Getting started RNA guide SQK-RNA004 (GSR_9203_v1_revA_19Jan2024)
Windows: Guide
Getting started RNA guide SQK-RNA004 V GSR_9203_v1_revA_19Jan2024
We aim to walk you through the set up of your MinION Mk1B and your control sequencing experiment.
Before you start sequencing your own RNA samples, we recommend that you sequence a control sample of the yeast enolase-2 transcript, which is supplied in your sequencing kit. Sequencing a control sample allows you to practise performing an end-to-end nanopore sequencing experiment and to become familiar with the technology.
The whole set up process typically takes 4 hours. Once started, the sequencing run takes 6 hours, but can be left unattended.
If at any point you get stuck, look out for explainers and FAQs to help you.
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Software installation
Hardware check
Flow cell check
Library preparation
- 9. Prepare your reagents
- 10. Reverse-transcribe your RNA
- 11. Ligate sequencing adapters to the RNA fragment ends
Sequencing run
- 12. Prepare your flow cell
- 13. Prepare your priming mix
- 14. Prime your flow cell
- 15. Prepare your pre-sequencing mix
- 16. Load your flow cell
- 17. Start your run
Results and metrics
- 18. Your data in MinKNOW
- 19. Experiment screen
- 20. How to assess the quality of your run
- 21. After 6 hours
Next steps
概要
We aim to walk you through the set up of your MinION Mk1B and your control sequencing experiment.
Before you start sequencing your own RNA samples, we recommend that you sequence a control sample of the yeast enolase-2 transcript, which is supplied in your sequencing kit. Sequencing a control sample allows you to practise performing an end-to-end nanopore sequencing experiment and to become familiar with the technology.
The whole set up process typically takes 4 hours. Once started, the sequencing run takes 6 hours, but can be left unattended.
If at any point you get stuck, look out for explainers and FAQs to help you.
1. Select your operating system
Select your operating system
Please select your operating system here. You will be presented with instructions specific to your OS for downloading and installing the software needed for nanopore sequencing.
2. Before you start...
装置
- Compatible computer
- Internet access
Turn off sleep modes
Turn off sleep modes:
- Navigate to Start > 'Settings' > 'System' > 'Power & Sleep'
- Set 'Sleep modes' to Never
Ensure your computer is plugged into a power source
Ensure your computer is plugged into a power source.
Defer Windows upgrades
Defer Windows upgrades:
- Navigate to Start > 'Settings' > ' Update & Security' > 'Windows Update' > 'Advanced options'
- Tick the Defer upgrades box
Note: on some versions of Windows, this will be called 'Pause updates'.
Check that you have sufficient disk space
Check that you have sufficient disk space. A typical Control experiment will require approximately 40 GB of space. However, for a full sequencing experiment using your own DNA or RNA sample, a minimum of 1 TB storage space is recommended. Please see this FAQ for more information.
Turn off the anti-virus
Turn off your anti-virus for the software download steps. You can enable it again once the software is installed on your computer.
Confirm that you have the required firewall settings
Confirm with your IT department that you have the firewall settings described in this FAQ.
If you are working behind a proxy
If you are working behind a proxy, follow the instructions in this FAQ, and speak to your IT department before implementing any changes.
3. Download and install MinKNOW
Note that you may be asked to reboot your computer before installation.
You may be asked to reboot your computer before installation. In case this happens, bookmark this page so you can return to it easily.
Install MinKNOW
Double-click the .exe file to run the MinKNOW installer.

Install MinKNOW
Allow the installer to make changes to your computer.
In the pop-up window, click Next.

Complete install
When the installer is complete, click Close.

Open MinKNOW
You will see the MinKNOW icon on your Desktop. Double-click on the icon to open the software and login using your Community login credentials.
![]()

You will be prompted to enter your email address and Nanopore password:
Deal with install issues
If the error message “MinKNOW was not successfully installed…please run the installer manually" appears, please follow the instructions in this FAQ.
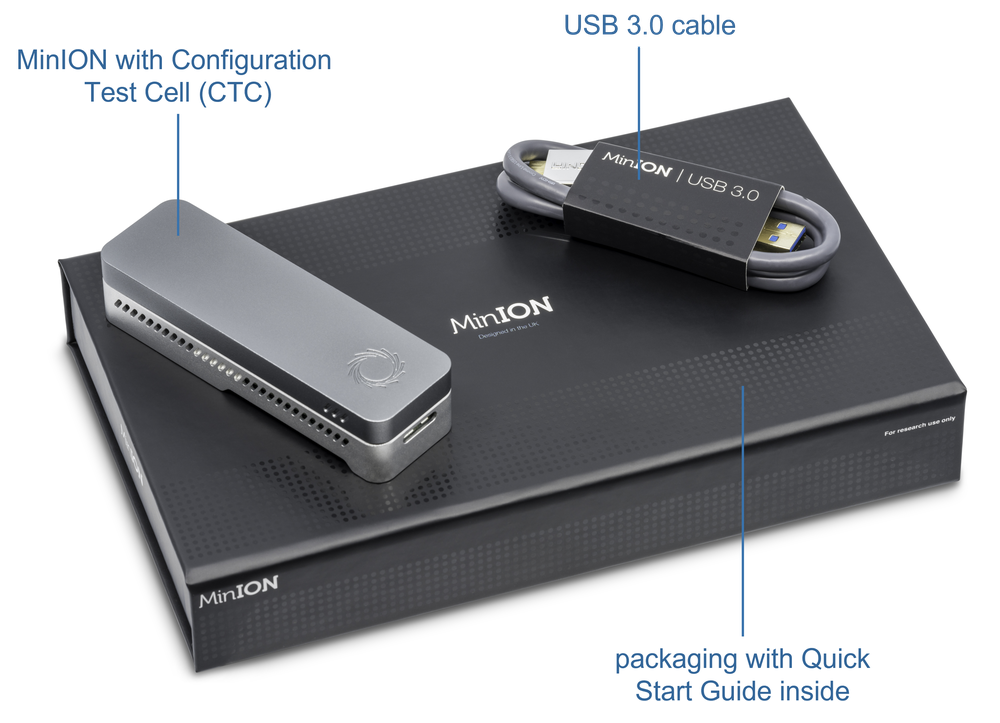
4. What's in the box?
装置
- MinION Mk1B device
- Configuration test cell
- USB 3.0 cable
- Compatible computer with software set up in previous section
Check your box contains your MinION Mk1B device, configuration test cell and USB 3.0 cable
Check your box contains your MinION Mk1B device, Configuration Test Cell and USB 3.0 cable.

