Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit V14 (SQK-ULK114) (ULK_9177_v114_revQ_06Nov2025)
PromethION: Protocol
V ULK_9177_v114_revQ_06Nov2025
FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY
Contents
Introduction to the protocol
Sample preparation
- 3. Isolation of white blood cells (WBCs) from whole blood
- 4. Preparation of tissue samples for gDNA extraction
- 5. uHMW gDNA extraction
- 6. (Optional) gDNA quantification
Library preparation
- 7. Tagmentation
- 8. Clean-up
- 9. Priming and loading the PromethION Flow Cell
- 10. Reloading ultra-long DNA library on a PromethION Flow Cell
Sequencing and data analysis
Troubleshooting
1. Overview of the protocol
This is an Early Access product.
For more information about our Early Access programmes, please see this article on product release phases.
Please ensure you always use the most recent version of the protocol.
Introduction to the Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit protocol (SQK-ULK114)
This protocol describes the complete workflow from extracting gDNA from frozen tissue or purified cells from whole blood to the sequencing of ultra-high molecular weight (uHMW) gDNA using the Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit (SQK-ULK114). We have also included the procedure to isolate white blood cells (WBC) from whole blood and how to quantify gDNA developed by Paul A ‘Giron’ Koetsier & Eric J Cantor, 2021.
We have used the Monarch® HMW DNA Extraction Kit for Tissue (NEB, T3060) to extract the uHMW gDNA for both input types when developing this protocol. Alternative kits are available from NEB which are specifically designed for the extraction from blood and cells. However, they have not been validated by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
For each reaction, there is sufficient library generated for multiple consecutive loads onto a flow cell to increase output. To load a library three times on a PromethION Flow Cell, a flow cell wash is required to recover channels.
Steps in the sequencing workflow
Prepare for your experiment
You will need to:
- If working with whole blood, isolate white blood cells. If working with frozen tissue, isolate cells from the tissue.
- Extract your uHMW gDNA.
- Quantify your sample.
- Ensure you have your sequencing kit, the correct equipment and third-party reagents.
- If not already installed, download the software for acquiring and analysing your data.
- Check your flow cell(s) to ensure it has enough pores for a good sequencing run.
Library preparation
You will need to:
- Tagment your DNA using a diluted fragmentation mix.
- Attach Rapid Adapters to the DNA ends.
- Clean-up your sample by precipitating your DNA and eluting overnight.
- Prime the flow cell and load your DNA library into the flow cell.
Sequencing and analysis
You will need to:
- Start a sequencing run using the MinKNOW software, which will collect raw data from the device and convert it into basecalled reads.
- Optional: Start the EPI2ME software and select a workflow for further analysis.
Flow cell loading and flushing
The Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit (SQK-ULK114) protocol generates viscous DNA which can affect flow cell loading. To account for this, we have modified the flow cell loading steps. Please take care and follow the steps carefully to avoid damaging the flow cell.
To increase output, we recommend loading an ultra-long library three times per flow cell. A flow cell wash using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) is required between each subsequent library load to recover channels. To run a second library straight away, please follow the modified method in this protocol: Reloading ultra-long DNA library on a PromethION Flow Cell.
Best practice for handling uHMW gDNA
When mixing, we recommend using wide-bore pipette tips to mix the full volume of a sample to ensure thorough mixing whilst minimising mechanical shearing of long fragments.
To preserve longer DNA, mix slower and more gently. Vortexing on low speeds may also be used at the expense of very long fragments.
While precautions should be taken to ensure that DNA fragment lengths are preserved, there should be no compromise to ensuring that reagents are thoroughly mixed with DNA. Insufficient mixing will lead to reduced read length and output.
For further information, please refer to the troubleshooting section.
Compatibility of this protocol
This protocol should only be used in combination with:
- Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit (SQK-ULK114)
- Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004)
- R10.4.1 flow cells (FLO-PRO114M)
- EEB Expansion (EXP-EEB001)
- Ultra-Long Auxiliary Vials (EXP-ULA001)
- PromethION 24/48 device - PromethION IT requirements document
- PromethION 2 Solo device - PromethION 2 Solo IT requirements document
2. Equipment and consumables
Material
- Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit V14 (SQK-ULK114)
- Monarch® HMW DNA Extraction Kit for Tissue (New England Biolabs, T3060)
- Kit Flow Cell Wash (EXP-WSH004)
Consumibles
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Tubos Eppendorf DNA LoBind de 2 ml
- 5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Tubos Falcon de 15 ml
- Isopropanol, 100% (Fisher Scientific, 10723124)
- Ethanol, 100% (e.g. Fisher, 16606002)
- Kit Qubit dsDNA BR (Invitrogen, Q32850)
- Qubit™ Assay Tubes (Invitrogen, Q32856)
Instrumental
- Thermal cycler or heat block
- Thermomixer set at 56°C (suitable for 1.5 ml, 2 ml and 5 ml tubes)
- Vortex mixer
- Microfuge
- Puntas de pipeta de orificio ancho
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- Qubit fluorometer (or equivalent)
- Ice bucket with ice
- Timer
The above list of materials, consumables, and equipment is for the library preparation section of the protocol. Depending on the sample type, additional reagents will be needed for sample processing and DNA extraction. These are listed in the "Sample preparation" section of the protocol.
For this protocol, you will need to extract gDNA from 6 million cells in 40 µl PBS before starting the library preparation.
This protocol has been developed using the Monarch® HMW DNA Extraction Kit for Tissue (NEB, T3060). Alternative kits are available from NEB which are specifically designed for the extraction from blood and cells. However, they have not been validated by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
This method has been validated for use on the following inputs:
- 6 million white blood cells isolated from 1.6 ml blood (bovine), using RBC Lysis Solution (QIAGEN, 158904)
- 6 million cells isolated from 1 g frozen tissue, using pluriSelect cell straining equipment.
Check your flow cell
We highly recommend that you check the number of pores in your flow cell prior to starting a sequencing experiment. This should be done within 12 weeks of purchasing your MinION/GridION/PromethION Flow Cells. Oxford Nanopore Technologies will replace any unused flow cell with fewer than the number of pores listed in the Table below, when the result is reported within two days of performing the flow cell check, and when the storage recommendations have been followed. To do the flow cell check, please follow the instructions in the Flow Cell Check document.
| Flow cell | Minimum number of active pores covered by warranty |
|---|---|
| MinION/GridION Flow Cell | 800 |
| PromethION Flow Cell | 5000 |
Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit (SQK-ULK114) contents

| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | Number of vials | Fill volume per vial (µl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Adapter | RA | Green | 1 | 40 |
| Fragmentation Mix | FRA | Amber | 1 | 50 |
| FRA Dilution Buffer | FDB | Clear | 1 | 1,600 |
| Elution Buffer | EB | Black | 2 | 1,500 |
| Extraction EB | EEB | Orange | 3 | 1,700 |
| Sequencing Buffer UL | SBU | Red | 2 | 1,000 |
| Loading Solution UL | LSU | White cap, pink label | 1 | 200 |
| Flush Tether UL | FTU | Purple | 1 | 600 |
| Flow Cell Flush | FCF | Blue | 2 | 15,500 |
| Precipitation Buffer | PTB | Blue | 2 | 1,700 |
| Precipitation Star | PS | Yellow | 6 | 1 star |
Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) contents
| Name | Volume (µl) | No. of tubes | No. of uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wash Mix (WMX) | 15 | 1 | 6 |
| Wash Diluent (DIL) | 1,300 | 2 | 6 |
| Storage Buffer (S) | 1,600 | 2 | 6 |
- Wash Mix (WMX) contains DNase I.
- Wash Diluent (DIL) contains the exonuclease buffer that maximises activity of the DNase I.
- The Storage Buffer allows flow cells to be stored for extended periods of time.
To maximise the use of the Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit V14, the EEB Expansion (EXP-EEB001) and the Ultra-Long Auxiliary Vials (EXP-ULA001) expansion packs are available.
These expansions provide extra library preparation and flow cell priming reagents to allow users to maximise the use of their Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit V14.
The EEB Expansion (EXP-EEB001) contains enough reagents for at least six standard extraction elution steps.
The Ultra-Long Auxiliary Vials (EXP-ULA001) provides enough reagents to carry out twelve additional flow cell loads on MinION or PromethION Flow Cells.
EEB Expansion (EXP-EEB001) contents:
| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | No. of vials | Fill volume per vial (μl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction EB | EEB | White | 1 | 6,000 |
Ultra-Long Auxiliary Vials (EXP-ULA001) contents:
| Name | Acronym | Cap colour | No. of vials | Fill volume per vial (μl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elution Buffer | EB | Black | 1 | 1,500 |
| Sequencing Buffer UL | SBU | Red | 2 | 1,000 |
| Loading Solution UL | LSU | White cap, pink label | 1 | 200 |
| Flush Tether UL | FTU | Purple | 1 | 600 |
| Flow Cell Flush | FCF | Clear cap, light blue label | 1 | 15,500 |
3. Isolation of white blood cells (WBCs) from whole blood
Material
- 1.6 ml of whole blood
Consumibles
- RBC Lysis Solution (QIAGEN, 158106)
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4 (Thermo Fisher, 10010023)
- Tubos Falcon de 15 ml
Instrumental
- Microfuge
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
White blood cell sample preparation for the Ultra-long DNA experiment
Approximately 6 million isolated white blood cells must be prepared from 1.6 ml of whole blood to use as input in the Ultra-long DNA experiment.
Users may isolate white blood cells by any means they feel are most appropriate for the whole blood sample to be used. If 6 million cells have been isolated, users can start from the uHMW gDNA extraction step.
Add 4.8 ml of RBC Lysis Solution to 1.6 ml of whole blood in a 15 ml Falcon tube.
Gently invert the tube ten times to mix.
Incubate for 5 minutes at room temperature and gently invert twice during the incubation.
Centrifuge at 2,000 x g for 2 minutes at 4°C to pellet the white blood cells.
Discard the supernatant by pouring. There will be ~200 µl supernatant remaining in the tube.
Resuspend the cells in the residual supernatant by gently flicking the tube.
Make up the volume to 1.6 ml with 1x PBS.
Repeat steps 1-7 twice more to complete three washes in total.
If any red colouration persists, repeat the wash step until the cell pellet is white.
After the final spin, remove the entire supernatant by pouring and aspirating any remaining supernatant.
Resuspend the cell pellet in 40 µl 1x PBS. There will be approximately 6 million cells in the suspension.
Take the cell pellet forward into the "uHMW gDNA extraction" step.
4. Preparation of tissue samples for gDNA extraction
Material
- Cell Suspension Buffer (CSB): 0.35 M sucrose, 100 mM EDTA, 50 mM Tris.HCl pH 8
- Frozen tissue sample
Consumibles
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4 (Thermo Fisher, 10010023)
- 1 M Tris-HCl pH 8.0 (Thermo Scientific, 15893661)
- EDTA 0,5 M, pH 8 (Thermo Scientific, R1021)
- 2.5 M sucrose
- Agua sin nucleasas (p. ej., ThermoFisher, AM9937)
- 50 ml Falcon tubes
- 5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Instrumental
- Centrifuge suitable for 5 ml Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf centrifuge 5804/5804 R or equivalent)
- Eppendorf tube rack suitable for 5 ml Eppendorf tubes
- Scalpel
- TissueRuptor II (QIAGEN, cat # 9002755)
- TissueRuptor Disposable Probes (QIAGEN, cat # 990890)
- Florescent microscope with functionality to quantify nuclei (Logos CELENA S Digital Imaging System or equivalent)
- Heat block equipped with thermoblock suitable for 5 ml Eppendorf tubes
- 200 µm PluriStrainer® (pluriSelect, 43-50200-03)
- 100 µm PluriStrainer® (pluriSelect, 43-50100-51)
- 50 µm PluriStrainer® (pluriSelect, 43-50050-03)
- 30 µm PluriStrainer® (pluriSelect, 43-50030-03)
- PluriStrainer® Connector Ring (pluriSelect, 41-50000-03)
- PluriStrainer® Funnel (pluriSelect, 42-50000)
- P1000 pipette and tips
- 10 ml syringe
Prepare the Cell Suspension Buffer (CSB) as follows:
| Reagent | Stock | Final conc. | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tris.HCl, pH 8 | 1 M | 0.05 M | 50 ml |
| EDTA | 0.5 M | 0.1 M | 200 ml |
| Sucrose | 2.5 M | 0.35 M | 140 ml |
| Nuclease-free water | - | - | 610 ml |
| Total | - | - | 1,000 ml |
Add 1 g of the frozen tissue sample to a weighing boat.
Using the scalpel, slice the tissue into thin strips and then dice the sample.
Transfer the tissue sample to a fresh 50 ml Falcon tube.
Add 10 ml of the Cell Suspension Buffer (CSB) into the 50 ml Falcon tube.
Using the QIAGEN TissueRuptor, gently homogenise the tissue sample.
- Insert the probe and pulse at minimum speed for one second. Stir the homogenate between each pulse.
- Repeat this five times.
During homogenisation, only apply as much force as is required to gently break up the tissue. Excessive force will damage the nuclei and make them difficult to quantify. It is not a problem if there is intact material remaining at the end of this step, as it will be re-processed in later steps.
Assemble the pluriStrainer apparatus with a 200 μm strainer, connector ring, funnel and 50 ml Falcon tube according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Pass the full volume of the tissue sample homogenate through the 200 µm PluriStrainer®.
The homogenate can be gently agitated, and a small amount of negative pressure can be applied with the syringe to help pass the homogenate through the strainer.
Disassemble the pluriStrainer® apparatus according to the manufacturer's instructions, setting aside the strained homogenate in the 50 ml Falcon tube for later use.
Repeat the homogenisation process on any intact tissue caught by the pluriStrainer®:
Transfer any intact tissue caught by the 200 µm pluriStrainer® into a fresh 50 ml Falcon tube by inverting the strainer and tapping out the intact tissue.
Tip: A spatula can be used to help remove the intact tissue from the strainer.Add 10 ml of the Cell Suspension Buffer (CSB) into the 50 ml Falcon tube.
Repeat steps 6-10 two more times to perform a total of three rounds of tissue homogenisation.
Combine the contents of the 50 ml Falcon tube with the original strained homogenate set aside in step 10.
The combined volume of 200 µm strained homogenate is ready for further processing.
Strain the 200 µm strained homogenate through the 100 µm pluriStrainer®:
Assemble the pluriStrainer apparatus with a 100 µm strainer, connector ring, funnel and 50 ml Falcon tube according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Pass the full volume of the 200 µm strained homogenate through the 100 µm PluriStrainer®. Tip: The homogenate can be gently agitated, and a small amount of negative pressure can be applied with the syringe to help pass the homogenate through the strainer.
Disassemble the pluriStrainer® and retain the 100 µm strained homogenate in the 50 ml Falcon tube.
Strain the 100 µm strained homogenate through the 50 µm pluriStrainer®:
Assemble the pluriStrainer apparatus with a 50 µm strainer, connector ring, funnel and 50 ml Falcon tube according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Pass the full volume of the 100 µm strained homogenate through the 50 µm PluriStrainer®. Tip: The homogenate can be gently agitated, and a small amount of negative pressure can be applied with the syringe to help pass the homogenate through the strainer.
