Whole-genome analysis of VREfm isolates with daptomycin resistance using Oxford Nanopore and Illumina sequencing
- shared.published_on: June 20 2019
- shared.source: ASM 2019
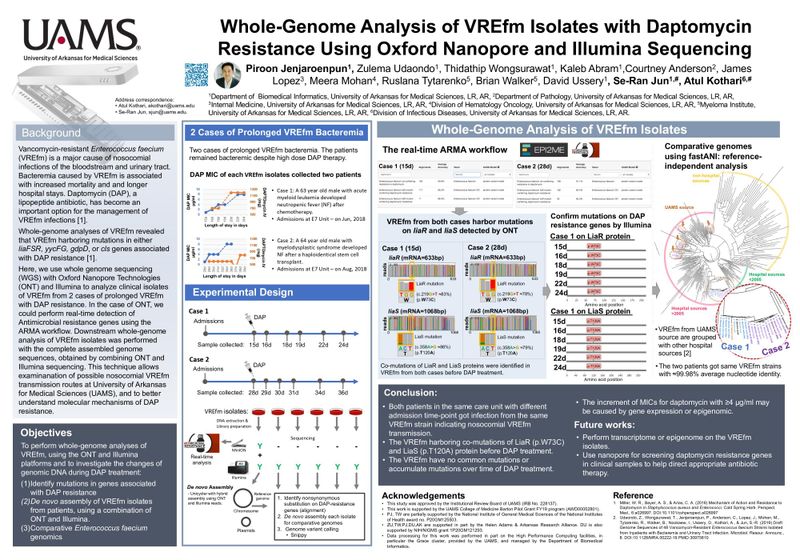
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VREfm) is a major cause of nosocomial infections of the bloodstream and urinary tract. Bacteremia caused by VREfm is associated with increased mortality and and longer hospital stays. Daptomycin (DAP), a lipopeptide antibiotic, has become an important option for the management of VREfm infections.
Whole-genome analyses of VREfm revealed that VREfm harboring mutations in either liaFSR, yycFG, gdpD, or cls genes associated with DAP resistance.
Here, we use whole genome sequencing (WGS) with Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) and Illumina to analyze clinical isolates of VREfm from 2 cases of prolonged VREfm with DAP resistance. In the case of ONT, we could perform real-time detection of Antimicrobial resistance genes using the ARMA workflow. Downstream whole-genome analysis of VREfm isolates was performed with the complete assembled genome sequences, obtained by combining ONT and Illumina sequencing. This technique allows examination of possible nosocomial VREfm transmission routes at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS), and to better understand molecular mechanisms of DAP resistance.