5. Install the MinION Mk1D device
The MinION Mk1D arrives with the configuration test cell already inserted. If the configuration test cell is separate, insert it into the MinION Mk1D and connect your MinION to the computer via the USB cable provided.
The MinION Mk1D arrives with the configuration test cell already inserted. The configuration test cell is of a similar shape to the flow cells, but white.
If the configuration test cell is separate, insert it into the MinION Mk1D and connect your MinION to the computer.
If you have multiple USB ports, please ensure the MinION Mk1B is plugged into the USB 3.0 port. On Windows computers, the USB 3.0 port is either coloured blue, or marked with 'SS' or "3.0"
If you have multiple USB ports, please ensure the MinION Mk1B is plugged into the USB 3.0 port.
On Windows computers, the USB 3.0 port is either coloured blue, or marked with "SS" or "3.0".
If you don't have a USB 3.0 port, please see this FAQ.
Check that the MinION Mk1B device is recognised by your computer.
Check that the MinION Mk1B device is recognised by your computer.
The MinION Mk1B status will be displayed on the Sequencing Overview page. The flow cell in the image below is ready for a hardware check.
The MinION Mk1B status will be displayed on the Sequencing Overview page. The flow cell in the image below is ready for a hardware check.

Navigate to the Start homepage and select the __Hardware Check__.
Navigate to the Start homepage and select the Hardware Check.

6. Hardware check
Select 'Start'.
Select Start.

The user will be automatically navigated to the System Overview page. A loading bar will be displayed under the flow cell during the checks.
The user will be automatically navigated to the System Overview page. A loading bar will be displayed under the flow cell during the checks.
The hardware check will complete after approximately one minute. A pass is indicated by a green check icon and a fail is an orange check.
The hardware check will complete after approximately one minute. A pass is indicated by a green check icon and a fail is an orange check.

Section 2 complete
You have now confirmed that the MinION Mk1B device is working correctly and can communicate with the MinKNOW control software.
7. Insert flow cell
材料
- MinION Mk1B, USB3 cable and compatible computer - set up in previous sections
- Flow cell
Take out the configuration test cell from the MinION Mk1B. You do not need to disconnect the MinION Mk1B from the computer, or close any software.
Take out the configuration test cell from the MinION Mk1B. You do not need to disconnect the MinION Mk1B from the computer, or close any software.
Push the flow cell into the clip, ensuring good contact between the flow cell and the MinION Mk1B. Close the lid.
Push the flow cell into the clip, ensuring good contact between the flow cell and the MinION Mk1B. Close the lid.

Press down on flowcell
Having a good connection will ensure correct temperature during sequencing so press down on the flow cell to ensure good contact between the flow cell and the MinION Mk1B.
Close the MinION Mk1B lid.
Close the MinION Mk1B lid.
Check flow cell connects
Navigate to the Sequencing overview page to check the MinKNOW software has detected the inserted flow cell.

8. Flow cell check
Navigate to the Start homepage and select 'Flow Cell Check'.
Navigate to the Start homepage and select Flow Cell Check.

The flow cell type will be recognised by the device. Click 'Start' to begin.
The flow cell type will be recognised by the device. Click 'Start' to begin.

The user will be automatically navigated to the System Overview page. A loading bar will be displayed under the flow cell during the checks.
The user will be automatically navigated to the System Overview page. A loading bar will be displayed under the flow cell during the checks.
The flow cell will cycle through the 2048 wells to see how many pores are active on the sensor array. It will do this in four groups of 512 at a time.
Wait for temperature
There may be a slight delay while the MinION Mk1B reaches its optimal sequencing temperature, as shown in the progress bar at the top of the GUI.
Please see this FAQ for more information.
Flow cell check complete
Flow cell check completion will be indicated on the System Overview page with an icon on the flow cell with the number of pores available.

