PCR tiling of SARS-CoV-2 virus - automated Agilent (SQK-RBK110.96 with EXP-MRT001) (MRTA_9157_v110_revH_12Mar2026)
MinION: Protocol
V MRTA_9157_v110_revH_12Mar2026
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
Automated library preparation
Sequencing and data analysis
Troubleshooting
1. Overview of the protocol
This is a Legacy product.
The SQK-RBK110.96 product has been discontinued. Should you require any assistance or have questions, please contact our Customer Support: support@nanoporetech.com.
The PCR tiling of SARS-CoV-2 virus - automated Agilent Bravo (SQK-RBK110.96 with EXP-MRT001) protocol is an automated version of the PCR tiling of SARS-CoV-2 virus with rapid barcoding and Midnight RT PCR Expansion (SQK-RBK110.96 and EXP-MRT001) using the Agilent Bravo liquid handling robot.
Introduction to the protocol
To enable support for the rapidly expanding user requests, the team at Oxford Nanopore Technologies have put together an updated workflow based on the ARTIC Network protocols and analysis methods. The protocol uses Oxford Nanopore Technologies' Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96) and Midnight RT PCR Expansion (EXP-MRT001) for barcoding and library preparation.
We have developed this automated protocol on the Agilent Bravo liquid handling robot. The majority of the process is automated with minimal hands-on time which is required for sample quantification and deck re-loading.
While this protocol is available in the Nanopore Community, we kindly ask users to ensure they are citing the members of the ARTIC network who have been behind the development of these methods.
This protocol is similar to the ARTIC amplicon sequencing protocol for MinION for SARS-CoV-2 v3 (LoCost) by Josh Quick and the method used in Freed et al., 2020. The protocol generates amplicons in a tiled fashion across the whole SARS-CoV-2 genome.
To generate tiled PCR amplicons from the SARS-CoV-2 viral cDNA for use with the Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96), primers were designed by Freed *et al.*, 2020 using Primal Scheme. These primers are in the Midnight RT PCR Expansion (EXP-MRT001) and are designed to generate 1.2 kb amplicons. Primer sequences can be found here.
Steps in the sequencing workflow:
Prepare for your experiment
you will need to:
Before starting - Manual steps:
- Extract your RNA
- Ensure you have your sequencing kit, the correct equipment and reagents
- Prepare your reagents, samples and labware to load on the Agilent Bravo
- Download the software for acquiring and analysing your data
- Check your flow cell to ensure it has enough pores for a good sequencing run
### Prepare your library You will need to:
Automated steps:
- Reverse transcribe your RNA samples with random hexamers
- Amplify the samples by tiled PCR using separate primer pools
- Combine the primer pools
- Attach Rapid Barcodes supplied in the kit to the DNA ends, pool the samples and SPRI purify
__Manual steps:__
- Quantify your DNA library as a quality control
- Prime the flow cell and load your DNA library into the flow cell
Overview of library preparation workflow:
The image below is representative of the steps that take place in the automated runs for X96 samples.
Note: Timings are dependent on number of samples and include hands on time, such as deck loading and sample quantification
Sequencing and analysis
You will need to:
- Start a sequencing run using the MinKNOW software, selecting SQK-RBK110.96 and EXP-MRT001 in kit selection, which will collect raw data from the device and convert it into basecalled reads
Timings
Note: Timings are approximate and subject to change with updates.
| Process | X24 samples | X48 samples | X96 samples | Hands-on time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deck set-up | ~30 minutes | |||
| Process 1: cDNA synthesis | 8 minutes | 16 minutes | 24 minutes | |
| Off-Deck thermocyler | 17 minutes | 17 minutes | 17 minutes | |
| Process 2: cDNA amplification | 10 minutes | 16 minutes | 21 minutes | |
| Off-Deck thermocyler | ~3 hours 30 minutes | ~3 hours 30 minutes | ~3 hours 30 minutes | |
| Process 3: Rapid Barcoding | 5 minutes | 8 minutes | 10 minutes | |
| Off-Deck thermocyler | 8 minutes | 8 minutes | 8 minutes | |
| Process 4: cDNA amplicon pooling/cleanup | 40 minutes | 50 minutes | 60 minutes | |
| Quantification | ~10 minutes | |||
| Total | 4 hours 58 minutes | 5 hours 25 minutes | 5 hours 50 minutes | ~40 minutes |
Nomenclature for automation protocol
Throughout this document, 'Protocol' is defined as the assay on the whole and 'Run' refers to the individual scripts for the automated liquid handling robot, which are specific to indicated protocol step(s).
Before starting
This protocol outlines how to carry out PCR tiling of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA samples on a 96-well plate using the Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96) with the Midnight RT PCR Expansion (EXP-MRT001) using the Agilent Bravo liquid handling robot.
When processing multiple samples at once, we recommend making master mixes following the indicated volumes to account for the necessary excess. We also recommend using a template-free pre-PCR hood for making up the master mixes, and a separate template pre-PCR hood for handling the samples. It is important to clean and/or UV irradiate these hoods between sample batches. Furthermore, to track and monitor cross-contamination events, it is important to run a negative control reaction at the reverse transcription stage using nuclease-free water instead of sample, and carrying this control through the rest of the prep.
All post-PCR procedures should be carried out in a separate area to the pre-PCR preparation, with dedicated equipment for liquid handling in each area to minimise risk of contamination.
If only one liquid handling robot is available, both pre-PCR and post-PCR sections of the assay can be performed in the same robot. In this scenario, cleaning the equipment thoroughly between runs is required and we recommend validating the process for your unique set-up.
Compatibility of this protocol
This protocol should only be used in combination with:
- Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96)
- Midnight RT PCR Expansion (EXP-MRT001)
- R9.4.1 flow cells (FLO-MIN106)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
2. Equipment and consumables
材料
- Input RNA in 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0
- Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96)
- Midnight RT PCR Expansion (EXP-MRT001)
耗材
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- 新制备的 80% 乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(Invitrogen, Q32851)
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- 2 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- 5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- Bravo Lab Disposable Pipette Tips 250 µl - compatible with Bravo 96LT head (19477-022)
- Arvensis B-Frame BIOCOMPOSITE 96 Well PCR Plate Fully Skirted Low Profile 0.2 ml wells
- Hard-Shell® 96-Well PCR Plates, low profile, thin-walled, skirted, white/clear (Bio-Rad, Cat # HSP9601)
- 96-well 0.8 ml MIDI plate (we recommend Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8 ml Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate: ThermoFisher, Cat # AB0859)
- PCR plate seals
仪器
- Agilent Bravo liquid handling robot
- Centrifuge capable of taking 96-well plates
- 迷你离心机
- 涡旋混匀仪
- 热循环仪
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- 计时器
- Qubit荧光计 (或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
可选仪器
- Eppendorf 5424 离心机(或等效器材)
- PCR hood with UV steriliser (optional but recommended to reduce cross-contamination)
- PCR-Cooler (Eppendorf)
- Stepper pipette and tips
Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96) contents
| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | No. of vials | Fill volume per vial (µl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Barcode plate | RB96 | - | 3 plates | 8 µl per well |
| AMPure XP Beads | AXP | Brown | 3 | 1,200 |
| Sequencing Buffer II | SBII | Red | 1 | 500 |
| Rapid Adapter F | RAP-F | Green | 1 | 25 |
| Elution Buffer | EB | Black | 1 | 500 |
| Loading Beads II | LBII | Pink | 1 | 360 |
| Loading Solution | LS | White cap, pink label | 1 | 400 |
| Flush Tether | FLT | Purple | 1 | 400 |
| Flush Buffer | FB | White | 1 bottle | 15,500 |
This product contains AMPure XP reagent manufactured by Beckman Coulter, Inc.
Midnight RT PCR Expansion (EXP-MRT001) contents
| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | Number of vials | Fill volume per vial (µl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LunaScript RT SuperMix | LS RT | Blue | 3 | 500 |
| Q5 HS Master Mix | Q5 | Orange | 6 | 1,500 |
| Midnight Primer Pool A | MP A | White | 3 | 15 |
| Midnight Primer Pool B | MP B | Clear | 3 | 15 |
Midnight Primer sequences
As mutations in SARS-CoV-2 variants emerge amplicon drop out may be observed; for users wishing to design their own primer spike-ins to address this we suggest adding to the appropriate primer pool at a final concentration between 3.33 µM and 6.66 µM.
Below are the sequences for the V3 primer scheme used in the Midnight RT PCR Expansion.
Pool A
| Primer name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
SARSCoV_1200_1_LEFT | ACCAACCAACTTTCGATCTCTTGT |
SARSCoV_1200_1_RIGHT | GGTTGCATTCATTTGGTGACGC |
SARSCoV_1200_3_LEFT | GGCTTGAAGAGAAGTTTAAGGAAGGT |
SARSCoV_1200_3_RIGHT | GATTGTCCTCACTGCCGTCTTG |