Disassemble the pluriStrainer® and retain the 50 µm strained homogenate in the 50 ml Falcon tube.
Strain the 50 µm strained homogenate through the 30 µm pluriStrainer®:
Assemble the pluriStrainer apparatus with a 30 µm strainer, connector ring, funnel and 50 ml Falcon tube according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Pass the full volume of the 50 µm strained homogenate through the 30 µm PluriStrainer®. Tip: The homogenate can be gently agitated, and a small amount of negative pressure can be applied with the syringe to help pass the homogenate through the strainer.
Disassemble the pluriStrainer® and retain the 30 µm strained homogenate in the 50 ml Falcon tube.
Determine the concentration of the nuclei in the purified homogenate using a fluorescent microscope and a stain appropriate for the nuclei in the sample.
Take forward a volume corresponding to 6 million nuclei and add this to a 5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Centrifuge the 5 ml Eppendorf tube at 16,000 x g for 5 minutes to pellet the nuclei/cells.
Pipette off all the supernatant and discard, taking care not to disturb the pellet.
Add 40 µl of PBS to the 5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Thoroughly mix the tube by repeatedly flicking. Ensure the pellet breaks up and no clumps remain in the nuclei/cell suspension.
Note: You may need to flick quite hard and thoroughly to ensure the pellet breaks up and no clumps remain.
Take the nuclei/cell suspension forward into the "uHMW gDNA extraction" step.
5. uHMW gDNA extraction
Material
- 6 million cells/nuclei isolated from frozen tissue or white blood cells isolated from whole blood
- Extraction EB (EEB)
- Monarch® HMW DNA Extraction Kit for Tissue (New England Biolabs, T3060)
Consumibles
- 5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4 (Thermo Fisher, 10010023)
- Isopropanol, 100% (Fisher Scientific, 10723124)
- Ethanol, 100% (e.g. Fisher, 16606002)
- Tubos Eppendorf DNA LoBind de 2 ml
Instrumental
- Heat block set at 56°C
- Thermomixer set at 56°C (suitable for 1.5 ml, 2 ml and 5 ml tubes)
- Hula mixer (gentle rotator mixer)
- Microfuge
- P1000 pipette and wide-bore pipette tips
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- Centrifugadora Eppendorf 5424 (o equivalente)
This method does NOT use the Monarch Elution Buffer II from the Monarch® HMW DNA Extraction Kit.
This method has been optimised using the Extraction EB (EEB) from the Oxford Nanopore sequencing kit.
Ensure ethanol is added to the Monarch gDNA Wash Buffer as per kit guidance.
Thaw the Extraction EB (EEB) at room temperature, mix by vortexing and place on ice.
Add 6 million cells resuspended in 40 µl PBS to a fresh 5 ml tube. Cells can be isolated from cell culture, white blood cells from blood, or tissue according to the above methods.
Thorough but gentle resuspension of cells is required to ensure efficient lysis and to prevent heterogeneity in the subsequent steps.
In a separate 2 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, combine the following reagents:
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Monarch HMW gDNA Tissue Lysis Buffer | 1,800 µl |
| Proteinase K | 60 µl |
| Total | 1860 µl |
Add 1.8 ml of mixed Monarch HMW gDNA Tissue Lysis Buffer and Proteinase K to the resuspended cells.
Gently mix by slowly pipetting the reaction five times using a 1 ml wide-bore pipette tip.
When using cell lines, we have found that the incubation step below can be omitted.
Incubate the reaction at 56°C for 10 minutes.
Using a regular pipette tip, add 15 µl of Monarch RNase A.
Gently mix by slowly pipetting the reaction five times using a 1 ml wide-bore pipette tip.
Incubate the reaction at 56°C for 10 minutes on a thermomixer at 650 rpm.
When using cell lines, we have found the protein removal steps can be omitted. If using cell lines, proceed directly to step 13.
Using a regular pipette tip, add 900 µl of the Monarch Protein Separation Solution to the reaction and mix using a Hula Mixer (rotator mixer) for 10 minutes, rotating at 3 rpm.
Centrifuge the reaction at 16,000 x g for 10 minutes at 4°C to separate the protein from the DNA.
DNA will be present in the upper phase, whereas protein and other contaminants will be in the lower phase.
Using a wide-bore pipette tip, carefully aspirate the upper phase containing the DNA and transfer to a fresh 5 ml tube without disturbing the phase below.
The DNA in the upper phase should be extremely viscous and should only be possible to aspirate using a wide-bore pipette tip.
If the protein phase is disturbed, the tube can be centrifuged again at 16,000 x g for 10 minutes at 4°C.
Add three Monarch DNA Capture Beads to the collected DNA phase (or to the lysis reaction if proceeded directly from Step 9).
Note: The first bead is a sacrificial bead and will remain at the bottom of the tube throughout the remainder of the process.
Add 2.5 ml isopropanol to the tube and mix using a Hula Mixer (rotator mixer) for 20 minutes rotating at 3 rpm. Ensure the DNA has fully precipitated around the glass beads.
Check the DNA is binding to the beads by looking for a viscous mass around the beads. The mixing step can be extended if the DNA is not obviously condensing around the beads.
Leave the tube to stand for 1 minute, without rotating, at room temperature.
Aspirate the supernatant from the tube, being careful not to aspirate the DNA that is bound to the beads. Check for and remove any supernatant remaining in the lid of the tube.
Note: If ~100 µl of supernatant is remaining in the tube, perfomance will not be affected.
Add 2 ml of Monarch gDNA Wash Buffer to the tube containing DNA bound to the beads and invert the tube to mix.
Ensure ethanol is added to the Monarch gDNA Wash Buffer as per kit guidance.
Aspirate the Wash Buffer, being careful not to aspirate the DNA that is bound to the beads. Check for and remove any Wash Buffer remaining in the lid of the tube.
Add 2 ml of Monarch gDNA Wash Buffer to the tube containing the DNA bound to the beads.
To a fresh 2 ml Eppendorf tube, add 560 µl of Extraction EB (EEB).
Aspirate the Wash Buffer, being careful not to aspirate the DNA that is bound to the beads. Check for and remove any Wash Buffer remaining in the lid of the tube.
Transfer the beads to a Monarch Bead Retainer inserted in a Monarch Collection Tube II.
Briefly spin the tube using a microfuge to remove any remaining Wash Buffer from the beads. Dispose of the collection tube containing residual wash buffer.
Do NOT use the Monarch Elution Buffer II in the Monarch® HMW DNA Extraction Kit for Tissue.
Immediately transfer the beads from the bead retainer into the 2 ml tube containing 560 µl of Extraction EB (EEB).
Beads should be transferred immediately to ensure that they do not over-dry, which could lead to increased solubilisation times.
Incubate the tube for 10 minutes at 56°C.
Pour the eluate and beads into a clean bead retainer inserted in a collection tube. Spin the tube at 1,000 x g for 1 minute to separate eluate from the beads. Dispose of beads and bead retainer.
Add 200 µl of Extraction EB (EEB) to the collection tube to bring the total elution volume to 760 µl.
Transfer the eluate to a fresh 2 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Incubate the eluate for 10 minutes at 56°C.
Gently mix the eluate by slowly pipetting 10 times using a 1 ml wide-bore pipette tip.
Thorough but gentle resuspension of DNA is required to prevent heterogeneity in the sample.
Take forward the resuspended DNA into the quantification step. However, at this point it is possible to store the sample at room temperature overnight.
6. (Optional) gDNA quantification
Material
- Monarch® DNA Capture Beads
- Monarch® Bead Retainer
- Monarch® Collection Tubes II
Consumibles
- Tubos Eppendorf DNA LoBind de 2 ml
- Kit Qubit dsDNA BR (Invitrogen, Q32850)
Instrumental
- Vortex mixer
- Centrifuge
- Qubit fluorometer (or equivalent)
- P200 pipette and tips
Quantification of uHMW gDNA
The method to quantify uHMW gDNA was developed by Paul A ‘Giron’ Koetsier & Eric J Cantor, 2021, which recommends the use of a regular P200 pipette and tip.
This optional uHMW gDNA quantification step has also been included in the protocol for user QC. However, this step can be omitted and 750 µl of DNA in Extraction EB (EEB) can be taken straight into the tagmentation step of the protocol.
Use a regular P200 pipette tip to aspirate 10 µl of gDNA.
If the DNA is particularly viscous, the aspirated DNA can be separated from the sample by forcing the sample against the side of the tube to break the DNA off. It is critical that the DNA is completely homogenous, so that the 10 µl of sample that is removed is representative of the entire sample.
Dispense the aspirated gDNA into a fresh 2 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Add a Monarch DNA Capture Bead to the 10 µl of gDNA and vortex aggressively for 1 minute to shear the gDNA.