At the end of the flow cell check, MinKNOW will report the total number of nanopores in the flow cell, and the number of pores in each of the four groups. The warranty for flow cells covers 800 pores or above. If you have fewer than 800 pores, please contact support@nanoporetech.com
At the end of the flow cell check, MinKNOW will report the total number of nanopores in the flow cell.
The warranty for flow cells covers 800 pores or above. If you have fewer than 800 pores, please follow the instructions in this FAQ. If you still see under 800 pores, contact support@nanoporetech.com .
Section 3 complete
You have confirmed that your flow cell is working correctly and is ready for sequencing a biological sample, which you will prepare in the next section.
9. Prepare your reagents
材料
- Direct RNA Sequencing Kit (SQK-RNA004)
消耗品
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- 0.2 ml 薄壁のPCRチューブ
- Nuclease-free water (e.g. ThermoFisher, AM9937)
- Freshly prepared 70% ethanol in nuclease-free water
- SuperScript™ III Reverse Transcriptase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat # 18080044)
- 10 mM dNTP solution (e.g. NEB N0447)
- T4 DNA Ligase 2M U/ml (NEB, cat # M0202M)
- RNaseOUT™ Recombinant Ribonuclease Inhibitor (Invitrogen, 10777019)
- NEBNext® Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer (NEB, B6058)
- Agencourt RNAClean XP beads (Beckman Coulter™, cat # A63987)
- Qubit RNA HS Assay Kit (ThermoFisher, Q32852)
- Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (ThermoFisher, Q32851)
- Qubit™ Assay Tubes (Invitrogen, Q32856)
装置
- P1000 ピペット及びチップ
- P200 ピペットとチップ
- P100 ピペットとチップ
- P20 ピペットとチップ
- P10 ピペットとチップ
- P2 ピペットとチップ
- Hula mixer(緩やかに回転するミキサー)
- マグネットラック
- タイマー
- 小型遠心機
- アイスバケツ(氷入り)
- ボルテックスミキサー
- サーマルサイクラー
オプション装置
- Qubit蛍光光度計(またはQCチェックのための同等品)
Spin down the following reagents, mix them by pipetting up and down, and then keep on ice:
Keep these on ice:
- RT Adapter (RTA)
- RNA Calibration Strand (RCS)
- RNA Ligation Adapter (RLA)
- 10 mM dNTP solution
Defrost these at room temperature:
Defrost these at room temperature:
- NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer
- T4 DNA Ligase
Once the contents of each tube have thawed, spin down the tubes in a microfuge and mix the contents by pipetting up and down for 10 full-volume pipette mixes.
Once the contents of each tube have thawed, spin down the tubes in a microfuge and mix the contents by pipetting up and down for 10 full-volume pipette mixes.
Defrost these at room temperature:
Defrost these at room temperature:
- Wash Buffer (WSB)
- RNA Elution Buffer (REB)
Vortex both tubes, then spin them down and place on ice.
Vortex both tubes, then spin them down and place on ice.
Keep the reagent tubes on ice when they are not in use.
Keep the reagent tubes on ice when they are not in use.
Set up a thermal cycler with the program 50°C for 50 minutes, then 70°C for 10 minutes, then hold at 4°C. Alternatively, set two heat blocks at 50°C and 70°C.
Set up a thermal cycler with the program 50°C for 50 minutes, then 70°C for 10 minutes, then hold at 4°C. Alternatively, set two heat blocks at 50°C and 70°C.
10. Reverse-transcribe your RNA
Transfer 3 µl of NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer into a clean 0.2 ml PCR tube (Tube 1).
Transfer 3 µl of NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer into a clean 0.2 ml PCR tube (Tube 1).

Add 8.5 µl RNA Calibration Strand (RCS) to Tube 1.
Add 8.5 µl RNA Calibration Strand (RCS) to Tube 1.

Add 1 µl RNaseOUT to the tube.
Add 1 µl RNaseOUT to the tube.

Add 1 µl RT Adapter (RTA) to the tube.
Add 1 µl RT Adapter (RTA) to the tube.

Add 1.5 µl T4 DNA Ligase to the tube.
Add 1.5 µl T4 DNA Ligase to the tube.

Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Incubate Tube 1 for 10 minutes at room temperature
Incubate Tube 1 for 10 minutes at room temperature. This is the adapter ligation reaction (Tube 1).
Take a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 2), and add 9 µl nuclease-free water.
Take a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 2), and add 9 µl nuclease-free water.

Add 2 µl of 10 mM dNTPs to Tube 2.
Add 2 µl of 10 mM dNTPs to Tube 2.

Add 8 µl first strand buffer from the SuperScript III kit to Tube 2.
Add 8 µl first strand buffer from the SuperScript III kit to Tube 2.

Add 4 µl of 0.1 M DTT to Tube 2.
Add 4 µl of 0.1 M DTT to Tube 2.

Mix the contents of the tube by flicking the tube with your finger. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Mix the contents of the tube by flicking the tube with your finger. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Add the contents of the 1.5 ml tube (Tube 2) to the 0.2 ml PCR tube (Tube 1) containing the RT adapter ligated RNA.
Add the contents of the 1.5 ml tube (Tube 2) to the 0.2 ml PCR tube (Tube 1) containing the RT adapter ligated RNA.

Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Add 2 µl of SuperScript III reverse transcriptase to the 0.2 ml tube (Tube 1).
Add 2 µl of SuperScript III reverse transcriptase to the 0.2 ml tube (Tube 1).

Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Incubate in heat blocks or a thermal cycler at 50°C for 50 minutes, then at 70°C for 10 minutes, then bring the reaction to 4°C on ice for approximately 30-60 seconds.
Incubate in heat blocks or a thermal cycler at 50°C for 50 minutes, then at 70°C for 10 minutes, then hold at 4°C for approximately 30-60 seconds. Take the tube out from the thermal cycler or heat block, and spin down briefly in a microfuge.

Transfer the sample to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 3). Tube 3 is the reverse transcription reaction.
Transfer the sample to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 3). Tube 3 is the reverse transcription reaction.

Resuspend the Agencourt RNAClean XP beads by vortexing.
Resuspend the Agencourt RNAClean XP beads by vortexing.
Add 72 µl of resuspended RNAClean XP beads to the reverse transcription reaction (Tube 3), and mix by pipetting up and down.
Add 72 µl of resuspended RNAClean XP beads to the reverse transcription reaction (Tube 3), and mix by pipetting up and down.

Put the tube in a Hula mixer, and leave to incubate for 5 minutes.
Put the tube in a Hula mixer, and leave to incubate for 5 minutes.
While the RNA sample is incubating, transfer 140 µl of pure ethanol to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
While the RNA sample is incubating, transfer 140 µl of pure ethanol to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.

Add 50 µl nuclease-free water to the ethanol.
Add 50 µl nuclease-free water to the ethanol.

Mix the tube of diluted ethanol by vortexing. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Mix the tube of diluted ethanol by vortexing. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Take Tube 3 with the reverse transcription reaction off the Hula mixer, and spin down in a microfuge.
Take Tube 3 with the reverse transcription reaction off the Hula mixer, and spin down in a microfuge.
Place the tube in a magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet, and the solution to become clear.
Place the tube in a magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet, and the solution to become clear.

Keep the tube on the magnet to pipette off and discard the supernatant. Take care not to disturb the pellet.
Keep the tube on the magnet to pipette off and discard the supernatant. Take care to not disturb the pellet.

