Ligation sequencing gDNA - automated Hamilton NGS STAR 96 with Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-MLK111.96-XL) (MLKH_9145_v111_revM_15Dec2021)
PromethION: Protocol
V MLKH_9145_v111_revM_15Dec2021
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
Automated library preparation
- 4. Prepare the deck
- 5. Pre-processes
- 6. Complete automated library preparation
- 7. Select steps in the automated library preparation
- 8. Priming and loading multiple flow cells on a PromethION
Sequencing and data analysis
Troubleshooting
1. Overview of the protocol
This is a Legacy product
This kit is soon to be discontinued and we recommend all customers to upgrade to the latest chemistry for their relevant kit which is available on the Store. If customers require further support for any ongoing critical experiments using a Legacy product, please contact Customer Support via email: support@nanoporetech.com. For further information on please see the product update page.
Automated Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL features:
This kit is recommended for users who:
- Would like to process multiple samples simultaneously, either with a multichannel pipette or a liquid handling robot
- Want to optimise their sequencing experiment for output
- Wish to low-plex samples for Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
- Need a PCR-free method of multiplexing to preserve additional information, such as base modifications
- Require control over read length
- Would like to utilise upstream processes, such as size selection or whole genome amplification
To use this automated method, method installation and training is required by Oxford Nanopore Technologies. For more information, please contact your local representative.
Introduction to the automated Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL protocol
The Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-MLK111.96-XL) is designed to enable low-plex sequencing. Oxford Nanopore Technologies has written an internal script which enables the liquid handling robot to carry out native barcoding of genomic DNA using this sequencing kit. We currently allow the multiplexing of two samples on a flow cell or three samples on two flow cells.
To efficiently load multiple PromethION Flow Cells, we recommend using the Loading multiple PromethION Flow Cells protocol as a guideline.
Steps in the sequencing workflow: Prepare for your experiment You will need to:
- Extract your DNA, and check its length, quantity and purity. The quality checks performed during the protocol are essential in ensuring experimental success.
- Ensure you have your sequencing kit, the correct equipment and third-party reagents
- Download the software for acquiring and analysing your data
- Check your flow cell to ensure it has enough pores for a good sequencing run
Automated library preparation
You will need to:
Off-deck:
- Prepare your sample input plate off-deck
On-deck:
- Repair the DNA, and prepare the DNA ends for adapter attachment
- Ligate Native barcodes supplied in the kit to the DNA ends
- Ligate sequencing adapters supplied in the kit to the DNA ends
Off-deck:
- Prime the flow cell, and load your DNA library into the flow cell
Sequencing
You will need to:
- Start a sequencing run using the MinKNOW software, which will collect raw data from the device and convert it into basecalled reads
- Demultiplex barcoded reads in MinKNOW or the Guppy basecalling
- Start the EPI2ME software and select a workflow for further analysis (this step is optional)
We do not recommend mixing barcoded libraries with non-barcoded libraries prior to sequencing.
Timings
96 samples with 2 samples per flow cell
| Process | Minutes per step |
|---|---|
| End Repair and Adenylation | 56 |
| Native Barcode Ligation | 75 |
| Adapter Ligation | 95 |
| Total | 226 |
96 samples with 3 samples across 2 flow cells
| Process | Minutes per step |
|---|---|
| End Repair and Adenylation | 56 |
| Native Barcode Ligation | 73 |
| Adapter Ligation | 78 |
| Total | 207 |
Optional fragmentation and size selection
By default, the protocol contains no DNA fragmentation step, however in some cases it may be advantageous to fragment your sample. For example, when working with lower amounts of input gDNA (100 ng – 500 ng), fragmentation will increase the number of DNA molecules and therefore increase throughput. Instructions are available in the DNA Fragmentation section of Extraction methods.
Additionally, we offer several options for size-selecting your DNA sample to enrich for long fragments - instructions are available in the Size Selection section of Extraction methods.
Compatibility of this protocol
This protocol should only be used in combination with:
- Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-MLK111.96-XL)
- R9.4.1 flow cells (FLO-PRO002)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
2. Equipment and consumables
Material
- Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-MLK111.96-XL)
- 1200 ng gDNA per sample
Consumibles
- NEB Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix (NEB, M0367)
- NEBNext® Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (NEB, B6058)
- NEBNext FFPE Repair Mix (NEB M6630)
- NEBNext Ultra II End Repair/dA-tailing Module (NEB E7546)
- NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (NEB E6056)
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Etanol al 80 % recién preparado con agua sin nucleasas
- Kit Qubit dsDNA HS (Invitrogen Q32851)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- 2.0 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Microesferas Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter™, A63881)
- Qubit™ Assay Tubes (Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton PCR ComfortLid (Cat# 814300)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
- Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid (Cat# 56694-01)
Instrumental
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- Ice bucket with ice
- Timer
- Qubit fluorometer (or equivalent)
- Hamilton NGS STAR 96 (NGS STAR with Multi-Probe Head 96)
- Hamilton On-Deck Thermal Cycler (ODTC)
- Hamilton MTP landscape carrier (cat# 182365)
- Hamilton Ambion magnet adapter (cat# 10107866)
Equipo opcional
- Bioanalizador Agilent (o equivalente)
- Centrifugadora Eppendorf 5424 (o equivalente)
For this protocol, you will need 1200 ng gDNA per sample for R9.4.1 flow cells.
We recommend using 80 ng/µl per sample with a minimum of 15 µl per well when preparing the input plate.
Input DNA
How to QC your input DNA
It is important that the input DNA meets the quantity and quality requirements. Using too little or too much DNA, or DNA of poor quality (e.g. highly fragmented or containing RNA or chemical contaminants) can affect your library preparation.
For instructions on how to perform quality control of your DNA sample, please read the Input DNA/RNA QC protocol.
Chemical contaminants
Depending on how the DNA is extracted from the raw sample, certain chemical contaminants may remain in the purified DNA, which can affect library preparation efficiency and sequencing quality. Read more about contaminants on the Contaminants page of the Community.
Input workfile
Input workfiles are required prior to running this protocol on the Hamilton NGS STAR 96.
Oxford Nanopore Technologies will provide a template of the input workfiles in an Excel file.
- In the DATA tab of the file, there will be the template for the library preparation data
- In the INFO tab, there will be the template for the identification data
Library preparation data example: 
Identification data example: 
Output workfiles will be generated. Below are examples of the output workfiles after a run through of the method.
Library preparation data example: 
Identification data example: 
Hamilton NGS STAR 96 and deck layout
This method has been tested and validated using the Hamilton NGS STAR 96 (with Multi-Probe Head 96), Hamilton Ambion magnet adapter, Hamilton MTP landscape carrier and Hamilton On-Deck Thermal Cycler (ODTC).
Deck layout
The deck layout has been updated from the standard layout. Please see the "Prepare the deck" step of this protocol for more details.