SARSCoV_1200_5_LEFT | ACCTACTAAAAAGGCTGGTGGC |
SARSCoV_1200_5_RIGHT | AGCATCTTGTAGAGCAGGTGGA |
SARSCoV_1200_7_LEFT | ACCTGGTGTATACGTTGTCTTTGG |
SARSCoV_1200_7_RIGHT | GCTGAAATCGGGGCCATTTGTA |
SARSCoV_1200_9_LEFT | AGAAGTTACTGGCGATAGTTGTAATAACT |
SARSCoV_1200_9_RIGHT | TGCTGATATGTCCAAAGCACCA |
SARSCoV_1200_11_LEFT | AGACACCTAAGTATAAGTTTGTTCGCA |
SARSCoV_1200_11_RIGHT | GCCCACATGGAAATGGCTTGAT |
SARSCoV_1200_13_LEFT | ACCTCTTACAACAGCAGCCAAAC |
SARSCoV_1200_13_RIGHT | CGTCCTTTTCTTGGAAGCGACA |
SARSCoV_1200_15_LEFT | TTTTAAGGAATTACTTGTGTATGCTGCT |
SARSCoV_1200_15_RIGHT | ACACACAACAGCATCGTCAGAG |
SARSCoV_1200_17_LEFT | TCAAGCTTTTTGCAGCAGAAACG |
SARSCoV_1200_17_RIGHT | CCAAGCAGGGTTACGTGTAAGG |
SARSCoV_1200_19_LEFT | GGCACATGGCTTTGAGTTGACA |
SARSCoV_1200_19_RIGHT | CCTGTTGTCCATCAAAGTGTCCC |
SARSCoV_1200_21_LEFT | TCTGTAGTTTCTAAGGTTGTCAAAGTGA |
SARSCoV_1200_21_RIGHT | GCAGGGGGTAATTGAGTTCTGG |
21_right_spike | GTGTATGATTGAGTTCTGGTTGTAAG |
SARSCoV_1200_23_LEFT | ACTTTAGAGTCCAACCAACAGAATCT |
23_left_spike | ACTTTAGAGTTCAACCAACAGAATCT |
SARSCoV_1200_23_RIGHT | TGACTAGCTACACTACGTGCCC |
SARSCoV_1200_25_LEFT | TGCTGCTACTAAAATGTCAGAGTGT |
SARSCoV_1200_25_RIGHT | CATTTCCAGCAAAGCCAAAGCC |
SARSCoV_1200_27_LEFT | TGGATCACCGGTGGAATTGCTA |
SARSCoV_1200_27_RIGHT | TGTTCGTTTAGGCGTGACAAGT |
SARSCoV_1200_29_LEFT | TGAGGGAGCCTTGAATACACCA |
SARSCoV_1200_29_RIGHT | TAGGCAGCTCTCCCTAGCATTG |
Pool B
| Primer name | Primer sequences |
|---|---|
SARSCoV_1200_2_LEFT | CCATAATCAAGACTATTCAACCAAGGGT |
SARSCoV_1200_2_RIGHT | ACAGGTGACAATTTGTCCACCG |
SARSCoV_1200_4_LEFT | GGAATTTGGTGCCACTTCTGCT |
SARSCoV_1200_4_RIGHT | CCTGACCCGGGTAAGTGGTTAT |
SARSCoV_1200_6_LEFT | ACTTCTATTAAATGGGCAGATAACAACTG |
SARSCoV_1200_6_RIGHT | GATTATCCATTCCCTGCGCGTC |
SARSCoV_1200_8_LEFT | CAATCATGCAATTGTTTTTCAGCTATTTTG |
SARSCoV_1200_8_RIGHT | TGACTTTTTGCTACCTGCGCAT |
SARSCoV_1200_10_LEFT | TTTACCAGGAGTTTTCTGTGGTGT |
SARSCoV_1200_10_RIGHT | TGGGCCTCATAGCACATTGGTA |
SARSCoV_1200_12_LEFT | ATGGTGCTAGGAGAGTGTGGAC |
SARSCoV_1200_12_RIGHT | GGATTTCCCACAATGCTGATGC |
SARSCoV_1200_14_LEFT | ACAGGCACTAGTACTGATGTCGT |
SARSCoV_1200_14_RIGHT | GTGCAGCTACTGAAAAGCACGT |
SARSCoV_1200_16_LEFT | ACAACACAGACTTTATGAGTGTCTCT |
SARSCoV_1200_16_RIGHT | CTCTGTCAGACAGCACTTCACG |
SARSCoV_1200_18_LEFT | GCACATAAAGACAAATCAGCTCAATGC |
SARSCoV_1200_18_RIGHT | TGTCTGAAGCAGTGGAAAAGCA |
SARSCoV_1200_20_LEFT | ACAATTTGATACTTATAACCTCTGGAACAC |
SARSCoV_1200_20_RIGHT | GATTAGGCATAGCAACACCCGG |
SARSCoV_1200_22_LEFT | GTGATGTTCTTGTTAACAACTAAACGAACA |
SARSCoV_1200_22_RIGHT | AACAGATGCAAATCTGGTGGCG |
22_right_spike | AACAGATGCAAATTTGGTGGCG |
SARSCoV_1200_24_LEFT | GCTGAACATGTCAACAACTCATATGA |
24_left_spike | GCTGAATATGTCAACAACTCATATGA |
SARSCoV_1200_24_RIGHT | ATGAGGTGCTGACTGAGGGAAG |
SARSCoV_1200_26_LEFT | GCCTTGAAGCCCCTTTTCTCTA |
SARSCoV_1200_26_RIGHT | AATGACCACATGGAACGCGTAC |
SARSCoV_1200_28_LEFT | TTTGTGCTTTTTAGCCTTTCTGCT |
SARSCoV_1200_28_RIGHT | GTTTGGCCTTGTTGTTGTTGGC |
SARSCoV_1200_28_LEFT_27837T | TTTGTGCTTTTTAGCCTTTCTGTT |
Rapid barcode sequences
| Component | Sequence |
|---|---|
| RB01 | AAGAAAGTTGTCGGTGTCTTTGTG |
| RB02 | TCGATTCCGTTTGTAGTCGTCTGT |
| RB03 | GAGTCTTGTGTCCCAGTTACCAGG |
| RB04 | TTCGGATTCTATCGTGTTTCCCTA |
| RB05 | CTTGTCCAGGGTTTGTGTAACCTT |
| RB06 | TTCTCGCAAAGGCAGAAAGTAGTC |
| RB07 | GTGTTACCGTGGGAATGAATCCTT |
| RB08 | TTCAGGGAACAAACCAAGTTACGT |
| RB09 | AACTAGGCACAGCGAGTCTTGGTT |
| RB10 | AAGCGTTGAAACCTTTGTCCTCTC |
| RB11 | GTTTCATCTATCGGAGGGAATGGA |
| RB12 | CAGGTAGAAAGAAGCAGAATCGGA |
| RB13 | AGAACGACTTCCATACTCGTGTGA |
| RB14 | AACGAGTCTCTTGGGACCCATAGA |
| RB15 | AGGTCTACCTCGCTAACACCACTG |
| RB16 | CGTCAACTGACAGTGGTTCGTACT |
| RB17 | ACCCTCCAGGAAAGTACCTCTGAT |
| RB18 | CCAAACCCAACAACCTAGATAGGC |
| RB19 | GTTCCTCGTGCAGTGTCAAGAGAT |
| RB20 | TTGCGTCCTGTTACGAGAACTCAT |
| RB21 | GAGCCTCTCATTGTCCGTTCTCTA |
| RB22 | ACCACTGCCATGTATCAAAGTACG |
| RB23 | CTTACTACCCAGTGAACCTCCTCG |
| RB24 | GCATAGTTCTGCATGATGGGTTAG |
| RB25 | GTAAGTTGGGTATGCAACGCAATG |
| RB26 | CATACAGCGACTACGCATTCTCAT |
| RB27 | CGACGGTTAGATTCACCTCTTACA |
| RB28 | TGAAACCTAAGAAGGCACCGTATC |
| RB29 | CTAGACACCTTGGGTTGACAGACC |
| RB30 | TCAGTGAGGATCTACTTCGACCCA |
| RB31 | TGCGTACAGCAATCAGTTACATTG |
| RB32 | CCAGTAGAAGTCCGACAACGTCAT |
| RB33 | CAGACTTGGTACGGTTGGGTAACT |
| RB34 | GGACGAAGAACTCAAGTCAAAGGC |
| RB35 | CTACTTACGAAGCTGAGGGACTGC |
| RB36 | ATGTCCCAGTTAGAGGAGGAAACA |
| RB37 | GCTTGCGATTGATGCTTAGTATCA |
| RB38 | ACCACAGGAGGACGATACAGAGAA |
| RB39 | CCACAGTGTCAACTAGAGCCTCTC |
| RB40 | TAGTTTGGATGACCAAGGATAGCC |
| RB41 | GGAGTTCGTCCAGAGAAGTACACG |
| RB42 | CTACGTGTAAGGCATACCTGCCAG |
| RB43 | CTTTCGTTGTTGACTCGACGGTAG |
| RB44 | AGTAGAAAGGGTTCCTTCCCACTC |
| RB45 | GATCCAACAGAGATGCCTTCAGTG |
| RB46 | GCTGTGTTCCACTTCATTCTCCTG |
| RB47 | GTGCAACTTTCCCACAGGTAGTTC |
| RB48 | CATCTGGAACGTGGTACACCTGTA |
| RB49 | ACTGGTGCAGCTTTGAACATCTAG |
| RB50 | ATGGACTTTGGTAACTTCCTGCGT |
| RB51 | GTTGAATGAGCCTACTGGGTCCTC |
| RB52 | TGAGAGACAAGATTGTTCGTGGAC |
| RB53 | AGATTCAGACCGTCTCATGCAAAG |
| RB54 | CAAGAGCTTTGACTAAGGAGCATG |
| RB55 | TGGAAGATGAGACCCTGATCTACG |
| RB56 | TCACTACTCAACAGGTGGCATGAA |
| RB57 | GCTAGGTCAATCTCCTTCGGAAGT |
| RB58 | CAGGTTACTCCTCCGTGAGTCTGA |
| RB59 | TCAATCAAGAAGGGAAAGCAAGGT |
| RB60 | CATGTTCAACCAAGGCTTCTATGG |
| RB61 | AGAGGGTACTATGTGCCTCAGCAC |
| RB62 | CACCCACACTTACTTCAGGACGTA |
| RB63 | TTCTGAAGTTCCTGGGTCTTGAAC |
| RB64 | GACAGACACCGTTCATCGACTTTC |
| RB65 | TTCTCAGTCTTCCTCCAGACAAGG |
| RB66 | CCGATCCTTGTGGCTTCTAACTTC |
| RB67 | GTTTGTCATACTCGTGTGCTCACC |
| RB68 | GAATCTAAGCAAACACGAAGGTGG |
| RB69 | TACAGTCCGAGCCTCATGTGATCT |
| RB70 | ACCGAGATCCTACGAATGGAGTGT |
| RB71 | CCTGGGAGCATCAGGTAGTAACAG |
| RB72 | TAGCTGACTGTCTTCCATACCGAC |
| RB73 | AAGAAACAGGATGACAGAACCCTC |
| RB74 | TACAAGCATCCCAACACTTCCACT |
| RB75 | GACCATTGTGATGAACCCTGTTGT |
| RB76 | ATGCTTGTTACATCAACCCTGGAC |
| RB77 | CGACCTGTTTCTCAGGGATACAAC |
| RB78 | AACAACCGAACCTTTGAATCAGAA |
| RB79 | TCTCGGAGATAGTTCTCACTGCTG |
| RB80 | CGGATGAACATAGGATAGCGATTC |
| RB81 | CCTCATCTTGTGAAGTTGTTTCGG |
| RB82 | ACGGTATGTCGAGTTCCAGGACTA |
| RB83 | TGGCTTGATCTAGGTAAGGTCGAA |
| RB84 | GTAGTGGACCTAGAACCTGTGCCA |
| RB85 | AACGGAGGAGTTAGTTGGATGATC |
| RB86 | AGGTGATCCCAACAAGCGTAAGTA |
| RB87 | TACATGCTCCTGTTGTTAGGGAGG |
| RB88 | TCTTCTACTACCGATCCGAAGCAG |
| RB89 | ACAGCATCAATGTTTGGCTAGTTG |
| RB90 | GATGTAGAGGGTACGGTTTGAGGC |
| RB91 | GGCTCCATAGGAACTCACGCTACT |
| RB92 | TTGTGAGTGGAAAGATACAGGACC |
| RB93 | AGTTTCCATCACTTCAGACTTGGG |
| RB94 | GATTGTCCTCAAACTGCCACCTAC |
| RB95 | CCTGTCTGGAAGAAGAATGGACTT |
| RB96 | CTGAACGGTCATAGAGTCCACCAT |
3. Computer requirements and software
MinION Mk1B IT requirements
Sequencing on a MinION Mk1B requires a high-spec computer or laptop to keep up with the rate of data acquisition. For more information, refer to the MinION Mk1B IT requirements document.
MinION Mk1C IT requirements
The MinION Mk1C contains fully-integrated compute and screen, removing the need for any accessories to generate and analyse nanopore data. For more information refer to the MinION Mk1C IT requirements document.
Software for nanopore sequencing
MinKNOW
The MinKNOW software controls the nanopore sequencing device, collects sequencing data and basecalls in real time. You will be using MinKNOW for every sequencing experiment to sequence, basecall and demultiplex if your samples were barcoded.
For instructions on how to run the MinKNOW software, please refer to the MinKNOW protocol.
EPI2ME (optional)
The EPI2ME cloud-based platform performs further analysis of basecalled data, for example alignment to the Lambda genome, barcoding, or taxonomic classification. You will use the EPI2ME platform only if you would like further analysis of your data post-basecalling.
For instructions on how to create an EPI2ME account and install the EPI2ME Desktop Agent, please refer to this link.
Check your flow cell
We highly recommend that you check the number of pores in your flow cell prior to starting a sequencing experiment. This should be done within 12 weeks of purchasing for MinION/GridION/PromethION or within four weeks of purchasing Flongle Flow Cells. Oxford Nanopore Technologies will replace any flow cell with fewer than the number of pores in the table below, when the result is reported within two days of performing the flow cell check, and when the storage recommendations have been followed. To do the flow cell check, please follow the instructions in the Flow Cell Check document.
| Flow cell | Minimum number of active pores covered by warranty |
|---|---|
| Flongle Flow Cell | 50 |
| MinION/GridION Flow Cell | 800 |
| PromethION Flow Cell | 5000 |
4. Pre-PCR
材料
- Input RNA in 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0
- Midnight Primer Pool A (MP A)
- Midnight Primer Pool B (MP B)
耗材
- Arvensis B-Frame BIOCOMPOSITE 96 Well PCR Plate Fully Skirted Low Profile 0.2 ml wells
- Bravo Lab Disposable Pipette Tips 250 µl - compatible with Bravo 96LT head (19477-022)
- PCR plate seals
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- LunaScript RT SuperMix (LS RT)
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
- Q5 HS Master Mix (Q5)
仪器
- 盛有冰的冰桶
- PCR hood with UV steriliser (optional but recommended to reduce cross-contamination)
- Agilent Bravo liquid handling robot
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P2 移液枪和枪头
- 迷你离心机
- 热循环仪
- Centrifuge capable of taking 96-well plates
Run setup:
Turn on the Agilent Thermocube and set Position 4 to 4°C.
To cool position 4 prior to the run: open the file, under the deck layout, and tick the box near the block you want to cool. Set up the temperature and hit 'Run' to execute.