Add 150 µl of the freshly-prepared ethanol to Tube 3, without taking the tube off the magnetic rack or disturbing the pellet.
Add 150 µl of the freshly-prepared ethanol to Tube 3, without taking the tube off the magnetic rack or disturbing the pellet.

Keeping the magnetic rack on the benchtop, rotate the bead-containing tube by 180°. Wait for the beads to migrate towards the magnet and form a pellet.
Rotate the tube 180° again (back to the starting position), and wait for the beads to pellet.
After this, pipette off and discard the ethanol.
Take the tube off the magnetic rack and spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Take the tube off the magnetic rack and spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Place the tube back in the magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet. There may be a small amount of residual liquid at the bottom of the tube. Pipette off and discard this liquid.
Place the tube back in the magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet. There may be a small amount of residual liquid at the bottom of the tube. Pipette off and discard this liquid.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack, add 20 µl nuclease-free water to the tube, and resuspend the beads by flicking the tube.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack, add 20 µl nuclease-free water to the tube, and resuspend the beads by flicking the tube.
Incubate for 5 minutes at room temperature.

Place the tube back in the magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet.
Place the tube back in the magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet.
Pipette off the 20 µl of eluate from Tube 3, and transfer it to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 4). Discard the Tube 3 with the pellet.
Pipette off the 20 µl of eluate from Tube 3, and transfer it to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 4). Discard Tube 3 with the pellet and retain Tube 4 with the eluate.

Reverse transcription complete
You now have 20 µl of reverse-transcribed RNA (Tube 4), and are ready to ligate sequencing adapters to the cDNA ends.
11. Ligate sequencing adapters to the RNA fragment ends
Add 8 µl of NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer to your reverse-transcribed RNA (Tube 4).
Add 8 µl of NEBNext Quick Ligation Reaction Buffer to your reverse-transcribed RNA (Tube 4).

Add 6 µl of RNA Ligation Adapter (RLA) to Tube 4.
Add 6 µl of RNA Ligation Adapter (RLA) to Tube 4.

Add 3 µl nuclease-free water to the tube.
Add 3 µl nuclease-free water to the tube.

Add 3 µl T4 DNA Ligase to the tube.
Add 3 µl T4 DNA Ligase to the tube.

Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Mix the contents of the tube by pipetting up and down. Spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Incubate Tube 4 for 10 minutes at room temperature. This is the adapter ligation reaction (Tube 4).
Incubate Tube 4 for 10 minutes at room temperature. This is the adapter ligation reaction (Tube 4).
Resuspend the Agencourt RNAClean XP beads by vortexing.
Resuspend the Agencourt RNAClean XP beads by vortexing.
Add 16 µl of resuspended RNAClean XP beads to the adapter ligation reaction (Tube 4), and mix by pipetting up and down.
Add 16 µl of resuspended RNAClean XP beads to the adapter ligation reaction (Tube 4), and mix by pipetting up and down.

Put the tube in a Hula mixer, and leave to incubate for 5 minutes.
Put the tube in a Hula mixer, and leave to incubate for 5 minutes.
Take Tube 4 with the reverse transcription reaction off the Hula mixer, and spin down in a microfuge.
Take Tube 4 with the reverse transcription reaction off the Hula mixer, and spin down in a microfuge.
Place the tube in a magnetic rack and wait for 5 minutes for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet, and the solution to become clear.
Place the tube in a magnetic rack and wait for 5 minutes for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet and the solution to become clear.

Keep the tube on the magnet to pipette off and discard the supernatant. Take care not to disturb the pellet.
Keep the tube on the magnet to pipette off and discard the supernatant. Take care to not disturb the pellet.

Add 150 µl of Wash Buffer (WSB) to the tube. Close the tube lid, and resuspend the beads by flicking the tube with your finger.
Add 150 µl of Wash Buffer (WSB) to Tube 4. Close the tube lid, and resuspend the beads by flicking the tube with your finger.
Return the tube to the magnetic rack, allow the beads to pellet, then pipette off and discard the buffer.

Place the tube in a magnetic rack and wait for 5 minutes for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet, and the solution to become clear.
Place the tube in a magnetic rack and wait for 5 minutes for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet and the solution to become clear.

Keep the tube on the magnet to pipette off and discard the supernatant. Take care not to disturb the pellet.
Keep the tube on the magnet to pipette off and discard the supernatant. Take care to not disturb the pellet.

Repeat the previous three steps.
Repeat the previous three steps: Add 150 µl of Wash Buffer (WSB) to Tube 4. Close the tube lid, and resuspend the beads by flicking the tube with your finger.
Return the tube to the magnetic rack, allow the beads to pellet for 5 minutes, then pipette off and discard the buffer.
Take the tube off the magnetic rack and spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Take the tube off the magnetic rack and spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Place the tube back in the magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet. There may be a small amount of residual liquid at the bottom of the tube. Pipette off and discard this liquid.
Place Tube 2 back in the magnetic rack, and wait for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet. There may be a small amount of residual liquid at the bottom of the tube. Pipette off and discard this liquid.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack, add 13 µl RNA Elution Buffer (REB) to the tube, and resuspend the beads by flicking the tube.
Remove the tube from the magnetic rack, add 13 µl RNA Elution Buffer (REB) to the tube, and resuspend the beads by flicking the tube.
Incubate for 10 minutes at room temperature.

Place the tube in a magnetic rack and wait for 5 minutes for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet, and the solution to become clear.
Place the tube in a magnetic rack and wait for 5 minutes for the beads to collect in a pellet near the magnet and the solution to become clear.

Pipette off the 13 µl of eluate from Tube 4 and transfer it to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 5). Discard Tube 4 with the pellet.
Pipette off the 13 µl of eluate from Tube 4 and transfer it to a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 5). Discard Tube 4 with the pellet.

Remove 1 µl of eluate from Tube 5 and use the Qubit fluorometer DNA HS assay to quantify the amount of cDNA in the sample.
Remove 1 µl of eluate from Tube 5 and use the Qubit fluorometer DNA HS assay to quantify the amount of RNA in the sample.