Data tracking
For data tracking purposes, we have included the option to add user ID before starting any process. This can be filled using any method the user prefers.
We recommend using barcode stickers to track the input and output plates for data tracking. These can be tracked on the workfile and entered on the UI alongside the reagent lot barcodes when prompted.
Convenient reagent kits are available on request from NEB for the Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL.
This will contain the appropriate NEB reagents and the required volumes for the protocol on the Hamilton NGS STAR 96. For more information from NEB, please see "Find Products for Nanopore Sequencing".
Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-MLK111.96-XL) contents
| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | Number of vials | Fill volume per vial (µl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adapter Mix II T | AMII T | Green | 1 | 320 |
| Sequencing Buffer II | SBII | Red | 4 | 1,500 |
| Loading Beads II | LBII | Pink | 4 | 1,500 |
| Loading Solution | LS | White cap, pink sticker | 4 | 1,500 |
| EDTA | EDTA | Clear | 1 | 700 |
| Elution Buffer | EB | 15 ml bottle | 1 | 10,000 |
| Long Fragment Buffer | LFB | 30 ml bottle | 1 | 20,000 |
| Flush Buffer XL | FB | 30 ml bottle | 6 | 15,500 |
| Flush Tether | FLT | White cap, purple sticker | 2 | 1,600 |
| Native Barcodes | NB01-96 | N/a | 1 plate | 8 µl per well |
Consumables and equipment quantities:
| Consumables | No. of consumables for all conditions |
|---|---|
| Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 960 |
| Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 960 |
| Hamilton 1000 µ CO-RE tips with filter | 96 |
| Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-well PCR Plate | 8 |
This protocol requires the tip decks to be completely filled before starting a run. Partially filled tip decks will cause an error with the liquid handling robot.
We recommend using Hamilton tips for efficient liquid handling.
Reagent quantities:
Note: Volumes for x48 samples will be available soon.
Full method
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 80 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
| Adapter Mix F (AMII F) | 1 vial |
| NEBNext FFRE DNA Repair Buffer | 130 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 90 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 130 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 120 µl |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | 590 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 310 µl |
__Multiple steps combined:__ ### End Repair and Adenylation step to Native Barcode Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 80 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| NEBNext FFRE DNA Repair Buffer | 130 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 90 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 130 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 120 µl |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
### Native Barcode Ligation step to Adapter Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 40 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
| Adapter Mix F (AMII F) | 1 vial |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | 590 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 310 µl |
__Individual steps:__ #### End Repair step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 40 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| NEBNext FFRE DNA Repair Buffer | 130 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 90 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 130 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 120 µl |
### Native Barcode Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 40 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
#### Adapter Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | 590 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 310 µl |
Native barcode sequences
| Component | Forward sequence | Reverse sequence |
|---|---|---|
| NB01 | CACAAAGACACCGACAACTTTCTT | AAGAAAGTTGTCGGTGTCTTTGTG |
| NB02 | ACAGACGACTACAAACGGAATCGA | TCGATTCCGTTTGTAGTCGTCTGT |
| NB03 | CCTGGTAACTGGGACACAAGACTC | GAGTCTTGTGTCCCAGTTACCAGG |
| NB04 | TAGGGAAACACGATAGAATCCGAA | TTCGGATTCTATCGTGTTTCCCTA |
| NB05 | AAGGTTACACAAACCCTGGACAAG | CTTGTCCAGGGTTTGTGTAACCTT |
| NB06 | GACTACTTTCTGCCTTTGCGAGAA | TTCTCGCAAAGGCAGAAAGTAGTC |
| NB07 | AAGGATTCATTCCCACGGTAACAC | GTGTTACCGTGGGAATGAATCCTT |
| NB08 | ACGTAACTTGGTTTGTTCCCTGAA | TTCAGGGAACAAACCAAGTTACGT |
| NB09 | AACCAAGACTCGCTGTGCCTAGTT | AACTAGGCACAGCGAGTCTTGGTT |
| NB10 | GAGAGGACAAAGGTTTCAACGCTT | AAGCGTTGAAACCTTTGTCCTCTC |
| NB11 | TCCATTCCCTCCGATAGATGAAAC | GTTTCATCTATCGGAGGGAATGGA |
| NB12 | TCCGATTCTGCTTCTTTCTACCTG | CAGGTAGAAAGAAGCAGAATCGGA |
| NB13 | AGAACGACTTCCATACTCGTGTGA | TCACACGAGTATGGAAGTCGTTCT |
| NB14 | AACGAGTCTCTTGGGACCCATAGA | TCTATGGGTCCCAAGAGACTCGTT |
| NB15 | AGGTCTACCTCGCTAACACCACTG | CAGTGGTGTTAGCGAGGTAGACCT |
| NB16 | CGTCAACTGACAGTGGTTCGTACT | AGTACGAACCACTGTCAGTTGACG |
| NB17 | ACCCTCCAGGAAAGTACCTCTGAT | ATCAGAGGTACTTTCCTGGAGGGT |
| NB18 | CCAAACCCAACAACCTAGATAGGC | GCCTATCTAGGTTGTTGGGTTTGG |
| NB19 | GTTCCTCGTGCAGTGTCAAGAGAT | ATCTCTTGACACTGCACGAGGAAC |
| NB20 | TTGCGTCCTGTTACGAGAACTCAT | ATGAGTTCTCGTAACAGGACGCAA |
| NB21 | GAGCCTCTCATTGTCCGTTCTCTA | TAGAGAACGGACAATGAGAGGCTC |
| NB22 | ACCACTGCCATGTATCAAAGTACG | CGTACTTTGATACATGGCAGTGGT |
| NB23 | CTTACTACCCAGTGAACCTCCTCG | CGAGGAGGTTCACTGGGTAGTAAG |
| NB24 | GCATAGTTCTGCATGATGGGTTAG | CTAACCCATCATGCAGAACTATGC |
| NB25 | GTAAGTTGGGTATGCAACGCAATG | CATTGCGTTGCATACCCAACTTAC |
| NB26 | CATACAGCGACTACGCATTCTCAT | ATGAGAATGCGTAGTCGCTGTATG |
| NB27 | CGACGGTTAGATTCACCTCTTACA | TGTAAGAGGTGAATCTAACCGTCG |
| NB28 | TGAAACCTAAGAAGGCACCGTATC | GATACGGTGCCTTCTTAGGTTTCA |
| NB29 | CTAGACACCTTGGGTTGACAGACC | GGTCTGTCAACCCAAGGTGTCTAG |
| NB30 | TCAGTGAGGATCTACTTCGACCCA | TGGGTCGAAGTAGATCCTCACTGA |
| NB31 | TGCGTACAGCAATCAGTTACATTG | CAATGTAACTGATTGCTGTACGCA |
| NB32 | CCAGTAGAAGTCCGACAACGTCAT | ATGACGTTGTCGGACTTCTACTGG |
| NB33 | CAGACTTGGTACGGTTGGGTAACT | AGTTACCCAACCGTACCAAGTCTG |
| NB34 | GGACGAAGAACTCAAGTCAAAGGC | GCCTTTGACTTGAGTTCTTCGTCC |
| NB35 | CTACTTACGAAGCTGAGGGACTGC | GCAGTCCCTCAGCTTCGTAAGTAG |
| NB36 | ATGTCCCAGTTAGAGGAGGAAACA | TGTTTCCTCCTCTAACTGGGACAT |
| NB37 | GCTTGCGATTGATGCTTAGTATCA | TGATACTAAGCATCAATCGCAAGC |
| NB38 | ACCACAGGAGGACGATACAGAGAA | TTCTCTGTATCGTCCTCCTGTGGT |
| NB39 | CCACAGTGTCAACTAGAGCCTCTC | GAGAGGCTCTAGTTGACACTGTGG |
| NB40 | TAGTTTGGATGACCAAGGATAGCC | GGCTATCCTTGGTCATCCAAACTA |
| NB41 | GGAGTTCGTCCAGAGAAGTACACG | CGTGTACTTCTCTGGACGAACTCC |
| NB42 | CTACGTGTAAGGCATACCTGCCAG | CTGGCAGGTATGCCTTACACGTAG |