Thaw and keep the samples, LunaScript, Q5 Hot Start Master mix, Midnight Primer Pool A (MPA) and Midnight Primer Pool B (MPB) on ice.
To minimise risk of contamination, we recommend handling the Lunascript and primers in a clean template-free PCR hood.
Prior to use, ensure all reagents have been thoroughly mixed by performing 20-30 full-volume pipette mixes.
Note: This is especially important with the Q5 Hot start master mix as the contents can precipitate following freeze-thaw cylces.
Take care when mixing and vortexing as this will introduce air bubbles, resulting in loss of volume.
In the template-free pre-PCR hood, prepare the following Primer master mixes in 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes and mix thoroughly as follows:
For x24 samples:
| Reagent | Pool A | Pool B | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | Nuclease-free water | 172 µl | 172 µl | | Midnight Primer Pool A (MP A) | 2 µl | - | | Midnight Primer Pool B (MP B) | - | 2 µl | | Q5 HS Master Mix (Q5) | 102 µl | 102 µl | | Total | 276 µl | 276 µl |
For x48 samples:
| Reagent | Pool A | Pool B | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | Nuclease-free water | 344 µl | 344 µl | | Midnight Primer Pool A (MP A) | 3 µl | - | | Midnight Primer Pool B (MP B) | - | 3 µl | | Q5 HS Master Mix (Q5) | 203 µl | 203 µl | | Total | 550 µl | 550 µl |
For x96 samples:
| Reagent | Pool A | Pool B | | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | | Nuclease-free water | 687 µl | 687 µl | | Midnight Primer Pool A (MP A) | 6 µl | - | | Midnight Primer Pool B (MP B) | - | 6 µl | | Q5 HS Master Mix (Q5) | 407 µl | 407 µl | | Total | 1,100 µl | 1,100 µl |
Note: Taking care not to introduce air bubbles, pipette mix 10-15 times between each addition and perform a final full-volume pipette mix 10 times.
Keep on ice until use.
In the template-free pre-PCR hood and using a clean Arvensis plate, prepare the reagent input plate as follows:
For x24 samples:

For x48 samples:

For x96 samples:

Note: Take care to not introduce air bubbles while aliquoting the reagents into the Arvensis plate.
Once complete seal the plate and keep on ice until ready to transfer over to the Agilent Bravo robot.
In a pre-PCR hood and using a clean Arvensis plate, prepare the RNA sample input plate as follows:
For x24 samples:

For x48 samples:

For x96 samples:

Note: Take care to not introduce air bubbles while aliquoting the samples into the Arvensis plate.
Once complete seal the plate and keep on ice until ready to transfer over to the Agilent Bravo robot.
On the Agilent Bravo, select the 'cDNA and Multiplex (X) samples' protocol, where (X) indicates the number of samples to be processed.
Set the number of columns of samples and the PCR plate type.
- For X24 samples, select 3
- For X48 samples, select 6
- For X96 samples, select 12
Select 'Display Deck Layout'.
Add the labware, sample plate and reagent input plate as indicated on the form display.
For X24 samples:

For X48 samples:

For X96 samples:

Select 'Run Protocol'.
To start the run, select 'Ok' from the figure below:

After the Agilent Bravo has added the 2 µl of LunaScript to the samples, the robot will stop with the the following message:

Remove the sample plate containing the LunaScript from the Agilent Bravo, seal it and spin it down.
Place the sample plate in a Thermal cycler and incubate using the following program:
| Step | Temperature | Time | Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primer annealing | 25°C | 2 min | 1 |
| cDNA synthesis | 55°C | 10 min | 1 |
| Heat inactivation | 95°C | 1 min | 1 |
| Hold | 4°C | ∞ |
After placing the sample plate in the Thermal cycler, press "Continue" on the Agilent Bravo to start the addition of the Primer master mixes into a clean Arvensis plate.
Once the thermal cycler has completed the cDNA synthesis, remove the sample plate and spin down.
When prompted, place the sample plate back in the Agilent Bravo deck into position 4.
After the Agilent Bravo has added the 2.5 µl of RT to the Primer master mix plate/plates, the robot will stop with the the following message:

Remove the PCR plate (or plates if processing X96 samples) from the Agilent Bravo, seal it and spin it down.
Place in the thermal cycler and incubate using the following program, with the heated lid set to 105°C:
| Step | Temperature | Time | Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial denaturation | 98°C | 30 sec | 1 |
| Denaturation Annealing and extension | 98°C 61°C 65°C | 15 sec 2 min 3 min | 35 |
| Hold | 4°C | ∞ |
Once the PCR amplification is complete, remove the plate(s) from the thermal cycler and spin down. The plate(s) will be taken forward to the Post-PCR section of the protocol.
If necessary, the protocol can be paused at this point. The samples should be kept at 4°C and can be stored overnight.
5. Post-PCR
材料
- Rapid Barcode Plate (RB96)
- AMPure XP Beads (AXP, or SPRI)
- Oxford Nanopore 试剂盒中的洗脱缓冲液(EB)
- Rapid Adapter F (RAP F)
耗材
- 无核酸酶水(如ThermoFisher,AM9937)
- 新制备的 80% 乙醇(用无核酸酶水配制)
- Bravo Lab Disposable Pipette Tips 250 µl - compatible with Bravo 96LT head (19477-022)
- Arvensis B-Frame BIOCOMPOSITE 96 Well PCR Plate Fully Skirted Low Profile 0.2 ml wells
- 96-well 0.8 ml MIDI plate (we recommend Abgene™ 96 Well 0.8 ml Polypropylene Deepwell Storage Plate: ThermoFisher, Cat # AB0859)
- PCR plate seals
- Qubit™ 分析管(Invitrogen, Q32856)
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay(双链DNA高灵敏度检测)试剂盒(Invitrogen, Q32851)
仪器
- Agilent Bravo liquid handling robot
- 热循环仪
- Centrifuge capable of taking 96-well plates
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P200 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P2 移液枪和枪头
- Qubit™ 荧光计(或用于质控检测的等效仪器)
Rapid Barcoding:
Select the 'Barcoding and clean-up' program on the Agilent Bravo.
Set the number of columns for your run:
- For three columns of each primer pool (6 in total), select 3 columns.
- For six columns of each primer pool (12 in total), select 6 columns.
- For twelve columns of each primer pool (24 in total), select 12 columns.
Select 'Display Deck Layout'.
Add the Primer plates, the Rapid barcode plate and the labware as indicated on the display.
Select 'Run protocol'.
To start the run, select 'Ok' from the figure below:

For runs using X24 or X48 samples, you will need to enter the starting index plate column for the RBK plate when prompted.
For example: If your barcode starts at column 4, enter "4" as seen in the figure below.

After the Agilent Bravo has completed the Rapid Barcoding plate, the robot will stop with the following message:

Remove the barcoded sample plate from the Agilent Bravo, seal it and spin it down.
Place the barcoded sample plate in the thermal cycler and incubate at 30°C for 2 minutes and then at 80°C for 2 minutes.
Sample pooling and clean-up:
Follow the instructions for the Agilent Bravo deck set-up on the screen prompt.

Resuspend the AMPure XP beads by vortexing.
While the barcoding plate is in the thermal cycler, using a clean MIDI 96 deep-well plate prepare the reagents as follows:
For X24 samples:

For X48 samples:

For X96 samples:

Note: Take care to not introduce air bubbles while aliquoting the reagents into the deep-well plate.
Ensure all reagents are properly mixed prior to use.
When preparing the plates, well A12 will be empty. This is where the final elution will be found at the end of the Agilent Bravo run.
Prepare the deck of the Agilent Bravo with the reagent plate and labware as follows:
For X24 or X48 samples:

For X96 samples:

Once the thermal cycler has finished, remove the plate and spin it down.
Remove the seal on the rapid barcoding plate and return it to the allocated position on the Agilent Bravo deck.
Select "Continue" on the Agilent Bravo screen prompt to continue the run.
Ensure all of the labware and reagent plates are in the correct positions, you have removed all of the lids and the plates are unsealed before continuing.
After the run ends, the final library can be collected from position A12 in the deep-well plate. Remove and retain the final elution into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube
Quantify DNA concentration of the final elution by using the Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit.
The quantified library is used for loading into the MinION flow cell. Store the library on ice until ready to load.
6. Priming and loading the SpotON Flow Cell
材料
- Flush Buffer (FB)
- Flush Tether (FLT)
- Loading Beads II (LBII)
- Sequencing Buffer II (SBII)
- Loading Solution (LS)
耗材
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind 离心管
仪器
- MinION device
- SpotON Flow Cell
- MinION 及GridION 测序芯片遮光片
- P1000 移液枪和枪头
- P100 移液枪和枪头
- P20 移液枪和枪头
- P10 移液枪和枪头
Priming and loading a flow cell
We recommend all new users watch the 'Priming and loading your flow cell' video before your first run.
Using the Loading Solution
We recommend using the Loading Beads II (LBII) for loading your library onto the flow cell for most sequencing experiments. However, if you have previously used water to load your library, you must use Loading Solution (LS) instead of water. Note: some customers have noticed that viscous libraries can be loaded more easily when not using Loading Beads II.
Thaw the Sequencing Buffer II (SBII), Loading Beads II (LBII) or Loading Solution (LS, if using), Flush Tether (FLT) and Flush Buffer (FB) at room temperature before mixing the reagents by vortexing, and spin down the SBII and FLT at room temperature.
Prepare the flow cell priming mix in a suitable vial for the number of flow cells to flush. Once combined, mix well by briefly vortexing.
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Flush Tether (FLT) | 30 µl |
| Flush Buffer (FB) | 1,170 µl |
Open the MinION device lid and slide the flow cell under the clip. Press down firmly on the priming port cover to ensure correct thermal and electrical contact.
Press down firmly on the flow cell to ensure correct thermal and electrical contact.
Complete a flow cell check to assess the number of pores available before loading the library.
This step can be omitted if the flow cell has been checked previously.
See the flow cell check instructions in the MinKNOW protocol for more information.
Slide the priming port cover clockwise to open the priming port.
Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the priming port, check for a small air bubble under the cover. Draw back a small volume to remove any bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette to 200 µl
- Insert the tip into the priming port
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, to draw back 20-30 µl, or until you can see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip
Note: Visually check that there is continuous buffer from the priming port across the sensor array.
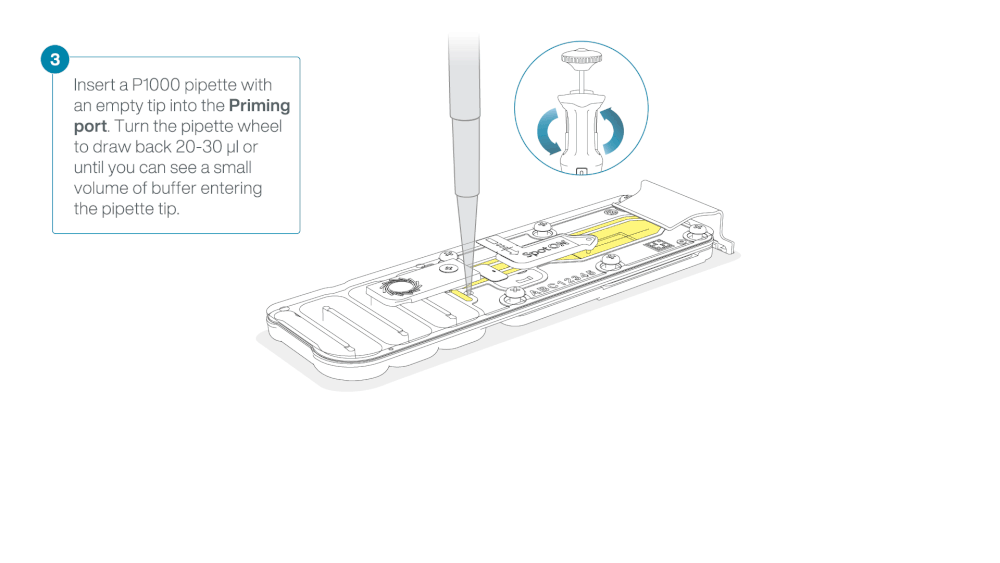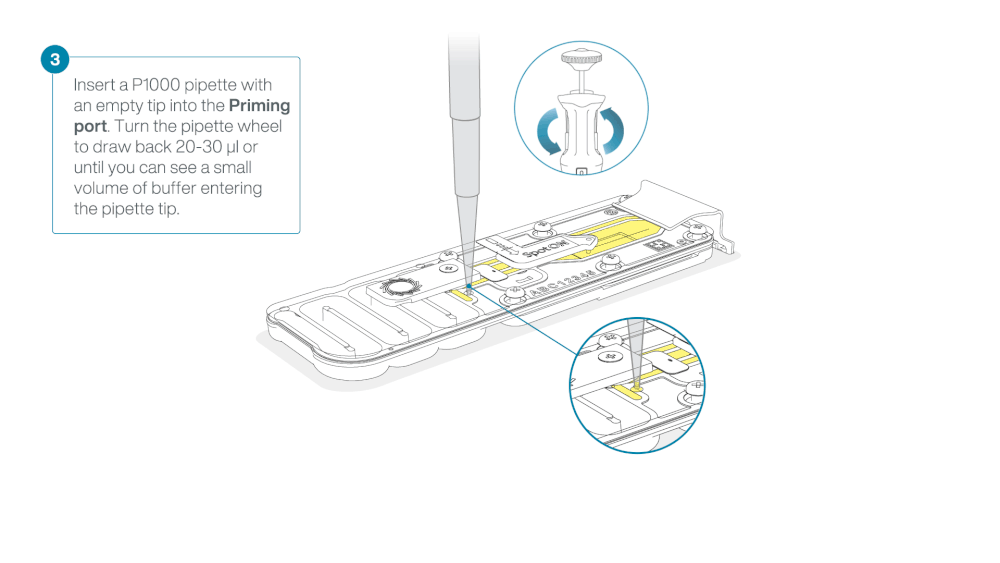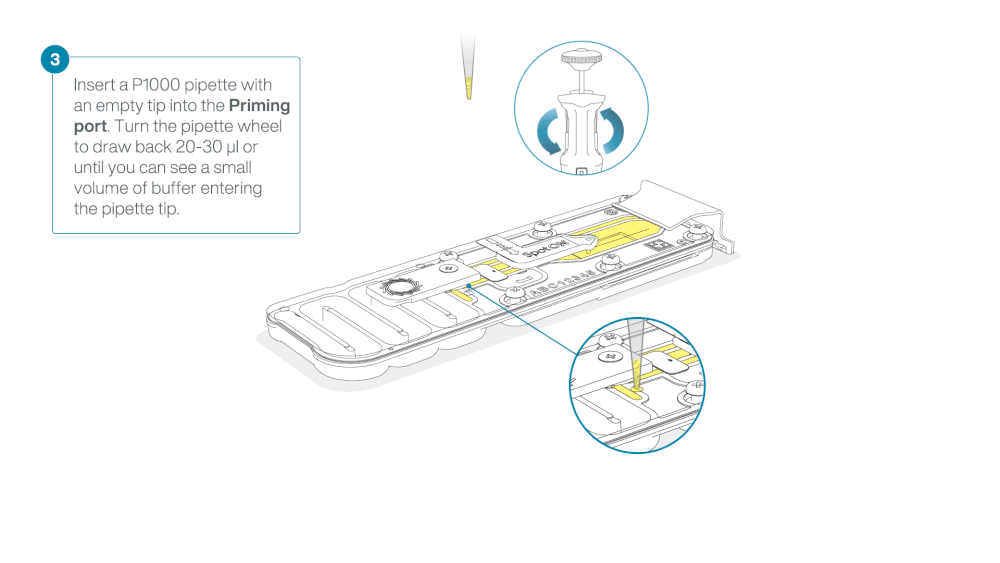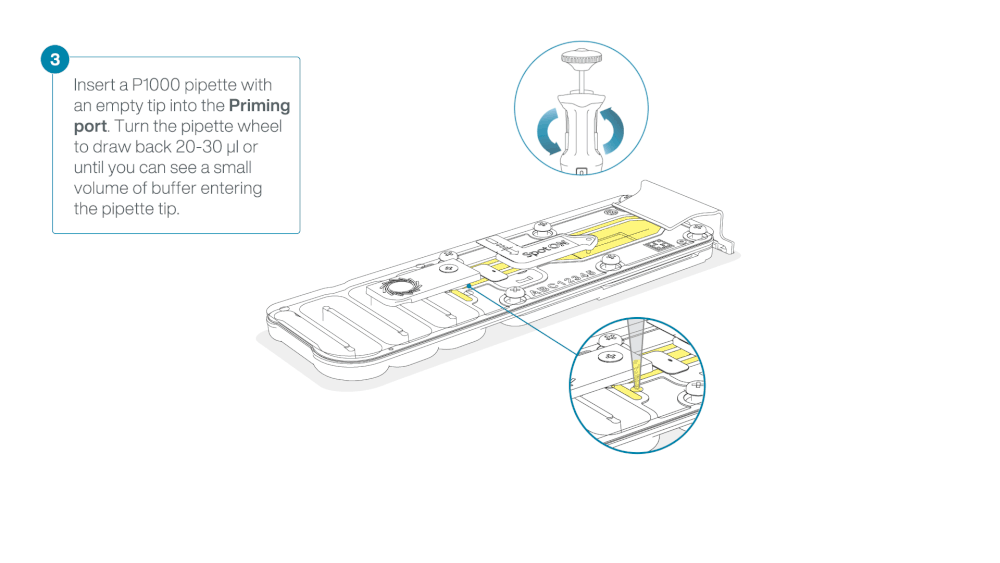
Load 800 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the priming port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait for five minutes. During this time, prepare the library for loading by following the steps below.