Section 4 complete.
You have now prepared control RNA library ready for nanopore sequencing. You will use this shortly once the flow cell has been primed. It will be referred to as Control RNA library (Tube 5).
12. Prepare your flow cell
材料
- Flow cell, MinION Mk1B, USB3 cable and compatible computer - set up in previous sections
- Control RNA library
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P100 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- Nuclease-free water
- RNA Flush Tether (RFT)
- Flow Cell Flush (FCF)
- Sequencing Buffer (SB)
- Library Solution (LIS)
- MinION Flow Cell Light Shield
About flow cells
The following steps will introduce you to flow cell fluidics and handling.
Flow cells are shipped with storage buffer to maintain product integrity. The priming step flushes out the storage buffer and replaces it with a mix of Flow Cell Flush (FCF) and RNA Flush Tether (RFT). The RNA library is then loaded into the flow cell.
Throughout the process it is essential that the sensor array remains submerged in buffer at all times. If an air bubble passes over any channels, those pores will be permanently damaged. It is therefore important to avoid introducing air in the pipette tips, and remove any air bubbles in the flow cell ports.
Priming and loading sample into flow cells is best done with minimal movement. For this reason, please do all subsequent steps on a MinION Mk1B device on a flat surface.
The video below highlights good practices for priming and loading the flow cell:
13. Prepare your priming mix
材料
- Flow Cell Flush (FCF)
- RNA Flush Tether (RFT)
装置
- P1000 ピペット及びチップ
- P100 ピペットとチップ
- ボルテックスミキサー
- 小型遠心機
Make sure the contents of the Flow Cell Flush (FCF) and RNA Flush Tether (RFT) tubes are fully defrosted. Mix the tubes by vortexing, and then spin down in a microfuge.
Make sure the contents of the Flow Cell Flush (FCF) and RNA Flush Tether (RFT) tubes are fully defrosted. Mix the tubes by vortexing and then spin down in a microfuge.
Take a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 6) and add 1,170 µl of Flow Cell Flush (FCF).
Take a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube (Tube 6) and add 1,170 µl of Flow Cell Flush (FCF).

Add 30 µl of RNA Flush Tether (RFT) to Tube 6.
Add 30 µl of RNA Flush Tether (RFT) to Tube 6.

Mix
Mix the contents of the tube by vortexing and then spin down briefly in a microfuge.
Priming Mix
The resulting buffer is now referred to as the Priming Mix (Tube 6). You will use this to flush out the storage buffer from the flow cell.
14. Prime your flow cell
Pipetting tips for flow cells
Pipetting tips
The following section will load fluid and sample into the flow cell. In the images below are some simple tips on pipetting technique which are essential to avoid introducing air bubbles and damaging the sensor array.
When drawing up solution:
- make sure there is no air plug at the bottom of the tip
When ejecting the solution:
- do not fully expel the liquid from the tip
- leave a small volume in the tip end so that no air can follow the solution into the inlet port

Open priming port
Open the priming port by sliding the cover clockwise so that the port is visible.

Do not remove storage buffer
- When carrying out the next step, do not remove a large volume of the storage buffer - the sensor array must stay covered
- Make sure there is continuous buffer from the sensor array to the priming port, with no air bubbles
Remove inlet channel air bubble
Remove inlet channel air plug
- Set a P1000 pipette to 500 µl; insert the tip into the priming port
- Keeping the tip inserted in the port, twist the wheel of the pipette until you reach 520-530 µl, or until you see a small amount of the yellow buffer in the tip. This removes any air plug that has developed in the port during shipping and storage, and a tiny volume of buffer to wet the port
- Remove the pipette tip from the priming port, and throw away the tip

Prime your flow cell
Prime your flow cell
- Using a P1000 pipette, slowly load 800 µl of the priming mix into the priming port
- Do not eject to the last stop of the pipette; take care to not introduce air bubbles
- Close the priming port
- Wait 5 minutes

15. Prepare your pre-sequencing mix
Pre-sequencing mix intro
The pre-sequencing mix is a mix of your RNA library, Sequencing Buffer (SB) and Library Solution (LIS) that is loaded into the flow cell.
Please ensure you have completed the Flow Cell Check section before preparing your pre-sequencing mix.
Take the 1.5 ml tube containing your control RNA library and add 37.5 µl Sequencing Buffer (SB).
Take the 1.5 ml tube containing your control RNA library and add 37.5 µl Sequencing Buffer (SB).

Add 25.5 µl RNA Library Solution (LIS) to the tube.
Add 25.5 µl RNA Library Solution (LIS) to the tube.

Mix thoroughly
- Mix the contents of the tube thoroughly by flicking the tube with your finger
- Spin down briefly in a microfuge
Pre-sequencing mix
The resulting solution is known as the Pre-Sequencing Mix (Tube 5).
16. Load your flow cell
Pipetting tips for flow cells
Pipetting tips
The following section will load fluid and sample into the flow cell. In the images below are some simple tips on pipetting technique which are essential to avoid introducing air bubbles and damaging the sensor array.
When drawing up solution:
- make sure there is no air plug at the bottom of the tip
When ejecting the solution:
- do not fully expel the liquid from the tip
- leave a small volume in the tip end so that no air can follow the solution into the inlet port

How to add your sample to your flow cell
The following steps will explain how to add your sample to your flow cell.
They should be done in quick succession to ensure correct operation of the product.
Keep your MinION Mk1B flat, espescially when the sample and priming ports are open.
Open priming port
Open the priming port by sliding the cover clockwise so that the port is visible.