| NB43 | CTTTCGTTGTTGACTCGACGGTAG | CTACCGTCGAGTCAACAACGAAAG |
| NB44 | AGTAGAAAGGGTTCCTTCCCACTC | GAGTGGGAAGGAACCCTTTCTACT |
| NB45 | GATCCAACAGAGATGCCTTCAGTG | CACTGAAGGCATCTCTGTTGGATC |
| NB46 | GCTGTGTTCCACTTCATTCTCCTG | CAGGAGAATGAAGTGGAACACAGC |
| NB47 | GTGCAACTTTCCCACAGGTAGTTC | GAACTACCTGTGGGAAAGTTGCAC |
| NB48 | CATCTGGAACGTGGTACACCTGTA | TACAGGTGTACCACGTTCCAGATG |
| NB49 | ACTGGTGCAGCTTTGAACATCTAG | CTAGATGTTCAAAGCTGCACCAGT |
| NB50 | ATGGACTTTGGTAACTTCCTGCGT | ACGCAGGAAGTTACCAAAGTCCAT |
| NB51 | GTTGAATGAGCCTACTGGGTCCTC | GAGGACCCAGTAGGCTCATTCAAC |
| NB52 | TGAGAGACAAGATTGTTCGTGGAC | GTCCACGAACAATCTTGTCTCTCA |
| NB53 | AGATTCAGACCGTCTCATGCAAAG | CTTTGCATGAGACGGTCTGAATCT |
| NB54 | CAAGAGCTTTGACTAAGGAGCATG | CATGCTCCTTAGTCAAAGCTCTTG |
| NB55 | TGGAAGATGAGACCCTGATCTACG | CGTAGATCAGGGTCTCATCTTCCA |
| NB56 | TCACTACTCAACAGGTGGCATGAA | TTCATGCCACCTGTTGAGTAGTGA |
| NB57 | GCTAGGTCAATCTCCTTCGGAAGT | ACTTCCGAAGGAGATTGACCTAGC |
| NB58 | CAGGTTACTCCTCCGTGAGTCTGA | TCAGACTCACGGAGGAGTAACCTG |
| NB59 | TCAATCAAGAAGGGAAAGCAAGGT | ACCTTGCTTTCCCTTCTTGATTGA |
| NB60 | CATGTTCAACCAAGGCTTCTATGG | CCATAGAAGCCTTGGTTGAACATG |
| NB61 | AGAGGGTACTATGTGCCTCAGCAC | GTGCTGAGGCACATAGTACCCTCT |
| NB62 | CACCCACACTTACTTCAGGACGTA | TACGTCCTGAAGTAAGTGTGGGTG |
| NB63 | TTCTGAAGTTCCTGGGTCTTGAAC | GTTCAAGACCCAGGAACTTCAGAA |
| NB64 | GACAGACACCGTTCATCGACTTTC | GAAAGTCGATGAACGGTGTCTGTC |
| NB65 | TTCTCAGTCTTCCTCCAGACAAGG | CCTTGTCTGGAGGAAGACTGAGAA |
| NB66 | CCGATCCTTGTGGCTTCTAACTTC | GAAGTTAGAAGCCACAAGGATCGG |
| NB67 | GTTTGTCATACTCGTGTGCTCACC | GGTGAGCACACGAGTATGACAAAC |
| NB68 | GAATCTAAGCAAACACGAAGGTGG | CCACCTTCGTGTTTGCTTAGATTC |
| NB69 | TACAGTCCGAGCCTCATGTGATCT | AGATCACATGAGGCTCGGACTGTA |
| NB70 | ACCGAGATCCTACGAATGGAGTGT | ACACTCCATTCGTAGGATCTCGGT |
| NB71 | CCTGGGAGCATCAGGTAGTAACAG | CTGTTACTACCTGATGCTCCCAGG |
| NB72 | TAGCTGACTGTCTTCCATACCGAC | GTCGGTATGGAAGACAGTCAGCTA |
| NB73 | AAGAAACAGGATGACAGAACCCTC | GAGGGTTCTGTCATCCTGTTTCTT |
| NB74 | TACAAGCATCCCAACACTTCCACT | AGTGGAAGTGTTGGGATGCTTGTA |
| NB75 | GACCATTGTGATGAACCCTGTTGT | ACAACAGGGTTCATCACAATGGTC |
| NB76 | ATGCTTGTTACATCAACCCTGGAC | GTCCAGGGTTGATGTAACAAGCAT |
| NB77 | CGACCTGTTTCTCAGGGATACAAC | GTTGTATCCCTGAGAAACAGGTCG |
| NB78 | AACAACCGAACCTTTGAATCAGAA | TTCTGATTCAAAGGTTCGGTTGTT |
| NB79 | TCTCGGAGATAGTTCTCACTGCTG | CAGCAGTGAGAACTATCTCCGAGA |
| NB80 | CGGATGAACATAGGATAGCGATTC | GAATCGCTATCCTATGTTCATCCG |
| NB81 | CCTCATCTTGTGAAGTTGTTTCGG | CCGAAACAACTTCACAAGATGAGG |
| NB82 | ACGGTATGTCGAGTTCCAGGACTA | TAGTCCTGGAACTCGACATACCGT |
| NB83 | TGGCTTGATCTAGGTAAGGTCGAA | TTCGACCTTACCTAGATCAAGCCA |
| NB84 | GTAGTGGACCTAGAACCTGTGCCA | TGGCACAGGTTCTAGGTCCACTAC |
| NB85 | AACGGAGGAGTTAGTTGGATGATC | GATCATCCAACTAACTCCTCCGTT |
| NB86 | AGGTGATCCCAACAAGCGTAAGTA | TACTTACGCTTGTTGGGATCACCT |
| NB87 | TACATGCTCCTGTTGTTAGGGAGG | CCTCCCTAACAACAGGAGCATGTA |
| NB88 | TCTTCTACTACCGATCCGAAGCAG | CTGCTTCGGATCGGTAGTAGAAGA |
| NB89 | ACAGCATCAATGTTTGGCTAGTTG | CAACTAGCCAAACATTGATGCTGT |
| NB90 | GATGTAGAGGGTACGGTTTGAGGC | GCCTCAAACCGTACCCTCTACATC |
| NB91 | GGCTCCATAGGAACTCACGCTACT | AGTAGCGTGAGTTCCTATGGAGCC |
| NB92 | TTGTGAGTGGAAAGATACAGGACC | GGTCCTGTATCTTTCCACTCACAA |
| NB93 | AGTTTCCATCACTTCAGACTTGGG | CCCAAGTCTGAAGTGATGGAAACT |
| NB94 | GATTGTCCTCAAACTGCCACCTAC | GTAGGTGGCAGTTTGAGGACAATC |
| NB95 | CCTGTCTGGAAGAAGAATGGACTT | AAGTCCATTCTTCTTCCAGACAGG |
| NB96 | CTGAACGGTCATAGAGTCCACCAT | ATGGTGGACTCTATGACCGTTCAG |
3. Computer requirements and software
PromethION 24/48 IT requirements
The PromethION device contains all the hardware required to control up to 24 (for the P24 model) or 48 (for the P48 model) sequencing experiments and acquire the data. The device is further enhanced with high performance GPU technology for real-time basecalling. Read more in the PromethION IT requirements document.
PromethION 2 Solo IT requirements
The PromethION 2 (P2) Solo is a device which directly connects into a GridION Mk1 or a stand-alone computer that meets the miminum specifications for real-time data streaming and analysis. Up to two PromethION flow cells can be can be run and each is independently addressable, meaning experiments can be run concurrently or individually. For information on the computer IT requirements, please see the PromethION 2 Solo IT requirements document.
Software for nanopore sequencing
MinKNOW
The MinKNOW software controls the nanopore sequencing device, collects sequencing data and basecalls in real time. You will be using MinKNOW for every sequencing experiment to sequence, basecall and demultiplex if your samples were barcoded.
For instructions on how to run the MinKNOW software, please refer to the MinKNOW protocol.
EPI2ME (optional)
The EPI2ME cloud-based platform performs further analysis of basecalled data, for example alignment to the Lambda genome, barcoding, or taxonomic classification. You will use the EPI2ME platform only if you would like further analysis of your data post-basecalling.
For instructions on how to create an EPI2ME account and install the EPI2ME Desktop Agent, please refer to this link.
Check your flow cell
We highly recommend that you check the number of pores in your flow cell prior to starting a sequencing experiment. This should be done within 12 weeks of purchasing for MinION/GridION/PromethION or within four weeks of purchasing Flongle Flow Cells. Oxford Nanopore Technologies will replace any flow cell with fewer than the number of pores in the table below, when the result is reported within two days of performing the flow cell check, and when the storage recommendations have been followed. To do the flow cell check, please follow the instructions in the Flow Cell Check document.
| Flow cell | Minimum number of active pores covered by warranty |
|---|---|
| Flongle Flow Cell | 50 |
| MinION/GridION Flow Cell | 800 |
| PromethION Flow Cell | 5000 |
4. Prepare the deck
Consumibles
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton PCR ComfortLid (Cat# 814300)
- Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid (Cat# 56694-01)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
Instrumental
- Hamilton NGS STAR 96 (NGS STAR with Multi-Probe Head 96)
- Hamilton Ambion magnet adapter (cat# 10107866)
- Hamilton MTP landscape carrier (cat# 182365)
- Hamilton On-Deck Thermal Cycler (ODTC)
Extra equipment required for the deck layout
- Hamilton MTP landscape carrier (cat # 182365)
- Hamilton Ambion magnet adapter (cat # 10107866)
Deck layout change
The deck layout has been updated from the standard NGS STAR 96 layout to improve the efficiency of the robot completing the protocol.
The changes will take approximately 3 minutes.
Final deck layout: 
Remove the plate stacker and two tube racks.
Plate stacker