Thoroughly mix the contents of the Loading Beads II (LBII) by pipetting.
The Loading Beads II (LBII) tube contains a suspension of beads. These beads settle very quickly. It is vital that they are mixed immediately before use.
In a new tube, prepare the library for loading as follows:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer II (SBII) | 37.5 µl |
| Loading Beads II (LBII) mixed immediately before use, or Loading Solution (LS), if using | 25.5 µl |
| DNA library | 12 µl |
| Total | 75 µl |
Note: Load the library onto the flow cell immediately after adding the Sequencing Buffer II (SBII) and Loading Beads II (LBII) because the fuel in the buffer will start to be consumed by the adapter.
Complete the flow cell priming:
- Gently lift the SpotON sample port cover to make the SpotON sample port accessible.
- Load 200 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell priming port (not the SpotON sample port), avoiding the introduction of air bubbles.

Mix the prepared library gently by pipetting up and down just prior to loading.
Add 75 μl of the prepared library to the flow cell via the SpotON sample port in a dropwise fashion. Ensure each drop flows into the port before adding the next.

Gently replace the SpotON sample port cover, making sure the bung enters the SpotON port and close the priming port.

Install the light shield on your flow cell as soon as library has been loaded for optimal sequencing output.
We recommend leaving the light shield on the flow cell when library is loaded, including during any washing and reloading steps. The shield can be removed when the library has been removed from the flow cell.
Place the light shield onto the flow cell, as follows:
Carefully place the leading edge of the light shield against the clip. Note: Do not force the light shield underneath the clip.
Gently lower the light shield onto the flow cell. The light shield should sit around the SpotON cover, covering the entire top section of the flow cell.

The MinION Flow Cell Light Shield is not secured to the flow cell and careful handling is required after installation.
Close the device lid and set up a sequencing run on MinKNOW.
7. Data acquisition and basecalling
Overview of nanopore data analysis
For a full overview of nanopore data analysis, which includes options for basecalling and post-basecalling analysis, please refer to the Data Analysis document.
Required settings in MinKNOW
The correct barcoding parameters must be set up on MinKNOW prior to the sequencing run. During the run setup, in the Analysis tab:
- Enable Barcoding.
- Select Edit options.
- Enable Mid-read barcode filtering.
- Enable Override minimum barcoding score and set the value to 60.
- Enable Override minimum mid-read barcoding score and set the value to 50.


How to start sequencing
The sequencing device control, data acquisition and real-time basecalling are carried out by the MinKNOW software. Please ensure MinKNOW is installed on your computer or device. There are multiple options for how to carry out sequencing:
1. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using MinKNOW on a computer
Follow the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol beginning from the "Starting a sequencing run" section until the end of the "Completing a MinKNOW run" section.
2. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the MinION Mk1B/Mk1D device
Follow the instructions in the MinION Mk1B user manual or the MinION Mk1D user manual.
3. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the MinION Mk1C device
Follow the instructions in the MinION Mk1C user manual.
4. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the GridION device
Follow the instructions in the GridION user manual.
5. Data acquisition and basecalling in real-time using the PromethION device
Follow the instructions in the PromethION user manual or the PromethION 2 Solo user manual.
6. Data acquisition using MinKNOW on a computer and basecalling at a later time using MinKNOW
Follow the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol beginning from the "Starting a sequencing run" section until the end of the "Completing a MinKNOW run" section. When setting your experiment parameters, set the Basecalling tab to OFF. After the sequencing experiment has completed, follow the instructions in the Post-run analysis section of the MinKNOW protocol.
8. Downstream analysis
Recommended pipeline analysis
The wf-artic is a bioinformatics workflow for the analysis of ARTIC sequencing data prepared using the Midnight protocol. The bioinformatics workflow is orchestrated by the Nextflow software. Nextflow is a publicly available and open-source project that enables the execution of scientific workflows in a scalable and reproducible way. The software is natively supported on the GridION device and can be simply installed on most Linux computers and servers. The installation is outlined later in the document.
The Midnight analysis uses the ARTIC bioinformatics workflow.
Demultiplexed sequence reads are processed using the ARTIC FieldBioinformatics software that has been subtly modified for the analysis of FASTQ sequences prepared using Oxford Nanopore rapid sequencing kits. The other modification to the ARTIC workflow is the use of a primer scheme that defines the sequencing primers used by the Midnight protocol and their genomic locations on the SARS-CoV-2 genome.
The wf-artic workflow includes other analytical steps that include cladistic analysis using Nextclade and strain assignment using Pangolin. The data facets included in the report are parameterised and additional information such as plots of depth-of-coverage across the reference genome is optional.
The complete source for wf-artic is linked and the Nextflow software will download the scripts and logic flow from this location.
On GridION devices, the wf-artic workflow will start automatically after sequencing. However, on other devices, this will have to be started manually as outlined further on this page under 'Running a Midnight analysis'.
Software set up and installation
The wf-artic workflow requires the Nextflow and Docker software to have been installed. The EPI2ME quickstart guide provides instructions for the installation of these requirements for GridION, PromethION and general Ubuntu Linux users and provides a little more introduction to the Nextflow software.
Automatic start on GridION:
To set up the Midnight analysis to start automatically after sequencing on GridION, select the Rapid Barcoding Kit 96 (SQK-RBK110.96) kit with the Midnight RT PCR Expansion (EXP-MRT001) pack on MinKNOW when setting up a sequencing run.
When the workflow has finished, the relevant analysis files will be available in the following output folder:
processing/artic/artic_DATE_TIME_67195e17
Post-run analysis on GridION:
The Midnight analysis can also be started post-run on GridION:
- On the start page, click 'Analysis'
- Click 'Workflow'
- From the dropdown menu, select 'post_processing/artic/artic'
- Select your input folder with the sequencing data and the location for the output folder

Using Linux command line:
The wf-artic workflow can be run from the Linux command line. The workflow can be installed or updated with the command:
$ nextflow pull epi2me-labs/wf-artic
Demultiplexing of multiple barcoded samples
The wf-artic requires FASTQ format sequence data that has already been demultiplexed. Sequences can either be demultiplexed directly in the MinKNOW software or as a post-sequencing step by the guppy_barcoder software provided by the Guppy software.
The Midnight protocol uses a rapid barcoding kit; it is therefore important to note that the demultiplexing step must not require barcodes at both ends of the sequence.
The expected input for wf-artic is a folder of folders as shown below. Each of the barcode folders should contain the FASTQ sequence data and files may either be uncompressed or gzipped.
$ tree -d MidnightFastq/
MidnightFastq/
├── barcode01
├── barcode02
├── barcode03
├── barcode04
├── barcode05
├── barcode06
└── unclassified
Running a Midnight analysis
The reference command for running a Midnight analysis is as follows. The parameters are explained further on in the document.
nextflow run epi2me-labs/wf-artic \
--scheme_name SARS-CoV-2 \
--scheme_version V1200 \
--min_len 200 \
--max_len 1100 \
--out_dir PATH_TO_OUTPUT \
--fastq PATH_TO_FASTQ_PASS \
-work-dir PATH_TO_INTERMEDIATE_FILES
Type the command into you linux terminal and press enter.