Open your sample port
Open the sample port by gently lifting the sample port cover. You will still need to use the priming port, so keep this open.
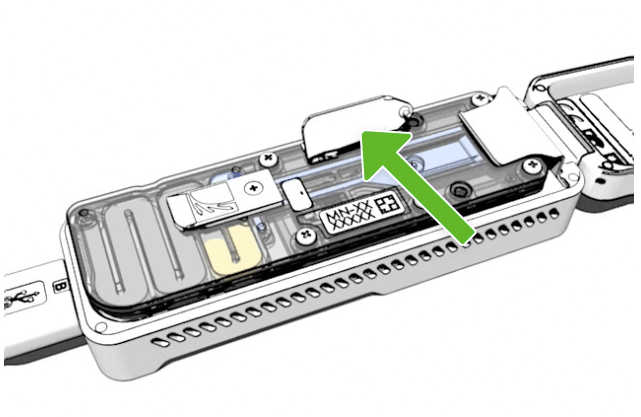
Spot On port
On the flow cell, the sample port is labelled SpotON.
Second flow cell priming step
Using a P1000 pipette, slowly load 200 µl of the Priming Mix into the priming port. Take care to not introduce air bubbles. Pipette slowly, to avoid the buffer bubbling out of the sample port. Carry out this step immediately before loading the library.
Load your sample
Using a P200 pipette, hold the pipette tip just above the sample port and slowly load 75 µl, drop by drop, of the Pre-Sequencing Mix (Tube 5).
Close flow cell ports
- Close the sample port with the cover ensuring the bung enters into the port
- Close the priming port
- Close the MinION Mk1B lid
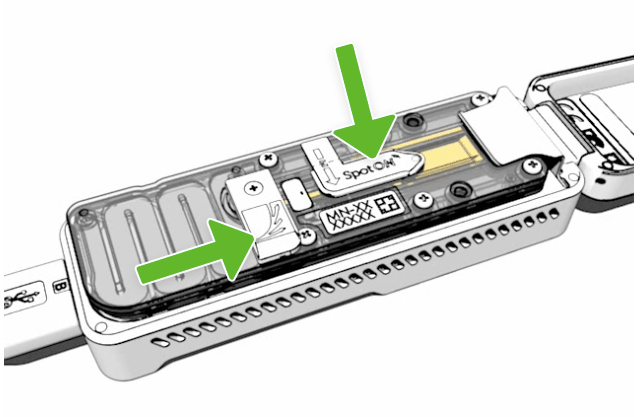
Place the light shield onto the flow cell
Place the light shield onto the flow cell. Carefully place the leading edge of the light shield against the clip. Do not force the light shield underneath the clip. Gently lower the light shield onto the flow cell. The light shield should sit around the SpotON cover, covering the entire top section of the flow cell.

17. Start your run
Check connections
Your MinION Mk1B and flow cell should still be connected. Check your MinION Mk1B is plugged in to your computer's USB 3.0 port, and the flow cell is clipped firmly into the MinION Mk1B device.
Open MinKNOW
Check the MinKNOW software is still open. If you have closed it, double-click the icon on the desktop and login.
Select Start Sequencing on the home page.
Select Start Sequencing on the home page.
Start your run
On the New experiment pop-up screen, select the running parameters for your experiment from the individual tabs.
Select positions The positions tab will show the chosen flow cell. Assign an experiment name and sample ID. The other tabs will not become available until an experiment name has been provided.
Kit selection The kit selection tab will provide a selection of available kits. Check the Control button, then click on SQK-RNA004.
Click Skip to final review.
Click Start
On the final page, there will be a summary of all the options chosen for the experiment. Click Start.
Mux scan
When sequencing is initiated, the software will move to the channel screen. The flow cell will cycle through all 2048 channels to select the best set of 512 to start the run.
Wait for temperature
There may be a slight delay while the MinION Mk1B reaches its optimal sequencing temperature, as shown in the progress bar at the top of the GUI.
Please see this FAQ for more information.
Start sequencing
Once the best combination of channels is selected, sequencing will begin on those channels automatically.
You will be indicated sequencing has started when flow cell health is displayed and a progress bar will appear beneath the flow cell.
Read file location
Your basecalled reads will be written out into the folder you specified when you installed MinKNOW. By default, this will be C:\data.
Sequencing started
Your sequencing run is now under way.
18. Your data in MinKNOW
材料
- Compatible computer - set up in previous sections
MinKNOW graphs intro
While your experiment is running, you can track how it is progressing using the MinKNOW software. To view your experiment metrics, click on the sequencing flow cell to open the quick view and a summay of the run. Use the arrows to move between real-time data, including channel panel and channel scan.

Example screen
Within the first half an hour you should have most active pores sequencing and already have obtained several thousand reads.
19. Experiment screen
Run metrics
At any time, the quick view shows how many reads you have obtained so far. After half an hour, you should already have obtained several thousand reads.
You can also monitor how the basecaller has progressed through the reads so far. Depending on sequencing system performance and computer specifications, there may be some lag between reads becoming available and being processed. This is indicated by the "Basecall statistics: Called x%". A small proportion of reads will fail - these are usually false positives and are discounted automatically.

Channel panel
This panel shows the current state of all the channels, arranged as they are located on the flow cells sensor array. Remember that the chip has 2048 wells in total, but a group of 512 channels are accessed at any one time. Each channel is classified by its current behaviour - whether it is currently sequencing, waiting for a strand, recovering, or unavailable.
The number of channels in each category depends on two factors:
- the performance of the sensor array (which is why we recommend a flow cell check)
- the performance of the sequencing sample
You should have a large number of channels in the 'Pore' (dark green) and 'Sequencing' (bright green) categories.
The majority of channels should be active, and therefore display as bright green (pore is sequencing) or dark green (pore is open and waiting for a DNA or RNA strand). If the sample added is of good quality, within a few minutes of the run starting you should see the channels going bright green as the pores capture the strands. If there is a problem with the sample preparation and there is little DNA/RNA available, they will stay dark green (empty pore). 
You will see the channels flickering as they capture a strand (turn to bright green) and briefly return to the empty state (darker green) before the next strand. You may also notice some pores occasionally become Recovering (dark blue) - this is normal behaviour, and the software will automatically reactivate them when possible.
Bubble tip
If you have a large group of channels clustered together which are light blue ('Inactive'), this may indicate an air bubble on the sensor array. In this case, these channels are permanently damaged, and it it is best not to attempt to remove the bubble as this may damage other channels as well.