Two tube racks

Place both tubes racks in positions 1 and 2.
Positions 1 and 2 are indicated by the arrow below:

Shift the four tip carriers to the left, starting from position 3.
Place the two trough carriers next to the 300 µl tips and insert the new carrier in the remaining slot on deck.

Place the Ambion magnet adapter on the Ambion magnet.

Once the deck is correctly set up, the robot can be prepared to run the automation protocol.
5. Pre-processes
Material
- 1200 ng gDNA per sample
- Long Fragment Buffer (LFB)
Consumibles
- Etanol al 80 % recién preparado con agua sin nucleasas
- Agua sin nucleasas (p. ej., ThermoFisher, AM9937)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
Users have the option to use pre-process to complete automated upstream methods to prepare their samples.

Click "Pre-processes" to open the following dialogue and select the method you would like to complete and click "Ok".

Enter the number of samples to process and click "Ok".

Enter the input volume of your samples to process and click "Ok".

Dialogue boxes will follow on the UI to illustrate how to correctly load the deck.
Once the process is complete, you will be returned to the method selection page, enabling the user to either start the library preparation process or another pre-process.
6. Complete automated library preparation
Material
- 1200 ng gDNA per sample
- Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-MLK111.96-XL)
Consumibles
- NEB Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix (NEB, M0367)
- NEBNext® Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (NEB, B6058)
- NEBNext FFPE Repair Mix (NEB M6630)
- NEBNext® Ultra™ II End Repair/dA-Tailing Module (E7546)
- NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (NEB E6056)
- Agua sin nucleasas (p. ej., ThermoFisher, AM9937)
- Etanol al 80 % recién preparado con agua sin nucleasas
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Microesferas Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter™, A63881)
- Qubit™ Assay Tubes (Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Kit Qubit dsDNA HS (ThermoFisher, Q32851)
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton PCR ComfortLid (Cat# 814300)
- Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid (Cat# 56694-01)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
Instrumental
- P100 pipette and tips
- Qubit fluorometer (or equivalent)
- Ice bucket with ice
Consumables and equipment quantities:
| Consumables | No. of consumables for all conditions |
|---|---|
| Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 960 |
| Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 960 |
| Hamilton 1000 µ CO-RE tips with filter | 96 |
| Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-well PCR Plate | 8 |
Note: We recommend using Hamilton tips for efficient liquid handling.
It is required to use full decks of tips to run this protocol for all conditions. Partially used tip decks will cause an error with the liquid handling robot.
Reagent quantities:
Full method
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 80 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
| Adapter Mix F (AMII F) | 1 vial |
| NEBNext FFRE DNA Repair Buffer | 130 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 90 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 130 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 120 µl |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | 590 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 310 µl |
Prepare the reagents as follows and store on ice.
| Reagent | 1. Thaw at room temperature | 2. Briefly spin down |
|---|---|---|
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Buffer | ✓ | - |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | ✓ | Note: Do no vortex |
| NEBNext Ultra II End-prep repair buffer | ✓ | - |
| NEBNext Ultra II End-prep enzyme mix | ✓ | Note: Do not vortex |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | ✓ | - |
| NEBNext Quick T4 DNA Ligase | ✓ | Note: Do not vortex |
| Native barcode plate | ✓ | ✓ |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | ✓ | - |
| Adapter Mix II F (AMII-F) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | ✓ | - |
Do not vortex the NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix, NEBNext Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix or NEBNext Quick T4 DNA Ligase.
In a clean hard shell PCR plate, prepare the sample input plate as follows:
- Dispense 1200 ng DNA into each sample well. Note: We suggest aliquoting your DNA at 80 ng/µl per sample.
- Make up the volume of each well containing DNA samples to at least 15 µl.
Switch on the Hamilton NGS STAR 96 robot and open the method from the desktop shortcut.
When the method is loaded, click 'Start'.
To find further information, click 'About MLK111.96-XL' to view the automation section of the Community in the default web browser.

Click 'MLK111.96-XL' to proceed to the method parameter selection.

Before starting, a user ID can be entered for traceability purposes.
Note: Any format of user ID can be used.

Choose the number of samples to process from the drop-down menu, your multiplexing method and the file directory to the input workfile. Click 'Ok' to continue.
Current multiplexing options include either:
- 2 samples on 1 flow cell
- 3 samples on 2 flow cells
__Note:__ When completing the full method, only 96 or 48 samples are available as options.

An error message will appear if an invalid number of samples is selected for your choosen multiplexing method.

Enter the barcode of the input plate containing the samples and the output plate which will contain the prepared DNA libraries.

If the entered barcodes do not match what is stored in the workfile, the correct barcodes will need to be re-entered.

Select where to start on a previously used native barcode plate when using 48 or fewer samples.

Click "Full method" to run the entire automated protocol.
Note: We recommend using the "Select steps" option if sample quantification is required after each step. Please see the "Select steps in the automated library preparation" step.

For traceability purposes, the lot barcodes of the reagents can be entered for the Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) reagents, the native barcode plate (NBD) and the NEB reagents used.