Transfer the gDNA and beads into a clean Monarch Bead Retainer inserted in a Monarch Collection Tube II. Spin the tube at 1,000 x g for 1 minute to separate gDNA from the beads. Dispose of beads and bead retainer.
Using a wide-bore pipette tip, transfer the gDNA into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube.
Quantify the sample using a Qubit fluorometer. The expected yield is 30-40 µg of DNA.
Take forward 750 µl DNA into the tagmentation step.
7. Tagmentation
Material
- 750 µl of extracted uHMW gDNA in EEB
- Rapid Adapter (RA)
- Fragmentation Mix (FRA)
- FRA Dilution Buffer (FDB)
Consumibles
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Instrumental
- Thermal cycler or heat block
- Microfuge
- P1000 pipette and wide-bore pipette tips
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
- Ice bucket with ice
Best practice for handling uHMW gDNA
When mixing, we recommend using wide-bore pipette tips to mix the full volume of a sample to ensure thorough mixing whilst minimising mechanical shearing of long fragments.
To preserve longer DNA, mix slower and more gently. Vortexing on low speeds may also be used at the expense of very long fragments.
While precautions should be taken to ensure that DNA fragment lengths are preserved, there should be no compromise to ensuring that reagents are thoroughly mixed with DNA. Insufficient mixing will lead to reduced read length and output.
For further information, please refer to the troubleshooting section.
Thaw the the kit components at room temperature, spin down briefly using a microfuge and mix by pipetting as indicated by the Table below:
Once thawed, keep all the kit components on ice.
| Reagent | Thaw at room temperature | Briefly spin down | Mix well by pipetting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fragmentation Mix (FRA) | Not frozen | ✓ | ✓ |
| FRA dilution buffer (FDB) | Not frozen | ✓ | ✓ |
| Rapid Adapter (RA) | Not frozen | ✓ | ✓ |
In a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, dilute the Fragmentation Mix (FRA) with FRA Dilution Buffer (FDB) as follows:
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Fragmentation Mix (FRA) | 6 µl |
| FRA dilution buffer (FDB) | 244 µl |
| Total | 250 µl |
Mix the diluted Fragmentation Mix (FRA) by pipetting.
Using a regular pipette tip, add 250 µl of diluted Fragmentation Mix (FRA) to the 750 µl of extracted DNA. Stir the reaction with the pipette tip whilst expelling the diluted Fragmentation Mix (FRA) to ensure an even distribution.
Immediately mix the reaction by slowly pipetting 10 times with a wide-bore pipette tip.
Visually check the reagents are thoroughly mixed. It is important to immediately mix the diluted Fragmentation Mix (FRA) with the DNA thoroughly.
Incubate the reaction as follows:
| Temperature | Time |
|---|---|
| Room temperature | 10 minutes |
| 75°C | 10 minutes |
| On ice | Cool on ice for a minimum of 10 minutes |
Note: the reaction must be cooled on ice before adding Rapid Adapter (RA) to prevent denaturing the enzyme.
Add 5 µl Rapid Adapter (RA) to the reaction using a regular pipette tip.
Gently mix the reaction by slowly pipetting five times using a 1 ml wide-bore pipette tip.
Note: visually check to ensure the reaction is thoroughly mixed.
Incubate the reaction for 30 minutes at room temperature.
8. Clean-up
Material
- Elution Buffer from the Oxford Nanopore kit (EB)
- Precipitation Buffer (PTB)
- Precipitation Star (PS)
Consumibles
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Instrumental
- Centrifuge
- Microfuge
- Hula mixer (gentle rotator mixer)
- P200 pipette and tips
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P1000 pipette and wide-bore pipette tips
Thaw the kit components at room temperature, spin down briefly using a microfuge and mix by vortexing as indicated by the Table below:
| Reagent | Thaw at room temperature | Briefly spin down | Mix well by pipetting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation buffer (PTB) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Elution Buffer (EB) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Once thawed, keep all the kit components on ice.
We strongly recommend using a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube for the clean-up method when using the Precipitation Star (PS)
Add a Precipitation Star (PS) to the sample.
Using a regular pipette tip, add 500 µl of Precipitation Buffer (PTB) to the sample.
Mix the sample by rotating on a Hula Mixer (rotator mixer) for 20 minutes at 3 rpm.
Visually inspect to check the DNA has precipitated around the Precipitation Star (PS).
Using a regular pipette tip, carefully remove the supernatant from the tube, taking care not to aspirate the DNA.
In the 1.5 ml Eppendorf LoBind DNA tube, the Precipitation Star (PS) should be suspended mid-way in the tube, allowing the supernatant beneath the star to be removed.
Briefly spin down the tube and remove any residual supernatant using a regular pipette tip, taking care not to aspirate the DNA.
Using a regular pipette tip, add 300 µl of Elution Buffer (EB) to the tube containing the Precipitation Star (PS) and DNA. Incubate overnight at room temperature, for a minimum of 12 hours.
Using a wide-bore pipette tip, remove and retain eluate containing the DNA library into a clean 1.5 ml Eppendorf LoBind DNA tube.
Briefly spin down the tube containing the Precipitation Star (PS) and remove any remaining eluate with a wide-bore pipette tip, ensuring there is no liquid remaining on the Precipitation Star (PS).
Dispose of the tube containing the Precipitation Star (PS).
Gently mix the DNA library by slowly pipetting 10 times with a wide-bore pipette tip.
Thorough but gentle resuspension of DNA is required to prevent heterogeneity in the sample.
Take the DNA library forwards for loading into the flow cell. Store the library on ice until ready to load.
Library storage recommendations
We recommend storing libraries in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes at 4°C for short-term storage or repeated use, for example, re-loading flow cells between washes. For single use and long-term storage of more than 3 months, we recommend storing libraries at -80°C in Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes.
9. Priming and loading the PromethION Flow Cell
Material
- Flow Cell Flush (FCF)
- Flush Tether UL (FTU)
- Loading Solution UL (LSU)
- Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU)
Consumibles
- Celdas de flujo PromethION
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Instrumental
- Dispositivo PromethION
- Dispositivo PromethION 24/48 o PromethION 2 Solo
- Pantalla protectora celdas de flujo PromethION
- P1000 pipette and wide-bore pipette tips
- P200 pipette and wide-bore pipette tips
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
Please note, this kit is only compatible with R10.4.1 flow cells (FLO-PRO114M).
Only use the reagents provided with the SQK-ULK114 kit for priming and loading the flow cell. Reagents from other kits are not compatible with this protocol.
After taking the flow cell out of the fridge, wait 20 minutes for the flow cell to reach room temperature, before inserting it into the PromethION. Condensation can form on the flow cell in humid environments. Inspect the gold connector pins on the top and underside of the flow cell for condensation and wipe off with a lint-free wipe if any is observed. Ensure the heat pad (black pad) is present on the underside of the flow cell.
Thaw the Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU), Loading Solution UL (LSU), Flush Tether UL (FTU) and one tube of Flow Cell Flush (FCF) at room temperature and mix by vortexing. Then spin down and place on ice.
In a fresh 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, prepare the DNA library for loading as follows using a wide-bore pipette tip for the addition of the DNA library:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU) | 100 µl |
| Loading Solution UL (LSU) | 10 µl |
| DNA library | 90 µl |
| Total | 200 µl |
Note: ensure the Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU) and Loading Solution UL (LSU) are thoroughly mixed by pipetting before the addition of the DNA library.
Gently mix the prepared DNA library by slowly pipetting ten times using a wide-bore pipette tip.
Incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes then gently mix by slowly pipetting with a wide-bore tip. Visually inspect to ensure the sample is homogenous.
Prepare the flow cell priming mix in a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube and mix by vortexing at room temperature.
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Flush Tether UL (FTU) | 30 µl |
| Flow Cell Flush (FCF) | 1,170 µl |
| Total | 1,200 µl |
For PromethION 2 Solo, load the flow cell(s) as follows:
Place the flow cell flat on the metal plate.
Slide the flow cell into the docking port until the gold pins or green board cannot be seen.