Basecalling
The Translocation speed and Qscore graph allows you to monitor the performance of your flow cell. The speed and quality score values should stay within the target range (in green).


Read lengths
Note that nanopore sequencing has no inherent maximum read length. A nanopore will continue reading an RNA strand with the same accuracy until it gets to the end of the strand and it exits the pore. Therefore, the lengths of the reads obtained follows the same distribution as the lengths of the strands available to the pore from the sample.
In this kit, we use the control RNA sample, which is a S. cerevisiae enolase 2 transcript of ~1.4 kbases. However, some users may wish to user longer length strands, and with DNA, it is commonplace to generate reads hundreds of kilobases long. Others may use short strands, e.g. PCR amplicons. There are many options for sample preparation depending on DNA/RNA extraction methods, desired read length, preparation speed etc. - designed to allow users the flexibility to use nanopore sequencing for any type of sample. More information and suggested protocols can be found on the Nanopore Community. To browse the available kits, please visit the Store.
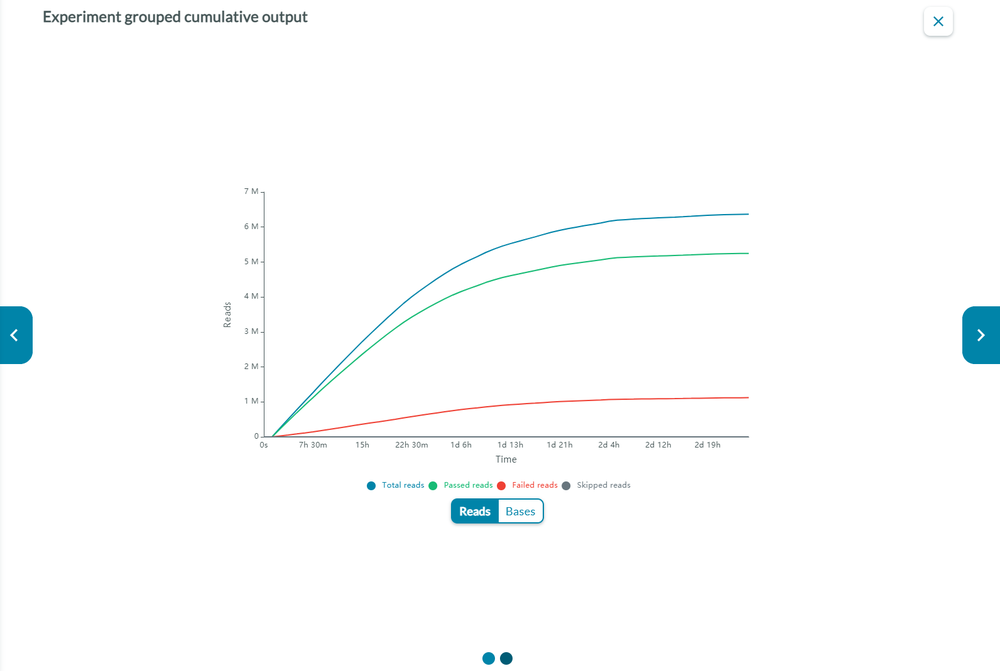
Cumulative output
The cumulative output graph shows:
the number of bases that have been sequenced and basecalled
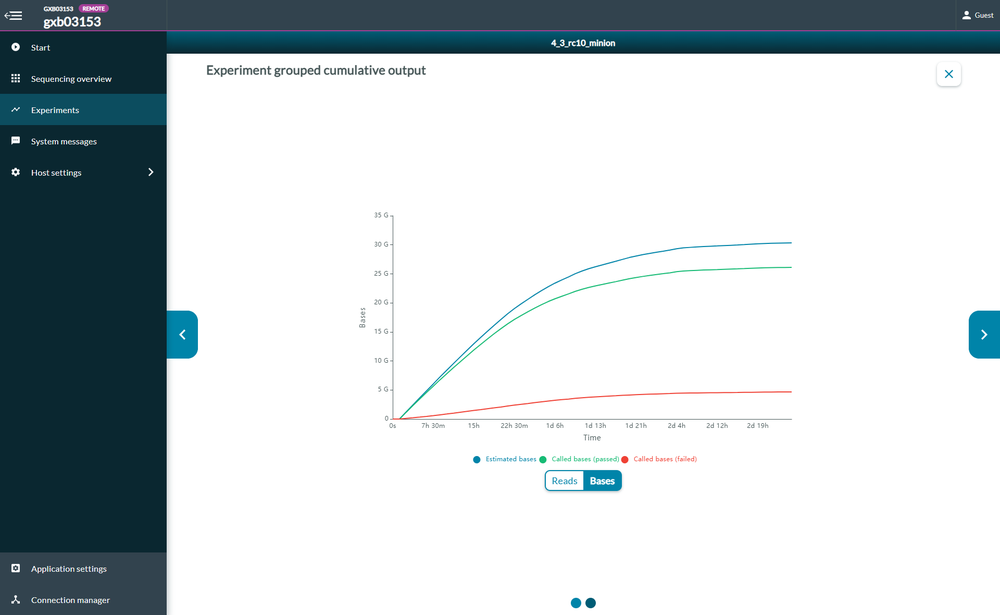
the number of reads that have been sequenced and basecalled; and whether the reads have passed of failed the quality filters
Temperature and bias voltage
Temperature vs time graph
The temperature graph gives a real-time representation of the temperature below the flow cell. If the temperature reading drifts out of the target zone, please consult Technical Services, otherwise the quality of your data may be compromised.