Once settings for the run have been selected, there will be a series of dialogues illustrating how to load the deck depending on steps selected.
Note: The following screenshots are an example of performing the full method for x96 samples.
Ensure all seals are removed from plates before loading the deck.
Place the Hamilton Comfort PCR lid on the PCR lid position.

Ensure the tip decks are full before running the protocol.
Load 50 µl tips as indicated on screen.

Load 300 µl tips as indicated on screen.

Mix by inverting and prepare the following reagents in troughs:
For X96 samples:
| Reagent | Volume per trough | No. of troughs | Total volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freshly prepared 80% ethanol | 40 ml | 2 | 80 ml |
| Agencourt AMPure XP beads | 15 ml | 1 | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml | 1 | 10 ml |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles | 1 | 2 bottles |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle | 1 | 1 bottle |
Ensure to use the correct volume of AMPure XP beads and they are well mixed before use by vortexing.
Adding a larger volume of AMPure XP beads may be detrimental to the run because the robot is programmed to mix a defined volume which may not sufficiently mix if a significantly higher volume than recommended is used.
Load the reagent troughs as indicated on screen.

Ensure the foil seal is removed from the native barcode plate foil seal.
Load the native barcode plate, 3 fresh PCR plates and the input plate containing the DNA samples.

Load 1000 µl tips as indicated on screen and ensure the magnet is in place with the adapter for PCR plates.

Load the CPAC module as indicated on screen with the reagent tubes before loading on deck.

| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | FFPE DNA Repair Buffer | Empty 1.5 ml Eppendorf LoBind tube | Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | AMII-F |
| B | FFPE DNA Repair Mix | - | EDTA | Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer |
| C | Ultra II End-prep Buffer | - | - | Quick T4 DNA Ligase |
| D | Ultra II End-prep Enzyme Mix | - | - | Empty 1.5 ml Eppendorf LoBind tube |
Volumes required:
| Reagent | x96 samples 3 samples across 2 flow cells | x96 samples 2 samples per flow cell | x48 samples 3 samples across 2 flow cells | x48 samples 2 samples per flow cell |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair buffer | 130 µl | 130 µl | 72.45 µl | 72.45 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Enzyme Mix | 90 µl | 90 µl | 41.4 µl | 41.4 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 130 µl | 130 µl | 72.45 µl | 72.45 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 120 µl | 120 µl | 62.1 µl | 62.1 µl |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl | 1210 µl | 738 µl | 738 µl |
| AMII T | 270.4 µl | 310 µl | 138 µl | 202.8 µl |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | 540.8 µl | 590 µl | 276 µl | 405.6 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 270.4 µl | 310 µl | 138 µl | 202.8 µl |
Once the deck is correctly loaded, click 'Begin method' to start with the parameters selected before loading.

During the thermal cycle step for Step 1: End repair and adenylation thermal cycling reaction, the user will be prompted to remove the input plate with the input samples and to load 3 fresh PCR plates as indicated on screen.
This dialogue will prompt the user to remove their input plate: 

Quantify 1 µl of eluted sample using a Qubit fluorometer.
We recommend loading >10 fmols of this final prepared library onto the flow cell for R9.4.1 flow cells.
The prepared library is used for loading into the flow cell. Store the library on ice or at 4°C until ready to load.
Library storage recommendations
We recommend storing libraries in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes at 4°C for short-term storage or repeated use, for example, re-loading flow cells between washes. For single use and long-term storage of more than 3 months, we recommend storing libraries at -80°C in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes.
If quantities allow, the libraries may be diluted in Elution Buffer (EB) for splittling across multiple flow cells.
7. Select steps in the automated library preparation
Material
- 1200 ng gDNA per sample
- Multiplex Ligation Sequencing Kit XL (SQK-MLK111.96-XL)
Consumibles
- NEB Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix (NEB, M0367)
- NEBNext® Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (NEB, B6058)
- NEBNext FFPE Repair Mix (NEB M6630)
- NEBNext® Ultra™ II End Repair/dA-Tailing Module (E7546)
- NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (NEB E6056)
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. Thermo Scientific, AM9937)
- Etanol al 80 % recién preparado con agua sin nucleasas
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Microesferas Agencourt AMPure XP (Beckman Coulter™, A63881)
- Qubit™ Assay Tubes (Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Kit Qubit dsDNA HS (ThermoFisher, Q32851)
- Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235948)
- Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235903)
- Hamilton 1000 µl CO-RE tips with filter (Cat# 235905)
- Hamilton PCR ComfortLid (Cat# 814300)
- Hamilton 60 ml Reagent Reservoir, Self-Standing with Lid (Cat# 56694-01)
- Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates (Cat# HSP9601)
Instrumental
- P100 pipette and tips
- Qubit fluorometer (or equivalent)
- Ice bucket with ice
Users have the option to run select steps in the protocol. We recommend quantification after End Repair for barcode balancing.
Consumables and equipment quantities:
| Consumables | No. of consumables for all conditions |
|---|---|
| Hamilton 50 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 960 |
| Hamilton 300 µl CO-RE tips with filter | 960 |
| Hamilton 1000 µ CO-RE tips with filter | 96 |
| Bio-Rad Hard-Shell® 96-well PCR Plate | 8 |
Note: We recommend using Hamilton tips for efficient liquid handling.
It is required to use full decks of tips to run this protocol for all conditions. Partially used tip decks will cause an error with the liquid handling robot.
Reagent quantities:
Note: Volumes for x48 samples will be available soon.
Multiple steps:
End Repair and Adenylation step to Native Barcode Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 80 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| NEBNext FFRE DNA Repair Buffer | 130 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 90 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 130 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 120 µl |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
### Native Barcode Ligation step to Adapter Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 40 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
| Adapter Mix F (AMII F) | 1 vial |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | 590 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 310 µl |
__Individual steps:__ ### End Repair step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 40 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| NEBNext FFRE DNA Repair Buffer | 130 µl |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | 90 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Reaction Buffer | 130 µl |
| Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix | 120 µl |
### Native Barcode Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| 80% ethanol | 40 ml |
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | 10 ml |
| Blunt/TA Ligase Master Mix | 1210 µl |
| EDTA | 1 vial |
| Native Barcode plate | 1 plate |
### Adapter Ligation step
| Reagents | x96 samples |
|---|---|
| AMPure XP Beads | 15 ml |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | 2 bottles |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | 1 bottle |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | 590 µl |
| Quick T4 DNA Ligase | 310 µl |
Prepare the reagents as follows and store on ice.
| Reagent | 1. Thaw at room temperature | 2. Briefly spin down |
|---|---|---|
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Buffer | ✓ | - |
| NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix | ✓ | Note: Do no vortex |
| NEBNext Ultra II End-prep repair buffer | ✓ | - |
| NEBNext Ultra II End-prep enzyme mix | ✓ | Note: Do not vortex |
| NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (5x) | ✓ | - |
| NEBNext Quick T4 DNA Ligase | ✓ | Note: Do not vortex |
| Native barcode plate | ✓ | ✓ |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | ✓ | - |
| Adapter Mix II F (AMII-F) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Long Fragment Buffer (LFB) | ✓ | - |
Do not vortex the NEBNext FFPE DNA Repair Mix, NEBNext Ultra II End Prep Enzyme Mix or NEBNext Quick T4 DNA Ligase.
In a clean hard shell PCR plate, prepare the sample input plate as follows:
- Dispense 1200 ng DNA into each sample well. Note: We suggest aliquoting your DNA at 80 ng/µl per sample.
- Make up the volume of each well containing DNA samples to at least 15 µl.
Switch on the Hamilton NGS STAR 96 robot and open the method from the desktop shortcut.
When the method is loaded, click 'Start'.
To find further information, click 'About MLK111.96-XL' to view the automation section of the Community in the default web browser.