For the PromethION 24/48, load the flow cell(s) into the docking ports:
- Line up the flow cell with the connector horizontally and vertically before smoothly inserting into position.
- Press down firmly onto the flow cell and ensure the latch engages and clicks into place.


Insertion of the flow cells at the wrong angle can cause damage to the pins on the PromethION and affect your sequencing results. If you find the pins on a PromethION position are damaged, please contact support@nanoporetech.com for assistance.

Complete a flow cell check to assess the number of pores available before loading the library.
This step can be omitted if the flow cell has been checked previously.
See the flow cell check document for more information.
Slide the inlet port cover clockwise to open.

Take care when drawing back buffer from the flow cell. Do not remove more than 20-30 µl, and make sure that the array of pores are covered by buffer at all times. Introducing air bubbles into the array can irreversibly damage pores.
After opening the inlet port, draw back a small volume to remove any air bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette tip to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the inlet port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip.

Load 500 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the inlet port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait five minutes.

Complete the flow cell priming by slowly loading 500 µl of the priming mix into the inlet port.

Ensure the inlet port cover of the flow cell is still open in preparation for loading.
Check that no air bubbles have been introduced to the inlet port during flow cell priming. If air is present, draw back a small volume to remove any air bubbles by using a P1000 pipette set to 200 µl and turning the pipette wheel (as per the instructions above).