Bias voltage v time graph
The bias voltage graph provides the running voltage in real-time. You will notice drops in the voltage at regular intervals and these will correspond to the channel scans that are defaulted to occur every one and a half hours. Here, each channel will be scanned to look for its availability for sequencing. The common voltage is reversed before and after each channel assessment for clearer results. 
You can toggle between the graphs above in the MinKNOW GUI.
Trace viewer intro
The trace viewer is an advanced option allowing the user to examine a pore and its sequencing at a fundamental level. You may skip this page if it is not of interest at this point.
However, if you are interested, the trace viewer allows you to observe for yourself the passing of a single DNA or RNA strand through a single nanopore. To view this live, a brief description is below.
Trace Viewer
Each channel in the flow cell array contains a nanopore which is a single molecule sensor; this plot allows you to look at these sensors in minute detail. On the vertical axis it shows the raw current flowing through each nanopore. As a strand passes through base-by-base, you will see "steps" as that current changes, depending on which bases are inside the pore. This signal known as a "squiggle" is fundamental to nanopore sequencing.
For more detail and a video overview of how nanopore sequencing works, you may wish to visit (https://nanoporetech.com/how-it-works)
The plot will show all channels at once, and when overlaid this can look confusing:
We recommend you choose a bright green channel from the panel on the 'Physical layout' page, hover over it to show its number, then select only that channel in the trace viewer.
Type your selected channel in the 'Selected channels' field. This will show just that one channel. Change the 'Time seconds' field to '2'. This will effectively "zoom in" on the timescale, so 2 seconds of data are displayed, which will show the squiggle more clearly. The plot below is an example, in this case showing 2 seconds of channel 80.
If that channel is showing a DNA/RNA strand in the pore, it will look like the trace below. Each "step" in the current occurs as different bases move through the pore - hundreds of bases pass through the pore every second.
Pore activity plots intro
The pore activity plot summarises the channel states over time.
Each bar shows the sum of all channel activity in a particular amount of time. This time bucket defaults to 1 minute, and scales to 5 minutes automatically after reaching 48 buckets. However, bucket size can be adjusted in the "Bucket size" box to the right of the graph.
The graph populates over time, and can be used as a way to assess the quality of your sequencing experiment, and make an early decision whether to continue with the experiment or to stop the run.
20. How to assess the quality of your run
How to assess run quality - intro
The run metrics and report displayed in MinKNOW can be used to judge the quality of your experiment.
This section contains guidance for how to read the MinKNOW pore activity plots, including some examples of good and bad sequencing runs, and troubleshooting steps.
Pore activity plot examples
Pore activity plots in MinKNOW
It is recommended to observe the duty time plot populating over the first 30 min-1 hr of the sequencing run. By this time, the channel state distribution will give an indication whether the DNA/RNA library is of a good quality, and whether the flow cell is performing well. Below are some examples of good and bad sequencing runs:
Good quality library
A good quality library will result in most of the pores being in the "Sequencing" state, and very few in "Pore", "Recovering" or "Inactive". A library that looks like this is likely to give a good sequencing throughput.

Channel blocking
Under certain conditions (usually the presence of contaminants in the library), pores may become blocked and therefore unable to sequence. This manifests itself as a build-up of "Recovering" pores over time.

Low pore occupancy
If there was insufficient starting material, or some sample has been lost during library prep, or the sequencing adapters did not ligate well to the strand ends, the pore activity plot will show a high ratio of "Pore" to "Sequencing" states, meaning that only a limited number of pores are sequencing at any one time.

Recommendation: Stop the sequencing run in MinKNOW. Then wash out the library from the flow cell using the instructions for the Flow Cell Wash Kit, which is included in your Starter Pack. Then prepare another library and load it on the flow cell.
High number of inactive channels
If the pore activity plot shows a high number of 'Inactive' channels building up over time, this could indicate that the channels or membranes have been damaged by e.g. air bubbles, osmotic imbalance, or the presence of detergents or surfactants in the library.

Recommendation: Check the channel panel: if the Inactive channels are all grouped in one part of the flow cell, this could indicate an air bubble that has been introduced during flow cell flushing or library loading. If the remaining channels are still sequencing, it is possible to carry on with the run. Do not try to move the air bubble, as this can damage even more channels. If the Inactive channels are distributed throughout the flow cell: Make a new batch of flow cell priming buffer. Flush the flow cell with the mixture, and load the library again.
RNA adapter
Opening up the "More" view gives more granular detail about channel states. For RNA in particular, this view may show a large proportion of pores sequencing Adapter. This happens because RNA strands are usually shorter than DNA, and the adapter takes up a larger proportion of the strand. Additionally, the RNA sequencing chemistry is optimised for sequencing RNA, whereas the adapter is DNA, and is processed slower. As long as the 'basic' pore activity plot view shows the majority of pores in "Sequencing", a high proportion of Adapter should not be a problem.

21. After 6 hours
Report available
When the sequencing run finishes, MinKNOW will return to the home screen. You can view a summary of information from your run by selecting "Export PDF Report":

22. Next steps
Congratulations!
You have completed your first MinION Mk1B run!
By completing this guide, you have:
- Learned to correctly handle flow cells
- Used a Direct RNA Kit to prepare a basic RNA library
- Run a nanopore sequencing experiment
- Examined your results
You are now ready to prepare your own sample and run it on the other flow cell in your Starter Pack.
Moving on
- If you are ready to start planning your own sequencing experiment, our interactive Protocol Builder tool allows you to plan your end-to-end workflow, which includes selecting the right DNA/RNA extraction protocol and data analysis method for your application.
- For more information, visit the Nanopore Community, where you can find recommended library preparation protocols. We also provide DNA and RNA extraction methods for various sample types.
- For any questions regarding your order, or technical questions about your experiment, please contact Support.
- Finally, you can also join forums on the Nanopore Community, where our enthusiastic and diverse community of users discuss their experiment plans and results, share hints and tips, and form collaborations.
Survey Section 6
Feedback
We'd love to hear how you got on! What did you think of this Getting Started Guide?
We value our customer feedback, so if you have a moment, please take the time to fill in a short survey about your experience: Quick survey