Click 'MLK111.96-XL' to proceed to the method parameter selection.

Before starting, a user ID can be entered for traceability purposes.
Note: Any format of user ID can be used.

Choose the number of samples to process from the drop-down menu, your multiplexing method and the file directory to the input workfile. Click 'Ok' to continue.
Current multiplexing options include either:
- 2 samples on 1 flow cell
- 3 samples on 2 flow cells
__Note:__ When the method is carried out using selected steps, there will be more sample number options for the "Adapter Ligation" step as this is after pooling.

An error message will appear if an invalid number of samples is selected for your choosen multiplexing method.

Enter the barcode of the input plate containing the samples and the output plate which will contain the prepared DNA libraries.

If the entered barcodes do not match what is stored in the workfile, the correct barcodes will need to be re-entered.

Select where to start on a previously used native barcode plate when using 48 or fewer samples.

Click "Select steps" and click "Ok".

Choose a specific starting point from the drop-down menu on the protocol step selection dialogue.

To perform a singular step, check "Perform only selected step" and click "Ok".
To perform multiple steps, leave the check box unselected and click "Ok".
Users will only be able to select a step that canonically comes after the first step selected.

Once settings and the steps for the run have been selected, there will be a series of dialogues illustrating how to load the deck depending on the steps selected.
For an example of the dialogues illustrating how to load the deck, please see the "Complete automated library preparation" step.
The library can be either stored or loaded onto a flow cell once adapter ligation has been completed.
We recommend loading >10 fmols of this final prepared library onto the flow cell for R9.4.1 flow cells.
Library storage recommendations
We recommend storing libraries in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes at 4°C for short-term storage or repeated use, for example, re-loading flow cells between washes. For single use and long-term storage of more than 3 months, we recommend storing libraries at -80°C in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes.
If quantities allow, the libraries may be diluted in Elution Buffer (EB) for splittling across multiple flow cells.
8. Priming and loading multiple flow cells on a PromethION
Material
- Flush Buffer (FB)
- Flush Tether (FLT)
Consumibles
- Celdas de flujo PromethION
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Tubos Eppendorf DNA LoBind de 2 ml
Instrumental
- Dispositivo PromethION 24/48 o PromethION 2 Solo
- Dispositivo PromethION
- Pantalla protectora celdas de flujo PromethION
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
Thaw the Flush Tether (FLT) and Flush Buffer (FB) at room temperature before mixing the reagents by vortexing and spin down at room temperature.
Scale up reagent volumes as needed.
Ensure to prepare enough reagents for the total number of flow cells being processed and to take into account extra volume required for pipetting errors.
Each vial provides enough reagent for the preparation of 12 samples. Thaw the appropriate number of vials of each reagent.
Prepare the flow cell priming mix in a suitable vial for the number of flow cells to flush. Once combined, mix well by briefly vortexing.
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Flush Tether (FLT) | 30 µl |
| Flush Buffer (FB) | 1,170 µl |
After taking flow cells out of the fridge, wait 20 minutes before inserting the flow cell into the PromethION for the flow cell to come to room temperature. Condensation can form on the flow cell in humid environments. Inspect the gold connector pins on the top and underside of the flow cell for condensation and wipe off with a lint-free wipe if any is observed. Ensure the heat pad (black pad) is present on the underside of the flow cell.
For PromethION 2 Solo, load the flow cell(s) as follows:
Place the flow cell flat on the metal plate.
Slide the flow cell into the docking port until the gold pins or green board cannot be seen.

For the PromethION 24/48, load the flow cell(s) into the docking ports:
- Line up the flow cell with the connector horizontally and vertically before smoothly inserting into position.
- Press down firmly onto the flow cell and ensure the latch engages and clicks into place.


Insertion of the flow cells at the wrong angle can cause damage to the pins on the PromethION and affect your sequencing results. If you find the pins on a PromethION position are damaged, please contact support@nanoporetech.com for assistance.

If not already completed, perform a flow cell check on all flow cells.
Please refer to the Flow Cell Check protocol for further information.
Slide the inlet port cover clockwise to open.

Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the inlet port, draw back a small volume to remove any air bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette tip to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the inlet port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip.

Load 500 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the inlet port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait five minutes.

Complete the flow cell priming by slowly loading 500 µl of the priming mix into the inlet port.

Mix the prepared library gently by pipetting up and down just prior to loading.
Using a P1000, insert the pipette tip into the inlet port and add 150 µl of library.

Close the valve to seal the inlet port.
Install the light shield on your flow cell as soon as library has been loaded for optimal sequencing output.
We recommend leaving the light shield on the flow cell when library is loaded, including during any washing and reloading steps. The shield can be removed when the library has been removed from the flow cell.
If the light shield has been removed from the flow cell, install the light shield as follows:
- Align the inlet port cut out of the light shield with the inlet port cover on the flow cell. The leading edge of the light shield should sit above the flow cell ID.
- Firmly press the light shield around the inlet port cover. The inlet port clip will click into place underneath the inlet port cover.


Close the PromethION lid when ready to start a sequencing run on MinKNOW.
Wait a minimum of 10 minutes after loading the flow cells onto the PromethION before initiating any experiments. This will help to increase the sequencing output.
For multiple flow cell washing, use the same experiment name and identifying sample IDs for all runs to enable all flow cells to be paused simultaneously.