Nextflow will describe the analysis as it progresses; the figure above shows an example run from a 48-plex analysis. We can see which processes have completed and the processes that are still running and or queued.
Parameter definitions
nextflow run epi2me-labs/wf-articAn instruction to use the Nextflow software to run a workflow, which is further explained here.--scheme_name SARS-CoV-2An instruction for the ARTIC software to use the primer scheme that corresponds to the amplicons tiled across the whole SARS-CoV-2 genome.--scheme_version V1200This defines the version of the ARTIC primers to use. The Midnight protocol uses the primer set refered to as V1200.–-min_len 200This sets the minimum allowed sequence length as 200 nucleotides.–-max_len 1100This sets the maximum allowed sequence length as 1100 nucleotides.--out_dir PATH_TO_OUTPUTThis instructs the Nextflow software where the results should be stored; please change PATH_TO_OUTPUT to the location on your computer where files should be stored.--fastq PATH_TO_FASTQ_PASSThis instructs Nextflow which sequences should be used in the analysis. Please changePATH_TO_FASTQ_PASSto an existingfastq_passfolder from a Midnight run.-work_dir PATH TO WORK DIRECTORYPlease note the single hyphen; this is a Nextflow parameter. This defines where the intermediate files are stored. This folder may contain a significant amount of information; please see the section on housekeeping.
Other command line parameters
Other commands and options can be provided to the Nextflow command:
--samplesThis describes a sample file that links barcode identifier with sample names. These sample names will be reported in the HTML format report and in the CSV file of genotypes. The sample file should be a comma-delimited file and must contain the column names barcode andsample_name.--helpThis will display the help-file which describes the available parameters and other information on default values and their meanings.--medaka_modelThis defines the model that should be used by the Medaka software for variant calling (and thus consensus preparation).
Basecalling model
If you are basecalling using a FAST model, then this should be changed to reflect the appropriate model and version of Guppy used.
- Default model used: r941_min_hac_variant_g507.
- If you have used FAST basecalling, please use: r941_min_fast_variant_g507.
- If HAC basecalling was performed using an earlier version of MinKNOW, please use: r941_min_high_g360.
Result files
Results will be written to the location specified by the --out_dir parameter. These output results include:
all_consensus.fastaA multi-FASTA format sequence file containing the consensus sequence for each of the samples investigated. This consensus sequence has been prepared for the whole SARS-CoV-2 genome, not just the spike protein region. The consensus sequence masks the non-spike regions and regions of low sequence coverage with N residues.all_variants.vcf.gzA gzipped VCF file that describes all high-quality genetic variants called by medaka from the sequenced samples.all_variants.vcf.gz.tbiAn index file for the gzipped VCF file.consensus_status.txtA tab delimited file that reports whether a consensus sequence has been successfully prepared for a sample, or not.wf-artic-report.htmlA report summarising these data. This HTML format report also includes the output of the Nextclade software that can be used for a visual inspection of, for example, primer drop out or other qualitative consensus sequence aspects.
Other files are included in the work-directory. This includes per sample VCF files of all genetic variants prior to filtering and other sequences.
Housekeeping and disk usage
The nextflow parameter, -work-dir, was introduced as a parameter to define where the workflow intermediate files are stored. This folder will accumulate a significant number of files that correspond to raw BAM files and other larger intermediates. We recommend this folder to be routinely cleared.
Updating the wf-artic software
Updated versions of the wf-artic software may be released and an alert to the availability of newer workflow versions will be noted by the Nextflow software at run-time.
To update the software:
nextflow pull epi2me-labs/wf-artic
It may be necessary to first delete the cached workflow files. This can be achieved with the command:
nextflow drop -f epi2me-labs/wf-artic
9. Flow cell reuse and returns
材料
- 测序芯片清洗剂盒(EXP-WSH004)
After your sequencing experiment is complete, if you would like to reuse the flow cell, please follow the Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol and store the washed flow cell at +2°C to +8°C.
The Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol is available on the Nanopore Community.
We recommend you to wash the flow cell as soon as possible after you stop the run. However, if this is not possible, leave the flow cell on the device and wash it the next day.
Alternatively, follow the returns procedure to send the flow cell back to Oxford Nanopore.
Instructions for returning flow cells can be found here.
If you encounter issues or have questions about your sequencing experiment, please refer to the Troubleshooting Guide that can be found in the online version of this protocol.
10. Issues during DNA/RNA extraction and library preparation
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Low sample quality
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low DNA purity (Nanodrop reading for DNA OD 260/280 is <1.8 and OD 260/230 is <2.0–2.2) | The DNA extraction method does not provide the required purity | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants document. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. Consider performing an additional SPRI clean-up step. |
| Low RNA integrity (RNA integrity number <9.5 RIN, or the rRNA band is shown as a smear on the gel) | The RNA degraded during extraction | Try a different RNA extraction method. For more info on RIN, please see the RNA Integrity Number document. Further information can be found in the DNA/RNA Handling page. |
| RNA has a shorter than expected fragment length | The RNA degraded during extraction | Try a different RNA extraction method. For more info on RIN, please see the RNA Integrity Number document. Further information can be found in the DNA/RNA Handling page. We recommend working in an RNase-free environment, and to keep your lab equipment RNase-free when working with RNA. |
Low DNA recovery after AMPure bead clean-up
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Low recovery | DNA loss due to a lower than intended AMPure beads-to-sample ratio | 1. AMPure beads settle quickly, so ensure they are well resuspended before adding them to the sample. 2. When the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio is lower than 0.4:1, DNA fragments of any size will be lost during the clean-up. |
| Low recovery | DNA fragments are shorter than expected | The lower the AMPure beads-to-sample ratio, the more stringent the selection against short fragments. Please always determine the input DNA length on an agarose gel (or other gel electrophoresis methods) and then calculate the appropriate amount of AMPure beads to use. 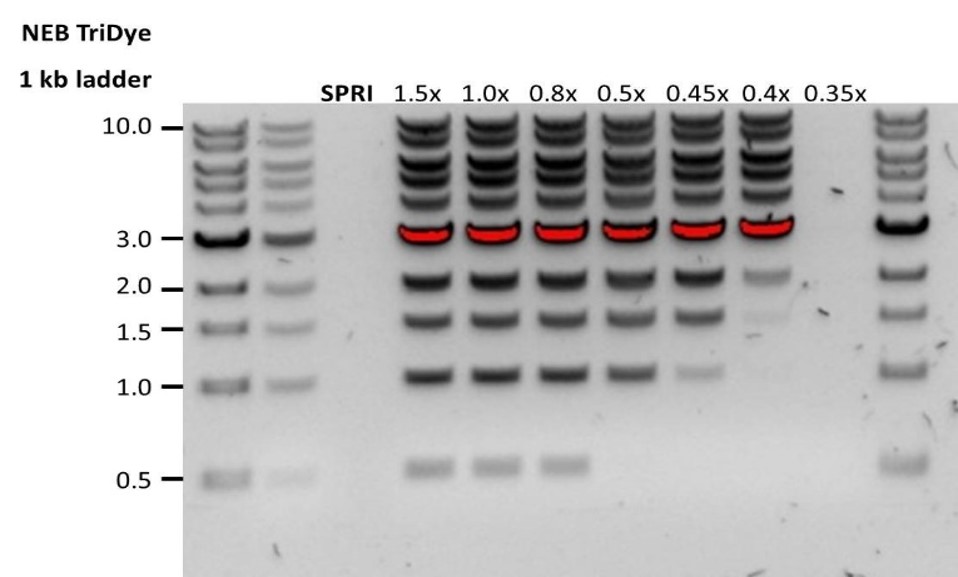 |
| Low recovery after end-prep | The wash step used ethanol <70% | DNA will be eluted from the beads when using ethanol <70%. Make sure to use the correct percentage. |
11. Issues during the sequencing run
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Fewer pores at the start of sequencing than after Flow Cell Check
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | An air bubble was introduced into the nanopore array | After the Flow Cell Check it is essential to remove any air bubbles near the priming port before priming the flow cell. If not removed, the air bubble can travel to the nanopore array and irreversibly damage the nanopores that have been exposed to air. The best practice to prevent this from happening is demonstrated in this video. |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | The flow cell is not correctly inserted into the device | Stop the sequencing run, remove the flow cell from the sequencing device and insert it again, checking that the flow cell is firmly seated in the device and that it has reached the target temperature. If applicable, try a different position on the device (GridION/PromethION). |
