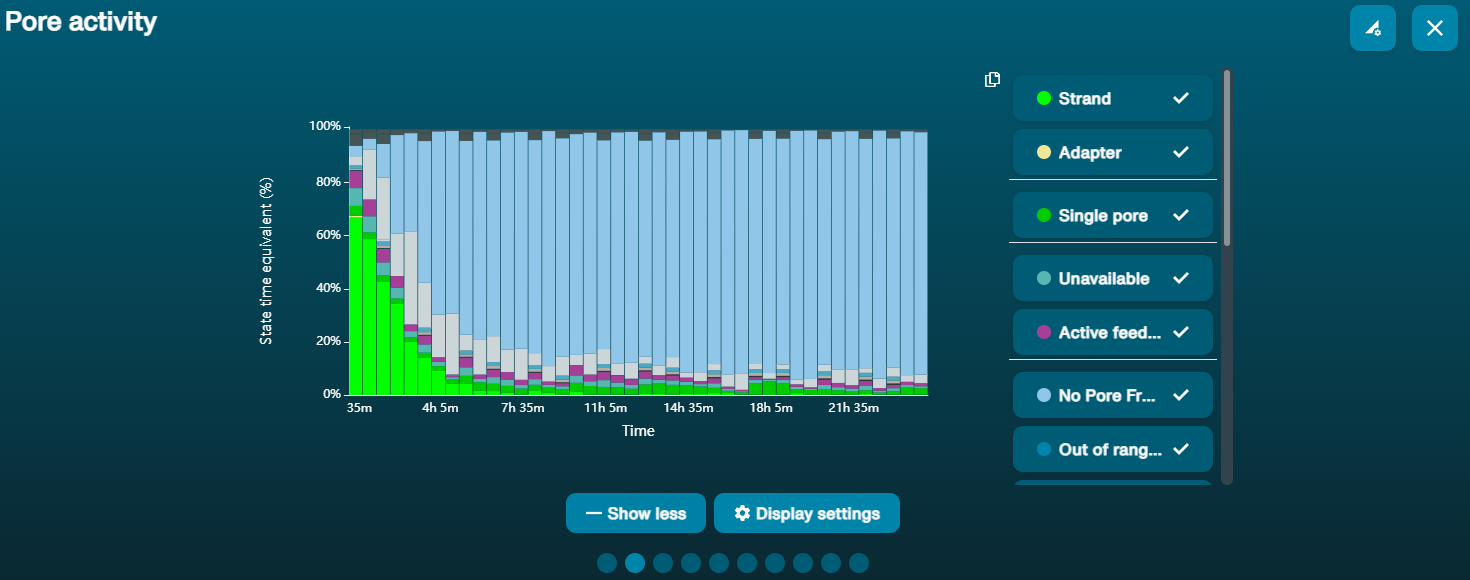 The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. | Contaminants are present in the sample | Some contaminants can be cleared from the pores by the unblocking function built into MinKNOW. If this is successful, the pore status will change to "sequencing pore". If the portion of unavailable pores stays large or increases: 1. A nuclease flush using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) can be performed, or 2. Run several cycles of PCR to try and dilute any contaminants that may be causing problems. |
Large proportion of inactive pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores (shown as light blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot. Pores or membranes are irreversibly damaged) | Air bubbles have been introduced into the flow cell | Air bubbles introduced through flow cell priming and library loading can irreversibly damage the pores. Watch the Priming and loading your flow cell video for best practice. |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Certain compounds co-purified with DNA | Known compounds include polysaccharides. 1. Clean-up using the QIAGEN PowerClean Pro kit. 2. Perform a whole genome amplification with the original gDNA sample using the QIAGEN REPLI-g kit. |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Contaminants are present in the sample | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run | For Kit 9 chemistry (e.g. SQK-LSK109), fast fuel consumption is typically seen when the flow cell is overloaded with library (please see the appropriate protocol for your DNA library to see the recommendation). | Add more fuel to the flow cell by following the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol. In future experiments, load lower amounts of library to the flow cell. |
Temperature fluctuation
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature fluctuation | The flow cell has lost contact with the device | Check that there is a heat pad covering the metal plate on the back of the flow cell. Re-insert the flow cell and press it down to make sure the connector pins are firmly in contact with the device. If the problem persists, please contact Technical Services. |
Failed to reach target temperature
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Failed to reach target temperature" | The instrument was placed in a location that is colder than normal room temperature, or a location with poor ventilation (which leads to the flow cells overheating) | MinKNOW has a default timeframe for the flow cell to reach the target temperature. Once the timeframe is exceeded, an error message will appear and the sequencing experiment will continue. However, sequencing at an incorrect temperature may lead to a decrease in throughput and lower q-scores. Please adjust the location of the sequencing device to ensure that it is placed at room temperature with good ventilation, then re-start the process in MinKNOW. |