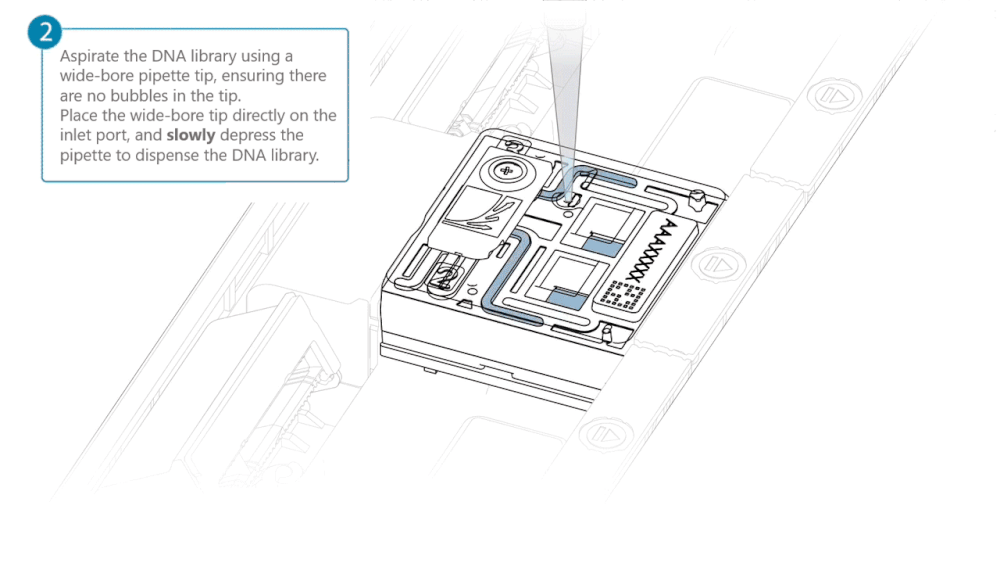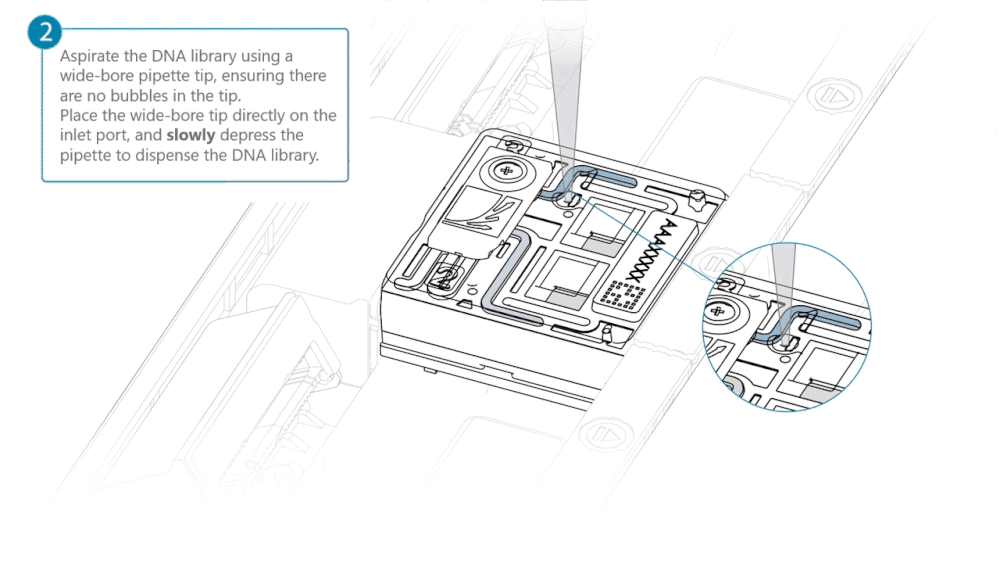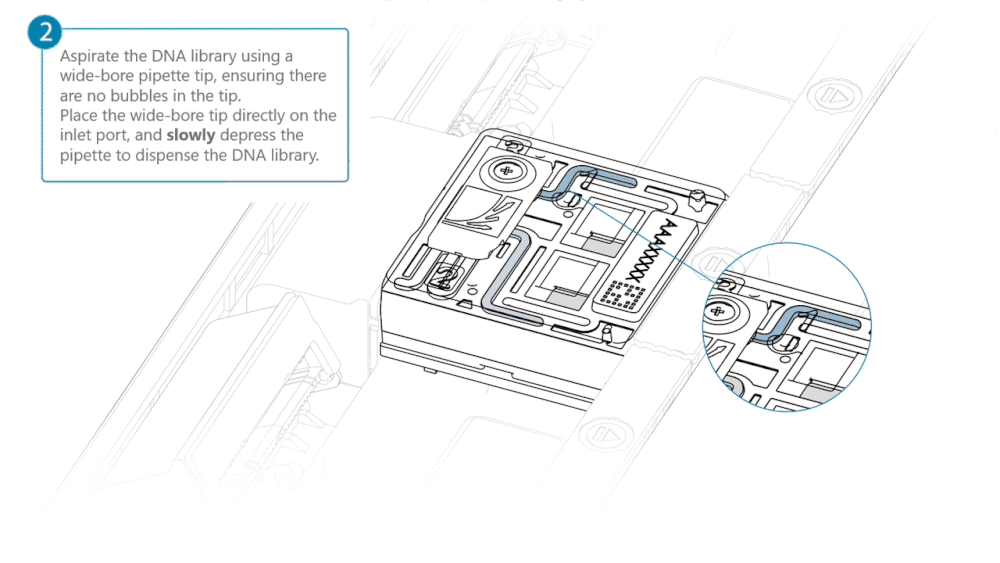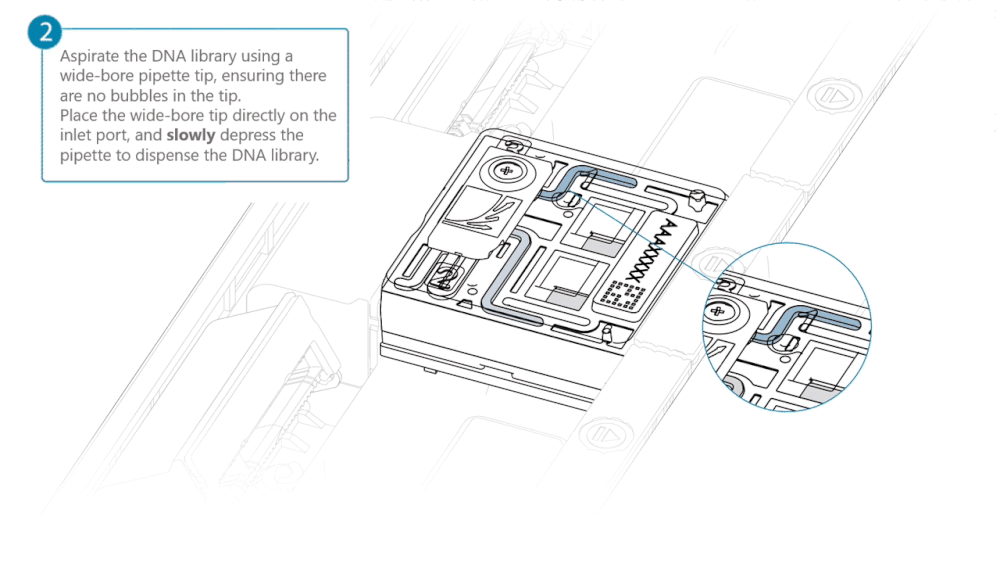
Aspirate the DNA library with a wide-bore pipette tip. Ensure there are no air bubbles in the pipette tip. Place the wide-bore pipette tip directly on the inlet port. Slowly depress the pipette to dispense the library into the inlet port.
There can be a delay between depressing the pipette and the library dispensing from the pipette tip. Dispense the library slowly, allowing the library to dispense from the pipette tip before depressing the pipette further.
It is important to dispense the library slowly to prevent air being introduced onto the flow cell.
Note: The DNA library loaded in this step is viscous and may not readily flow through the inlet port into the flow cell. In this case, we recommend applying negative pressure in the flow cell as explained in the steps below.
Using a P200 pipette, set the pipette to 50 µl and insert the tip into Port 2.