9. Data acquisition and basecalling
Overview of nanopore data analysis
For a full overview of nanopore data analysis, which includes options for basecalling and post-basecalling analysis, please refer to the Data Analysis document.
How to start sequencing
The sequencing device control, data acquisition and real-time basecalling are carried out by the MinKNOW software. Please ensure MinKNOW is installed on your computer or device. There are multiple options for how to carry out sequencing:
1. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using MinKNOW on a computer
Follow the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol beginning from the "Starting a sequencing run" section until the end of the "Completing a MinKNOW run" section.
2. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the MinION Mk1B/Mk1D device
Follow the instructions in the MinION Mk1B user manual or the MinION Mk1D user manual.
3. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the MinION Mk1C device
Follow the instructions in the MinION Mk1C user manual.
4. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the GridION device
Follow the instructions in the GridION user manual.
5. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the PromethION device
Follow the instructions in the PromethION user manual or the PromethION 2 Solo user manual.
6. Data acquisition using MinKNOW on a computer and basecalling at a later time using MinKNOW
Follow the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol beginning from the "Starting a sequencing run" section until the end of the "Completing a MinKNOW run" section. When setting your experiment parameters, set the Basecalling tab to OFF. After the sequencing experiment has completed, follow the instructions in the Post-run analysis section of the MinKNOW protocol.
10. Downstream analysis
Post-basecalling analysis
There are several options for further analysing your basecalled data:
1. EPI2ME platform
The EPI2ME platform is a cloud-based data analysis service developed by Metrichor Ltd., a subsidiary of Oxford Nanopore Technologies. The EPI2ME platform offers a range of analysis workflows, e.g. for metagenomic identification, barcoding, alignment, and structural variant calling. The analysis requires no additional equipment or compute power, and provides an easy-to-interpret report with the results. For instructions on how to run an analysis workflow in EPI2ME, please follow the instructions in the EPI2ME protocol, beginning at the "Starting an EPI2ME workflow" step.
2. Bioinformatics tutorials
For more in-depth data analysis, Oxford Nanopore Technologies offers a range of bioinformatics tutorials, which are available in the Bioinformatics resource section of the Community. The tutorials take the user through installing and running pre-built analysis pipelines, which generate a report with the results. The tutorials are aimed at biologists who would like to analyse data without the help of a dedicated bioinformatician, and who are comfortable using the command line.
3. Research analysis tools
Oxford Nanopore Technologies' Research division has created a number of analysis tools, which are available in the Oxford Nanopore GitHub repository. The tools are aimed at advanced users, and contain instructions for how to install and run the software. They are provided as-is, with minimal support.
4. Community-developed analysis tools
If a data analysis method for your research question is not provided in any of the resources above, please refer to the Community-developed data analysis tool library. Numerous members of the Nanopore Community have developed their own tools and pipelines for analysing nanopore sequencing data, most of which are available on GitHub. Please be aware that these tools are not supported by Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and are not guaranteed to be compatible with the latest chemistry/software configuration.
11. Flow cell reuse and returns
Material
- Kit Flow Cell Wash (EXP-WSH004)
After your sequencing experiment is complete, if you would like to reuse the flow cell, please follow the Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol and store the washed flow cell at +2°C to +8°C.
The Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol is available on the Nanopore Community.
We recommend you to wash the flow cell as soon as possible after you stop the run. However, if this is not possible, leave the flow cell on the device and wash it the next day.
Alternatively, follow the returns procedure to send the flow cell back to Oxford Nanopore.
Instructions for returning flow cells can be found here.
If you encounter issues or have questions about your sequencing experiment, please refer to the Troubleshooting Guide that can be found in the online version of this protocol.
12. Issues during DNA/RNA extraction and library preparation
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Low sample quality
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low DNA purity (Nanodrop reading for DNA OD 260/280 is <1.8 and OD 260/230 is <2.0–2.2) | The DNA extraction method does not provide the required purity | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants document. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. Consider performing an additional SPRI clean-up step. |
| Low RNA integrity (RNA integrity number <9.5 RIN, or the rRNA band is shown as a smear on the gel) | The RNA degraded during extraction | Try a different RNA extraction method. For more info on RIN, please see the RNA Integrity Number document. Further information can be found in the DNA/RNA Handling page. |
| RNA has a shorter than expected fragment length | The RNA degraded during extraction | Try a different RNA extraction method. For more info on RIN, please see the RNA Integrity Number document. Further information can be found in the DNA/RNA Handling page. We recommend working in an RNase-free environment, and to keep your lab equipment RNase-free when working with RNA. |
Low DNA recovery after AMPure bead clean-up
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low recovery | DNA loss due to a lower than intended AMPure beads-to-sample ratio | 1. AMPure beads settle quickly, so ensure they are well resuspended before adding them to the sample. 2. When the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio is lower than 0.4:1, DNA fragments of any size will be lost during the clean-up. |
| Low recovery | DNA fragments are shorter than expected | The lower the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio, the more stringent the selection against short fragments. Please always determine the input DNA length on an agarose gel (or other gel electrophoresis methods) and then calculate the appropriate amount of AMPure beads to use. 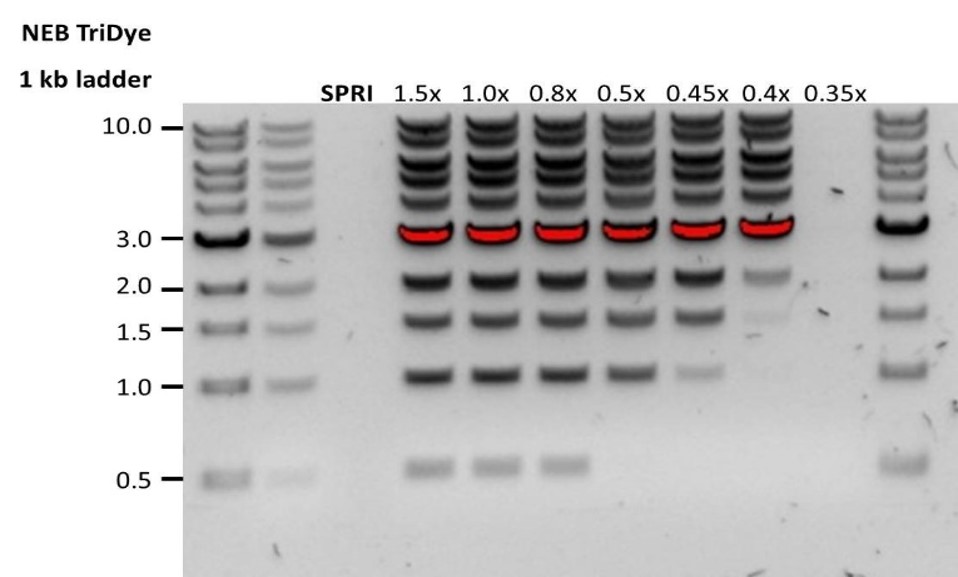 |
| Low recovery after end-prep | The wash step used ethanol <70% | DNA will be eluted from the beads when using ethanol <70%. Make sure to use the correct percentage. |
13. Issues during the sequencing run
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Fewer pores at the start of sequencing than after Flow Cell Check
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | An air bubble was introduced into the nanopore array | After the Flow Cell Check it is essential to remove any air bubbles near the priming port before priming the flow cell. If not removed, the air bubble can travel to the nanopore array and irreversibly damage the nanopores that have been exposed to air. The best practice to prevent this from happening is demonstrated in this video. |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | The flow cell is not correctly inserted into the device | Stop the sequencing run, remove the flow cell from the sequencing device and insert it again, checking that the flow cell is firmly seated in the device and that it has reached the target temperature. If applicable, try a different position on the device (GridION/PromethION). |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | Contaminations in the library damaged or blocked the pores | The pore count during the Flow Cell Check is performed using the QC DNA molecules present in the flow cell storage buffer. At the start of sequencing, the library itself is used to estimate the number of active pores. Because of this, variability of about 10% in the number of pores is expected. A significantly lower pore count reported at the start of sequencing can be due to contaminants in the library that have damaged the membranes or blocked the pores. Alternative DNA/RNA extraction or purification methods may be needed to improve the purity of the input material. The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