| MinKNOW reported a lower number of pores at the start of sequencing than the number reported by the Flow Cell Check | Contaminations in the library damaged or blocked the pores | The pore count during the Flow Cell Check is performed using the QC DNA molecules present in the flow cell storage buffer. At the start of sequencing, the library itself is used to estimate the number of active pores. Because of this, variability of about 10% in the number of pores is expected. A significantly lower pore count reported at the start of sequencing can be due to contaminants in the library that have damaged the membranes or blocked the pores. Alternative DNA/RNA extraction or purification methods may be needed to improve the purity of the input material. The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
MinKNOW script failed
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Script failed" | Restart the computer and then restart MinKNOW. If the issue persists, please collect the MinKNOW log files and contact Technical Support. If you do not have another sequencing device available, we recommend storing the flow cell and the loaded library at 4°C and contact Technical Support for further storage guidance. |
Pore occupancy below 40%
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Pore occupancy <40% | Not enough library was loaded on the flow cell | Ensure you load the recommended amount of good quality library in the relevant library prep protocol onto your flow cell. Please quantify the library before loading and calculate mols using tools like the Promega Biomath Calculator, choosing "dsDNA: µg to pmol" |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and sequencing adapters did not ligate to the DNA | Make sure to use the NEBNext Quick Ligation Module (E6056) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Buffer (LNB, provided in the sequencing kit) at the sequencing adapter ligation step, and use the correct amount of each reagent. A Lambda control library can be prepared to test the integrity of the third-party reagents. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | The Ligation Sequencing Kit was used, and ethanol was used instead of LFB or SFB at the wash step after sequencing adapter ligation | Ethanol can denature the motor protein on the sequencing adapters. Make sure the LFB or SFB buffer was used after ligation of sequencing adapters. |
| Pore occupancy close to 0 | No tether on the flow cell | Tethers are adding during flow cell priming (FLT/FCT tube). Make sure FLT/FCT was added to FB/FCF before priming. |
Shorter than expected read length
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Shorter than expected read length | Unwanted fragmentation of DNA sample | Read length reflects input DNA fragment length. Input DNA can be fragmented during extraction and library prep. 1. Please review the Extraction Methods in the Nanopore Community for best practice for extraction. 2. Visualise the input DNA fragment length distribution on an agarose gel before proceeding to the library prep. 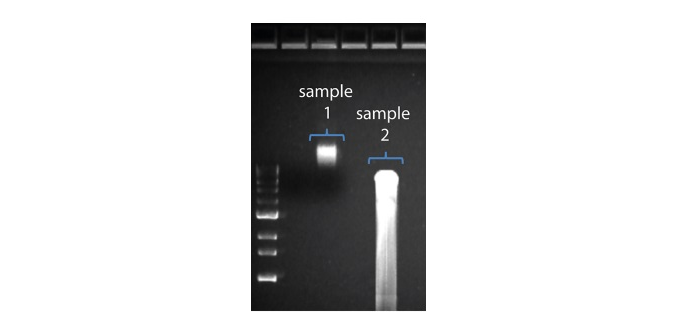 In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented. In the image above, Sample 1 is of high molecular weight, whereas Sample 2 has been fragmented.3. During library prep, avoid pipetting and vortexing when mixing reagents. Flicking or inverting the tube is sufficient. |
Large proportion of unavailable pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
Large proportion of unavailable pores (shown as blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot) 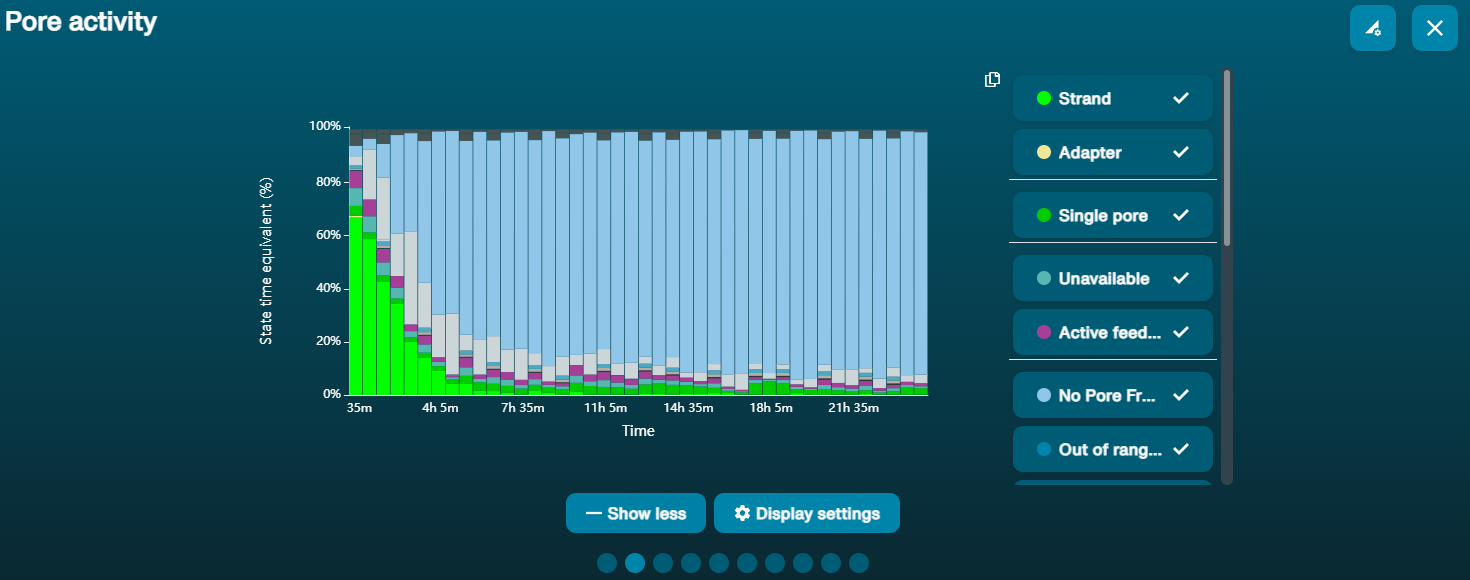 The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. The pore activity plot above shows an increasing proportion of "unavailable" pores over time. | Contaminants are present in the sample | Some contaminants can be cleared from the pores by the unblocking function built into MinKNOW. If this is successful, the pore status will change to "sequencing pore". If the portion of unavailable pores stays large or increases: 1. A nuclease flush using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) can be performed, or 2. Run several cycles of PCR to try and dilute any contaminants that may be causing problems. |
Large proportion of inactive pores
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores (shown as light blue in the channels panel and pore activity plot. Pores or membranes are irreversibly damaged) | Air bubbles have been introduced into the flow cell | Air bubbles introduced through flow cell priming and library loading can irreversibly damage the pores. Watch the Priming and loading your flow cell video for best practice |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Certain compounds co-purified with DNA | Known compounds, include polysaccharides, typically associate with plant genomic DNA. 1. Please refer to the Plant leaf DNA extraction method. 2. Clean-up using the QIAGEN PowerClean Pro kit. 3. Perform a whole genome amplification with the original gDNA sample using the QIAGEN REPLI-g kit. |
| Large proportion of inactive/unavailable pores | Contaminants are present in the sample | The effects of contaminants are shown in the Contaminants Know-how piece. Please try an alternative extraction method that does not result in contaminant carryover. |
Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction in sequencing speed and q-score later into the run | For Kit 9 chemistry (e.g. SQK-LSK109), fast fuel consumption is typically seen when the flow cell is overloaded with library (please see the appropriate protocol for your DNA library to see the recommendation). | Add more fuel to the flow cell by following the instructions in the MinKNOW protocol. In future experiments, load lower amounts of library to the flow cell. |
Temperature fluctuation
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature fluctuation | The flow cell has lost contact with the device | Check that there is a heat pad covering the metal plate on the back of the flow cell. Re-insert the flow cell and press it down to make sure the connector pins are firmly in contact with the device. If the problem persists, please contact Technical Services. |
Failed to reach target temperature
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| MinKNOW shows "Failed to reach target temperature" | The instrument was placed in a location that is colder than normal room temperature, or a location with poor ventilation (which leads to the flow cells overheating) | MinKNOW has a default timeframe for the flow cell to reach the target temperature. Once the timeframe is exceeded, an error message will appear and the sequencing experiment will continue. However, sequencing at an incorrect temperature may lead to a decrease in throughput and lower q-scores. Please adjust the location of the sequencing device to ensure that it is placed at room temperature with good ventilation, then re-start the process in MinKNOW. Please refer to this link for more information on MinION temperature control. |
Guppy – no input .fast5 was found or basecalled
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| No input .fast5 was found or basecalled | input_path did not point to the .fast5 file location | The --input_path has to be followed by the full file path to the .fast5 files to be basecalled, and the location has to be accessible either locally or remotely through SSH. |
| No input .fast5 was found or basecalled | The .fast5 files were in a subfolder at the input_path location | To allow Guppy to look into subfolders, add the --recursive flag to the command |
Guppy – no Pass or Fail folders were generated after basecalling
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| No Pass or Fail folders were generated after basecalling | The --qscore_filtering flag was not included in the command | The --qscore_filtering flag enables filtering of reads into Pass and Fail folders inside the output folder, based on their strand q-score. When performing live basecalling in MinKNOW, a q-score of 7 (corresponding to a basecall accuracy of ~80%) is used to separate reads into Pass and Fail folders. |
Guppy – unusually slow processing on a GPU computer
| Observation | Possible cause | Comments and actions |
|---|---|---|
| Unusually slow processing on a GPU computer | The --device flag wasn't included in the command | The --device flag specifies a GPU device to use for accelerate basecalling. If not included in the command, GPU will not be used. GPUs are counted from zero. An example is --device cuda:0 cuda:1, when 2 GPUs are specified to use by the Guppy command. |