Very slowly turn the wheel of the pipette to pull the DNA library into the inlet port. Closely watch the DNA library on the inlet port and completely remove the pipette as soon as the library starts to be pulled into the port.
This step is required if the DNA library has not been fully absorbed into the inlet port.
Note: Take care to not apply too much negative pressure too quickly to avoid bringing air bubbles into the flow cell. Air bubbles will cause irreversible damage to the flow cell.

Close the valve to seal the inlet port.
For optimal sequencing output, install the light shield on your flow cell as soon as the library has been loaded.
We recommend leaving the light shield on the flow cell when library is loaded, including during any washing and reloading steps. The shield can be removed when the library has been removed from the flow cell.
If the light shield has been removed from the flow cell, install the light shield as follows:
- Align the inlet port cut out of the light shield with the inlet port cover on the flow cell. The leading edge of the light shield should sit above the flow cell ID.
- Firmly press the light shield around the inlet port cover. The inlet port clip will click into place underneath the inlet port cover.


Close the PromethION lid when ready to start a sequencing run on MinKNOW.
Wait a minimum of 10 minutes after loading the flow cells onto the PromethION before initiating any experiments. This will help to increase the sequencing output.
We recommend loading an ultra-long DNA library three times per flow cell to increase output.
A nuclease wash using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) is required between each subsequent library load to recover channels and maximise sequencing output.
For PromethION flow cells, there is enough ultra-long DNA library generated for three consecutive loads per reaction, using 90 µl of fresh library combined with 100 µl of Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU) and 10 µl of Loading Solution UL (LSU) before re-loading for further sequencing.
Please follow Flushing a PromethION Flow Cell in the Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol for the nuclease wash instructions. To run another ultra-long library straight away, follow the instructions below.
10. Reloading ultra-long DNA library on a PromethION Flow Cell
Material
- Kit Flow Cell Wash (EXP-WSH004)
- Flush Tether UL (FTU)
- Flow Cell Flush (FCF)
- Loading Solution UL (LSU)
- Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU)
Consumibles
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tubes
Instrumental
- P1000 pipette and wide-bore pipette tips
- P200 pipette and wide-bore pipette tips
- P1000 pipette and tips
- P200 pipette and tips
- P20 pipette and tips
Before reloading your library or loading a new library, please ensure you wash the flow cell using the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004).
Follow the instructions in the Flow Cell Wash Kit (EXP-WSH004) for PromethION protocol.
- This washing procedure aims to remove most of the initial library and prepare the flow cell for loading of a subsequent library.
- Data acquisition in MinKNOW should be paused during the wash procedure and library loading.
- After the flow cell has been washed, another library can be loaded.
We recommend keeping the light shield on the flow cell during washing if a second library will be loaded straight away.
If the flow cell is to be washed and stored, the light shield can be removed.
To run a second library of ultra-long DNA straight after flushing a flow cell, we recommend removing all fluid from the waste channel after each priming step.
Thaw the Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU), Loading Solution UL (LSU), Flush Tether UL (FTU) and one tube of Flow Cell Flush (FCF) at room temperature and mix by vortexing. Then spin down and place on ice.
In a fresh 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube, prepare the DNA library for loading as follows using a wide-bore pipette tip for the addition of the DNA library:
| Reagent | Volume per flow cell |
|---|---|
| Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU) | 100 µl |
| Loading Solution UL (LSU) | 10 µl |
| DNA library | 90 µl |
| Total | 200 µl |
Note: ensure the Sequencing Buffer UL (SBU) and Loading Solution UL (LSU) are thoroughly mixed by pipetting before the addition of the DNA library.
Gently mix the prepared DNA library by slowly pipetting ten times using a wide-bore pipette tip.
Incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes then gently mix by slowly pipetting with a wide-bore tip. Visually inspect to ensure the sample is homogenous.
Prepare the flow cell priming mix in a 1.5 ml Eppendorf DNA LoBind tube and mix by vortexing at room temperature.
| Reagent | Volume |
|---|---|
| Flush Tether UL (FTU) | 30 µl |
| Flow Cell Flush (FCF) | 1,170 µl |
| Total | 1,200 µl |
Turn the valve to expose the inlet port.

After opening the inlet port, draw back a small volume to remove any air bubbles:
- Set a P1000 pipette tip to 200 µl.
- Insert the tip into the inlet port.
- Turn the wheel until the dial shows 220-230 µl, or until you see a small volume of buffer entering the pipette tip.

Load 500 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the inlet port, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles. Wait five minutes.

It is vital to wait five minutes between the priming mix flushes to ensure effective removal of the nuclease.
It is vital that the inlet port is closed before removing waste to prevent air from being drawn across the sensor array area, which would lead to a significant loss of sequencing channels.
Remove waste buffer, as follows:
- Close the inlet port.
- Insert a P1000 pipette into a waste port and remove the waste buffer.
Note: As both the inlet port is closed, no fluid should leave the sensor array area.
Slide open the inlet port and load 500 µl of the priming mix into the flow cell via the inlet port to complete a second flow cell flush, avoiding the introduction of air bubbles.

Close the inlet port and use a P1000 to remove all fluid from the waste channel through a waste port again.
Open the inlet port cover of the flow cell in preparation for loading.

Aspirate the DNA library with a wide-bore pipette tip. Ensure there are no air bubbles in the pipette tip. Place the wide-bore pipette tip directly on the inlet port. Slowly depress the pipette to dispense the library into the inlet port.
There can be a delay between depressing the pipette and the library dispensing from the pipette tip. Dispense the library slowly, allowing the library to dispense from the pipette tip before depressing the pipette further.
It is important to dispense the library slowly to prevent air being introduced onto the flow cell.
Note: The DNA library loaded in this step is viscous and may not readily flow through the inlet port into the flow cell. In this case, we recommend applying negative pressure in the flow cell as explained in the steps below.

Using a P200 pipette, set the pipette to 50 µl and insert the tip into Port 2.