MinKNOW script failed
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Script failed" | Restart the computer and then restart MinKNOW. If the issue persists, please collect the MinKNOW log files and contact Technical Support. If you do not have another sequencing device available, we recommend storing the flow cell and the loaded library at 4°C and contact Technical Support for further storage guidance. |
Pore occupancy below 40%
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Pore occupancy <40% | Not enough library was loaded on the flow cell | Ensure you load the recommended amount of good quality library in the relevant library prep protocol onto your flow cell. Please quantify the library before loading and calculate mols using tools like the Promega Biomath Calculator, choosing "dsDNA: µg to pmol" |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and sequencing adapters did not ligate to the DNA | Make sure to use the NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (E6056) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Buffer (LNB, provided in the sequencing kit) at the sequencing adapter ligation step, and use the correct amount of each reagent. A Lambda control library can be prepared to test the integrity of the third-party reagents. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and ethanol was used instead of LFB or SFB at the wash step after sequencing adapter ligation | Ethanol can denature the motor protein on the sequencing adapters. Make sure the LFB or SFB buffer was used after ligation of sequencing adapters. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | No tether on the flow cell | Tethers are adding during flow cell priming (FLT/FCT tube). Make sure FLT/FCT was added to FB/FCF before priming. |
Shorter than expected read length
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Shorter than expected read length | Unwanted fragmentation of DNA sample | Read length reflects input DNA fragment length. Input DNA can be fragmented during extraction and library prep. 1. Please review the Extraction Methods in the Nanopore Community for best practice for extraction. 2. Visualise the input DNA fragment length distribution on an agarose gel before proceeding to the library prep. 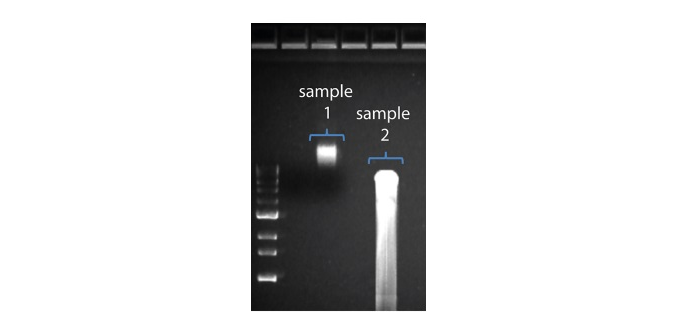 In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented. In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented.3. During library prep, avoid pipetting and vortexing when mixing reagents. Flicking or inverting the tube is sufficient. |
Large proportion of unavailable pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
Large proportion of unavailable pores (shown as blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot) 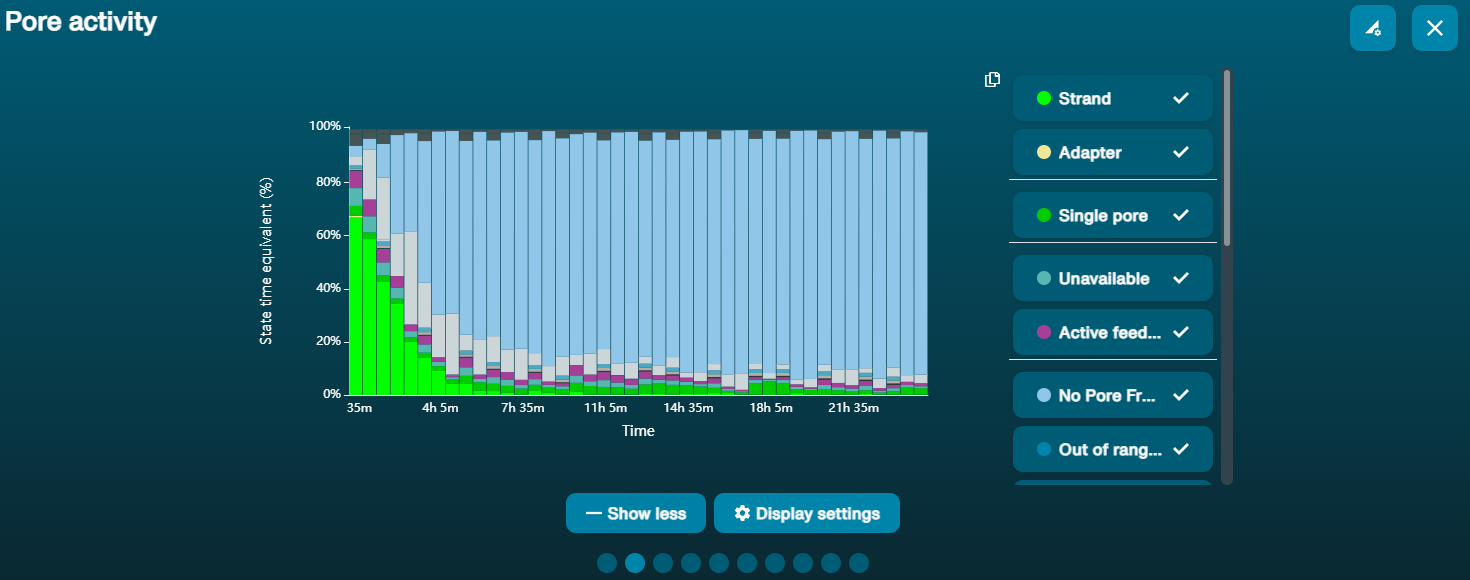 The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. | Contaminants are present in the sample | Some contaminants can be cleared from the pores by the unblocking function built into MinKNOW. If this is successful, the pore status will change to "sequencing pore". If the portion of unavailable pores stays large or increases: 1. A nuclease flush using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) can be performed, or 2. Run several cycles of PCR to try and dilute any contaminants that may be causing problems. |
Large proportion of inactive pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores (shown as light blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot. Pores or membranes are irreversibly damaged) | Air bubbles have been introduced into the flow cell | Air bubbles introduced through flow cell priming and library loading can irreversibly damage the pores. Watch the Priming and loading your flow cell video for best practice |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Certain compounds co-purified with DNA | Known compounds, include polysaccharides, typically associate with plant genomic DNA. 1. Please refer to the Plant leaf DNA extraction method. 2. Clean-up using the QIAGEN PowerClean Pro kit. 3. Perform a whole genome amplification with the original gDNA sample using the QIAGEN REPLI-g kit. |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Contaminants are present in the sample | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run | For Kit 9 chemistry (e.g. SQK-LSK109), fast fuel consumption is typically seen when the flow cell is overloaded with library (please see the appropriate protocol for your DNA library to see the recommendation). | Add more fuel to the flow cell by following the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol. In future experiments, load lower amounts of library to the flow cell. |
Temperature fluctuation
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature fluctuation | The flow cell has lost contact with the device | Check that there is a heat pad covering the metal plate on the back of the flow cell. Re-insert the flow cell and press it down to make sure the connector pins are firmly in contact with the device. If the problem persists, please contact Technical Services. |
Failed to reach target temperature
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Failed to reach target temperature" | The instrument was placed in a location that is colder than normal room temperature, or a location with poor ventilation (which leads to the flow cells overheating) | MinKNOW has a default timeframe for the flow cell to reach the target temperature. Once the timeframe is exceeded, an error message will appear and the sequencing experiment will continue. However, sequencing at an incorrect temperature may lead to a decrease in throughput and lower q-scores. Please adjust the location of the sequencing device to ensure that it is placed at room temperature with good ventilation, then re-start the process in MinKNOW. Please refer to this link for more information on MinION temperature control. |
Guppy – no input .fast5 was found or basecalled
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| No input .fast5 was found or basecalled | input_path did not point to the .fast5 file location | The --input_path has to be followed by the full file path to the .fast5 files to be basecalled, and the location has to be accessible either locally or remotely through SSH. |
| No input .fast5 was found or basecalled | The .fast5 files were in a subfolder at the input_path location | To allow Guppy to look into subfolders, add the --recursive flag to the command |
Guppy – no Pass or Fail folders were generated after basecalling
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| No Pass or Fail folders were generated after basecalling | The --qscore_filtering flag was not included in the command | The --qscore_filtering flag enables filtering of reads into Pass and Fail folders inside the output folder, based on their strand q-score. When performing live basecalling in MinKNOW, a q-score of 7 (corresponding to a basecall accuracy of ~80%) is used to separate reads into Pass and Fail folders. |
Guppy – unusually slow processing on a GPU computer
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Unusually slow processing on a GPU computer | The --device flag wasn't included in the command | The --device flag specifies a GPU device to use for accelerate basecalling. If not included in the command, GPU will not be used. GPUs are counted from zero. An example is --device cuda:0 cuda:1, when 2 GPUs are specified to use by the Guppy command. |