Very slowly turn the wheel of the pipette to pull the DNA library into the inlet port. Closely watch the DNA library on the inlet port and completely remove the pipette as soon as the library starts to be pulled into the port.
This step is required if the DNA library has not been fully absorbed into the inlet port.
Note: Take care to not apply too much negative pressure too quickly to avoid bringing air bubbles into the flow cell. Air bubbles will cause irreversible damage to the flow cell.

Close the valve to seal the inlet port.
For optimal sequencing output, install the light shield on your flow cell as soon as the library has been loaded.
We recommend leaving the light shield on the flow cell when library is loaded, including during any washing and reloading steps. The shield can be removed when the library has been removed from the flow cell.
If the light shield has been removed from the flow cell, install the light shield as follows:
- Align the inlet port cut out of the light shield with the inlet port cover on the flow cell. The leading edge of the light shield should sit above the flow cell ID.
- Firmly press the light shield around the inlet port cover. The inlet port clip will click into place underneath the inlet port cover.


Once the flow cell is reloaded, resume the sequencing run on MinKNOW and trigger a pore scan.
To resume sequencing run, navigate to the Experiments page, click 'Resume' and select flow cell position.
To manually trigger a channel scan, click 'Start pore scan' and select flow cell position.
For further information, please see the MinKNOW protocol.
Resume run:
Pore scan:
11. Data acquisition and basecalling
How to start sequencing
Once you have loaded your flow cell, the sequencing run can be started on MinKNOW, our sequencing software that controls the device, data acquisition and real-time basecalling. For more detailed information on setting up and using MinKNOW, please see the MinKNOW protocol.
MinKNOW can be used and set up to sequence in multiple ways:
- On a computer either direcly or remotely connected to a sequencing device.
- Directly on a GridION or PromethION 24/48 sequencing device.
For more information on using MinKNOW on a sequencing device, please see the device user manuals:
To start a sequencing run on MinKNOW:
1. Navigate to the start page and click Start sequencing.
2. Fill in your experiment details, such as name and flow cell position and sample ID.
3. Select the Ultra-Long DNA Sequencing Kit (SQK-ULK114) on the Kit page.
4. Configure the sequencing and output parameters for your sequencing run or keep to the default settings on the Run configuration tab.
Note: If basecalling was turned off when a sequencing run was set up, basecalling can be performed post-run on MinKNOW. For more information, please see the MinKNOW protocol.
5. Click Start to initiate the sequencing run.
Data analysis after sequencing
After sequencing has completed on MinKNOW, the flow cell can be reused or returned, as outlined in the Flow cell reuse and returns section.
After sequencing and basecalling, the data can be analysed. For further information about options for basecalling and post-basecalling analysis, please refer to the Data Analysis document.
In the Downstream analysis section, we outline further options for analysing your data.
12. Flow cell reuse and returns
Material
- Kit Flow Cell Wash (EXP-WSH004)
After your sequencing experiment is complete, if you would like to reuse the flow cell, please follow the Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol and store the washed flow cell at +2°C to +8°C.
The Flow Cell Wash Kit protocol is available on the Nanopore Community.
We recommend you to wash the flow cell as soon as possible after you stop the run. However, if this is not possible, leave the flow cell on the device and wash it the next day.
Alternatively, follow the returns procedure to send the flow cell back to Oxford Nanopore.
Instructions for returning flow cells can be found here.
If you encounter issues or have questions about your sequencing experiment, please refer to the Troubleshooting Guide that can be found in this protocol.
13. Downstream analysis
Post-basecalling analysis
There are several options for further analysing your basecalled data:
EPI2ME workflows
For in-depth data analysis, Oxford Nanopore Technologies offers a range of bioinformatics tutorials and workflows available in EPI2ME. The platform provides a vehicle where workflows deposited in GitHub by our Research and Applications teams can be showcased with descriptive texts, functional bioinformatics code and example data.
Research analysis tools
Oxford Nanopore Technologies' Research division has created a number of analysis tools, which are available in the Oxford Nanopore GitHub repository. The tools are aimed at advanced users, and contain instructions for how to install and run the software. They are provided as-is, with minimal support.
Community-developed analysis tools
If a data analysis method for your research question is not provided in any of the resources above, please refer to the resource centre and search for bioinformatics tools for your application. Numerous members of the Nanopore Community have developed their own tools and pipelines for analysing nanopore sequencing data, most of which are available on GitHub. Please be aware that these tools are not supported by Oxford Nanopore Technologies, and are not guaranteed to be compatible with the latest chemistry/software configuration.
14. Issues during library preparation
Below is a list of the most commonly encountered issues, with some suggested causes and solutions.
We also have an FAQ section available on the Nanopore Community Support section.
If you have tried our suggested solutions and the issue still persists, please contact Technical Support via email (support@nanoporetech.com) or via LiveChat in the Nanopore Community.
Troubleshooting
| Observation | Comments and actions |
|---|---|
| Low throughput | 1. Vortex gently after adding the diluted Fragmentation Mix (FRA) to break up the largest fragments. 2. Ensure the diluted Fragmentation Mix (FRA) is thoroughly mixed with the gDNA. 3. Use less input material if the DNA library was too viscous to load onto the flow cell. |
| DNA is too viscous and will not load onto a flow cell | 1. Lower the input material to reduce the amount of gDNA going into the library preparation and reduce viscosity. 2. If DNA library will not load using the method outlined in this protocol, slowly pipette mix 5 times with a standard P200 pipette set to the full volume of the library and reload the flow cell. |
| Read lengths are not long enough | 1. Increase input material. Note: Library viscosity increases with more gDNA. 2. Reduce volume of Fragmentation Mix (FRA) added to FRA Dilution Buffer (FDB) to avoid over-fragmentation of gDNA. Note: We do not recommend diluting less than 2 µl Fragmentation Mix (FRA). 3. We recommend using PFGE to check the extracted gDNA is of ultra-high molecular weight (uHMW), thus capable of generating ultra-long read lengths. |
| No sequencing output | 1. Check gDNA has been recovered in library preparation using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer. 2. Check viscosity of the sample. The library should be viscous if it contains uHMW gDNA in this protocol. |
| Aspirating supernatant when the DNA has precipitated | Take care to not aspirate the DNA. Remove smaller volumes of supernatant incrementally to reduce the risk of aspirating the DNA. |
| Mixing | Mix slowly and carefully to prevent DNA shearing. Low vortexing can be used to mix at the expense of ultra-long reads. With vortexing, long read lengths of ~90 kb N50 can still be generated with improved outputs. |
| No DNA recovered from the library preparation clean-up | If the DNA is no longer viscous or the NanoDrop reading is low, DNA may have been lost during the clean-up step of the library preparation. 1. Ensure uHMW DNA is used or users risk DNA loss. 2. Take care to not aspirate the precipitated DNA during the clean-up step. To avoid this, remove smaller volumes of supernatant incrementally. Ensure as much supernatant is removed as possible. |







